Rainbow Electronics MAX15051 User Manual
Page 10
MAX15050/MAX15051
High-Efficiency, 4A, 1MHz, Step-Down Regulators
with Integrated Switches in 2mm x 2mm Package
10
______________________________________________________________________________________
turns off when the ramp voltage exceeds the V
COMP
signal or the current-limit threshold is exceeded. The
low-side switch then turns on for the remainder of the
oscillator cycle.
Skip Mode (MAX15050)
The MAX15050 features a skip function. In skip mode,
the MAX15050 switches only as necessary to maintain
the output at light loads (not capable of sinking current
from the output). This maximizes light-load efficiency
and reduces the input quiescent current.
In skip mode, the low-side switch is turned off when the
inductor current decreases to 0.2A (typ) to ensure no
reverse current flowing from the output capacitor.
The high-side switch minimum on-time is controlled to
guarantee that 0.9A current is reached to avoid high
frequency bursts at no-load conditions, which prevents
a rapid increase of the supply current caused by addi-
tional switching losses. Under heavy load, the device
operates as a PWM converter.
Current Limit
The internal, high-side MOSFET has a typical 8A peak
current-limit threshold. When current flowing out of LX
exceeds this limit, the high-side MOSFET turns off and
the low-side MOSFET turns on. The low-side MOSFET
remains on until the inductor current falls below the low-
side current limit. This lowers the duty cycle and caus-
es the output voltage to droop until the current limit is
no longer exceeded. The MAX15050/MAX15051 use a
hiccup mode to prevent overheating during short-cir-
cuit output conditions.
During current limit, if V
FB
drops below 70% of
V
REFIN/SS
and stays below this level for typically 36µs
or more, the device enters hiccup mode. The high-side
MOSFET and the low-side MOSFET turn off and both
COMP and REFIN/SS are internally pulled low. The
device remains in this state for 896 clock cycles and
then attempts to restart for 112 clock cycles. If the fault-
causing current limit has cleared, the device resumes
normal operation. Otherwise, the device reenters hic-
cup mode.
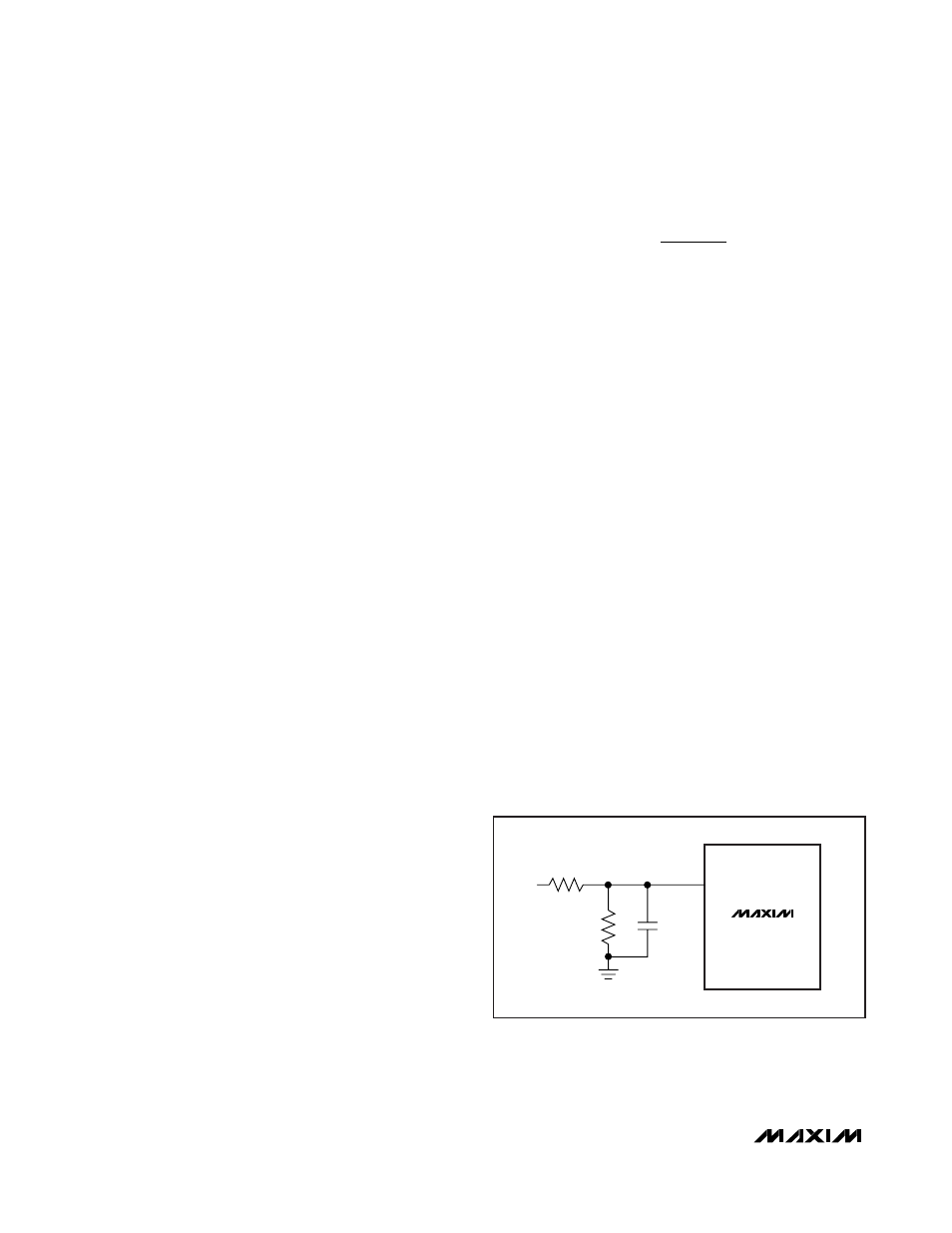
Soft-Start and Reference Input (REFIN/SS)
The MAX15050/MAX15051 utilize an adjustable soft-
start function to limit inrush current during startup. An
8µA (typ) current source charges an external capacitor
connected to REFIN/SS. The soft-start time is adjusted
by the value of the external capacitor from REFIN/SS to
GND. The required capacitance value is determined as:
where t
SS
is the required soft-start time in seconds.
Connect a minimum 1nF capacitor between REFIN/SS
and GND. REFIN/SS is also an external reference input
(REFIN/SS). The device regulates FB to the voltage
applied to REFIN/SS. The internal soft-start is not avail-
able when using an external reference. Figure 2 shows
a method of soft-start when using an external refer-
ence. If an external reference is not applied, the device
uses the internal 0.6V reference.
Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
The UVLO circuitry inhibits switching when V
DD
is
below 2.55V (typ). Once V
DD
rises above 2.6V (typ),
UVLO clears and the soft-start function activates. A
50mV hysteresis is built-in for glitch immunity.
BST
The gate-drive voltage for the high-side, n-channel
switch is generated by a flying-capacitor boost circuit.
The capacitor between BST and LX is charged from the
V
IN
supply while the low-side MOSFET is on. When the
low-side MOSFET is switched off, the voltage of the
capacitor is stacked above LX to provide the necessary
turn-on voltage for the high-side internal MOSFET.
Power-Good Output (PWRGD)
PWRGD is an open-drain output that goes high
impedance when V
FB
is above 92.5% x V
REFIN/SS
and
V
REFIN/SS
is above 0.54V. PWRGD pulls low when V
FB
is below 90% of V
REFIN/SS
for at least 48 clock cycles
or V
REFIN/SS
is below 0.54V. PWRGD is low during
shutdown.
C
A
t
V
SS
=
×
8
0 6
µ
.
C
R2
R1
REFIN/SS
MAX15050
MAX15051
Figure 2. Typical Soft-Start Implementation with External
Reference
