Write-zero time slot, Read-data time slot, Power transfer – Rainbow Electronics DS1957 User Manual
Page 21
DS1957
21 of 25
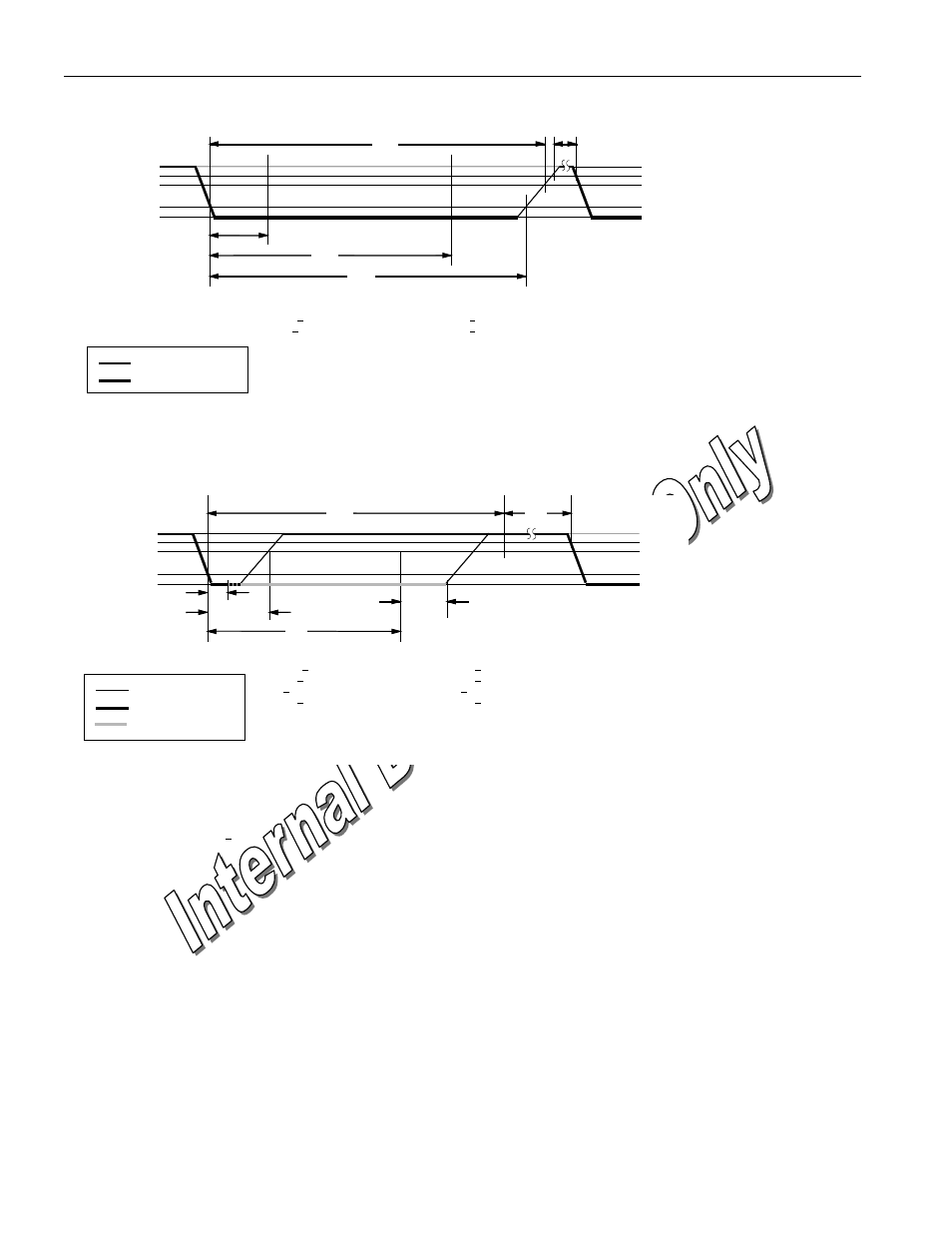
WRITE-ZERO TIME SLOT
V
PULLUP
V
PULLUP MIN
V
IH MIN
V
IL MAX
0V
t
SLOT
t
REC
t
LOW0
DS1954
SAMPLING WINDOW
60
µ
s
15
µ
s
(OD: 2
µ
s)
(OD: 6
µ
s)
Regular Speed
60
µ
s < t
LOW0
< t
SLOT
< 120
µ
s
1
µ
s < t
REC
< 1
Overdrive Speed
6
µ
s < t
LOW0
< t
SLOT
< 16
µ
s
1
µ
s < t
REC
< 1
RESISTOR
MASTER
READ-DATA TIME SLOT
V
PULLUP
V
PULLUP MIN
V
IH MIN
V
IL MAX
0V
t
SLOT
t
REC
t
RDV
t
LOWR
Regular Speed
60
µ
s < t
SLOT
< 120
µ
s
1
µ
s < t
LOWR
< 15
µ
s
0 < t
RELEASE
< 45
µ
s
1
µ
s < t
REC
< 1
t
RDV
= 15
µ
s
t
SU
< 1
µ
s
t
RELEASE
MASTER SAMPLING
WINDOW
Overdrive Speed
6
µ
s < t
SLOT
< 16
µ
s
1
µ
s < t
LOWR
< 2
µ
s
0 < t
RELEASE
< 4
µ
s
1
µ
s < t
REC
< 1
t
RDV
= 2
µ
s
t
SU
< 1
µ
s
t
SU
RESISTOR
MASTER
DS1954
POWER TRANSFER
The DS1957 Crypto iButton communicates and gets power through the 1-Wire data line. Typically the
DS1957 will see four different power situations on the 1-Wire bus: A) no power at all; B) parasitic supply
for initial and repeated communication; C) full power for (repeated) times of computation; and D)
parasitic supply for final communication prior to removal from the 1-Wire bus (Figure 9). During
communication, the microcomputer and accelerator inside the DS1957 remain in a STOP mode (time
period B and D). Once data has been transferred, the microcomputer and accelerator are enabled to
process the data (period C). After the data processing has been completed the microcomputer and
accelerator return to a low power STOP mode and the resulting data is then extracted through the 1-Wire
interface by the bus master (period D). The amount of data and the required calculations associated with
the data will govern the number of periods (B & C) that the master and the DS1957 will use to transfer
and process data. The time associated with period C depends on the assigned task. When the
microcomputer is loading data through the 1-Wire interface, the time will be short. When the
microcomputer and accelerator are being used to perform calculations the time for period C will be
significantly longer. During 1-Wire communication, the DS1957 gets the power through the 1-Wire pull-
up resistor of 1.5 kΩ (see Figure 5). A diode plus a capacitor on chip form a parasitic power supply
