Detailed description – Rainbow Electronics MAX4284 User Manual
Page 11
MAX4174/5, MAX4274/5, MAX4281/2/4
SOT23, Rail-to-Rail, Fixed-Gain
GainAmps/Open-Loop Op Amps
______________________________________________________________________________________
11
Detailed Description
Maxim’s GainAmp fixed-gain amplifiers combine a low-
cost rail-to-rail op amp with internal gain-setting resis-
tors. Factory-trimmed on-chip resistors provide 0.1%
gain accuracy while decreasing design size, cost, and
layout. Three versions are available in this amplifier
family: single/dual/quad open-loop, unity-gain-stable
devices (MAX4281/MAX4282/MAX4284); single/dual
fixed-gain devices (MAX4174/MAX4274); and single/
dual devices with fixed gain plus internal V
CC
/ 2 bias
at the noninverting input (MAX4175/MAX4275). All
amplifiers feature rail-to-rail outputs and drive a 1k
Ω
load while maintaining excellent DC accuracy.
Open-Loop Op Amps
The single/dual/quad MAX4281/MAX4282/MAX4284
are high-performance, open-loop op amps with rail-to-
rail outputs. These devices are compensated for unity-
gain stability, and feature a gain bandwidth (GBW) of
2MHz. The op amps in these ICs feature an input com-
mon-mode range that extends from 150mV below the
negative rail to within 1.2V of the positive rail. These
high performance op amps serve as the core for this
family of GainAmp fixed-gain amplifiers. Although the
-3dB bandwidth will not correspond to that of a fixed-
gain amplifier in higher gain configurations, these
open-loop op-amps can be used to prototype designs.
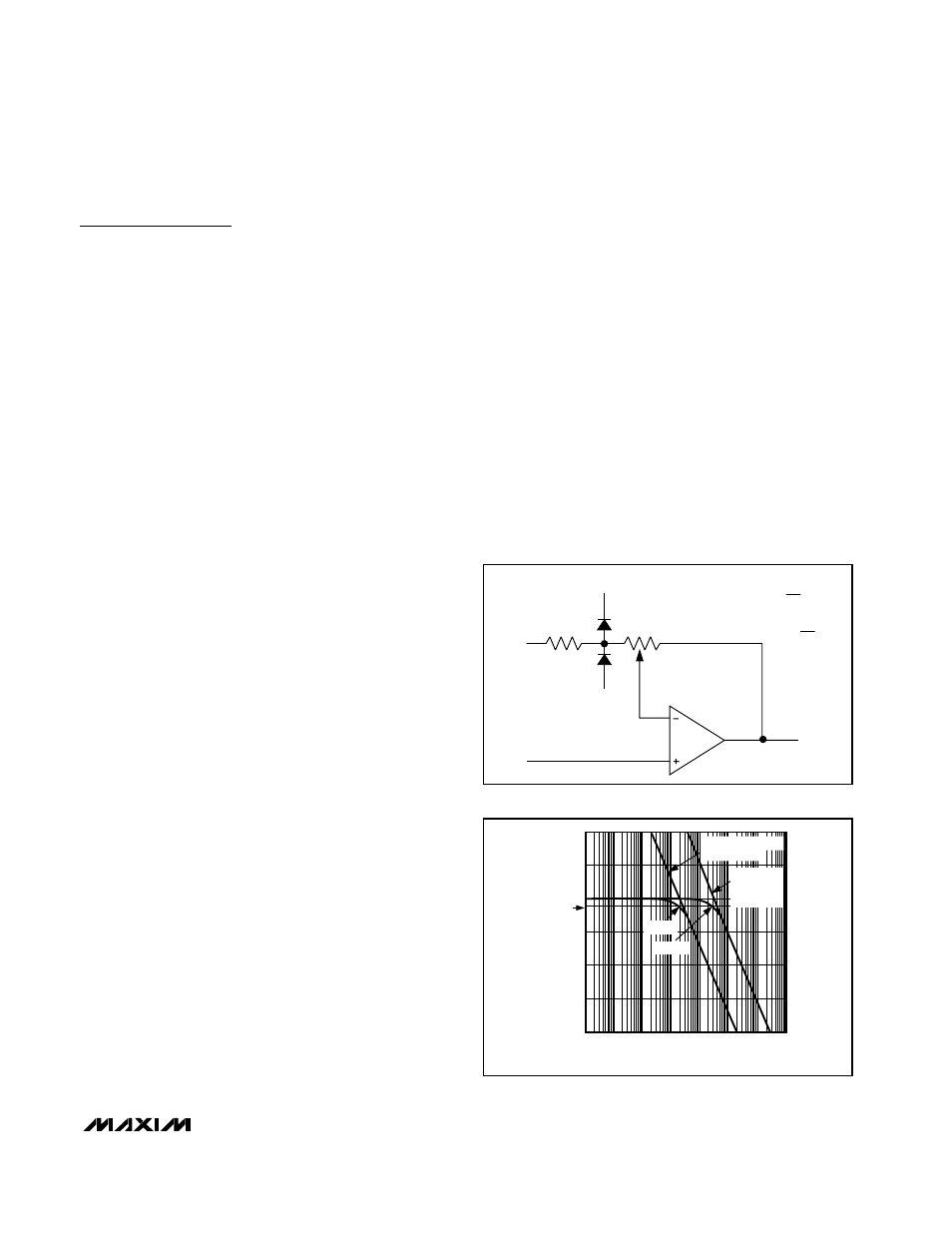
Internal Gain-Setting Resistors
Maxim’s proprietary laser trimming techniques produce
the necessary R
F
/R
G
values (Figure 1), so many gain
offerings are easily available. These GainAmp fixed-gain
amplifiers feature a negative-feedback resistor network
that is laser trimmed to provide a gain-setting feedback
ratio (R
F
/R
G
) with 0.1% typical accuracy. The standard
op amp pinouts allow the GainAmp fixed-gain amplifiers
to drop in directly to existing board designs, easily
replacing op-amp-plus-resistor gain blocks.
GainAmp Bandwidth
GainAmp fixed-gain amplifiers feature factory-trimmed
precision resistors to provide fixed inverting gains from
-0.25V/V to -100V/V or noninverting gains from
+1.25V/V to +101V/V. The op-amp core is decompen-
sated strategically over the gain-set options to maxi-
mize bandwidth. Open-loop decompensation increases
GBW product, ensuring that usable bandwidth is main-
tained with increasing closed-loop gains. A GainAmp
with a fixed gain of A
V
= 100V/V has a -3dB bandwidth
of 230kHz. By comparison, a unity-gain-stable op amp
configured for A
V
= 100V/V would yield a -3dB band-
width of only 20kHz (Figure 2). Decompensation is per-
formed at five intermediate gain sets, as shown in the
Gain Selection Guide
. Low gain decompensation great-
ly increases usable bandwidth, while decompensation
above gains of +25V/V offers diminished returns.
V
CC
/ 2 Internal Bias
The MAX4175/MAX4275 GainAmp fixed-gain amplifiers
with the V
CC
/ 2 bias option are identical to standard
GainAmp fixed-gain amplifiers, with the added feature
of V
CC
/ 2 internal bias at the noninverting inputs. Two
150k
Ω
resistors form a voltage-divider for self-biasing
the noninverting input, eliminating external bias resis-
tors for AC-coupled applications, and allowing maxi-
mum signal swing at the op amp’s rail-to-rail output for
single-supply systems (see
Typical Operating Circuit
).
For DC-coupled applications, use the MAX4174/
MAX4274.
High-Voltage (±17V) Input Fault Protection
The MAX4174/MAX4175/MAX4274/MAX4275 include
±17V input fault protection. For normal operation, see
the input voltage range specification in the
Electrical
Characteristics
. Overdriven inputs up to ±17V will not
OUT
A
V
=
-R
F
R
G
R
G
R
F
IN-
IN+
V
CC
V
EE
A
V
= 1 +
R
F
R
G
Figure 1. Internal Gain-Setting Resistors
FREQUENCY (Hz)
GAIN (dB)
60
0
10
20
30
40
-3dB
50
10
10k
100k
1M
10M
100
1k
20kHz
230kHz
MAX4281, A
V
= 100
2MHz GBW
MAX4174,
A
V
= 100
23MHz GBW
Figure 2. Gain-Bandwidth Comparison
