Alarm threshold registers, Alert interrupt mode – Rainbow Electronics MAX6636 User Manual
Page 9
Alarm Threshold Registers
There are 11 alarm threshold registers that store over-
temperature
ALERT and OVERT threshold values.
Seven of these registers are dedicated to store one
local alert temperature threshold limit and six remote
alert temperature threshold limits (see the
ALERT
Interrupt Mode
section). The remaining four registers
are dedicated to remote channels 1, 4, 5, and 6 to store
overtemperature threshold limits (see the
OVERT
Overtemperature Alarms
section). Access to these reg-
isters is provided through the SMBus interface.
ALERT Interrupt Mode
An
ALERT interrupt occurs when the internal or external
temperature reading exceeds a high-temperature limit
(user programmable). The
ALERT interrupt output sig-
nal can be cleared by reading the status register(s)
associated with the fault(s) or by successfully respond-
ing to an alert response address transmission by the
master. In both cases, the alert is cleared but is
reasserted at the end of the next conversion if the fault
condition still exists. The interrupt does not halt automat-
ic conversions. The
ALERT output is open drain so that
multiple devices can share a common interrupt line. All
ALERT interrupts can be masked using the configuration
3 register. The POR state of these registers is shown in
Table 1.
MAX6636
7-Channel Precision Temperature Monitor
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
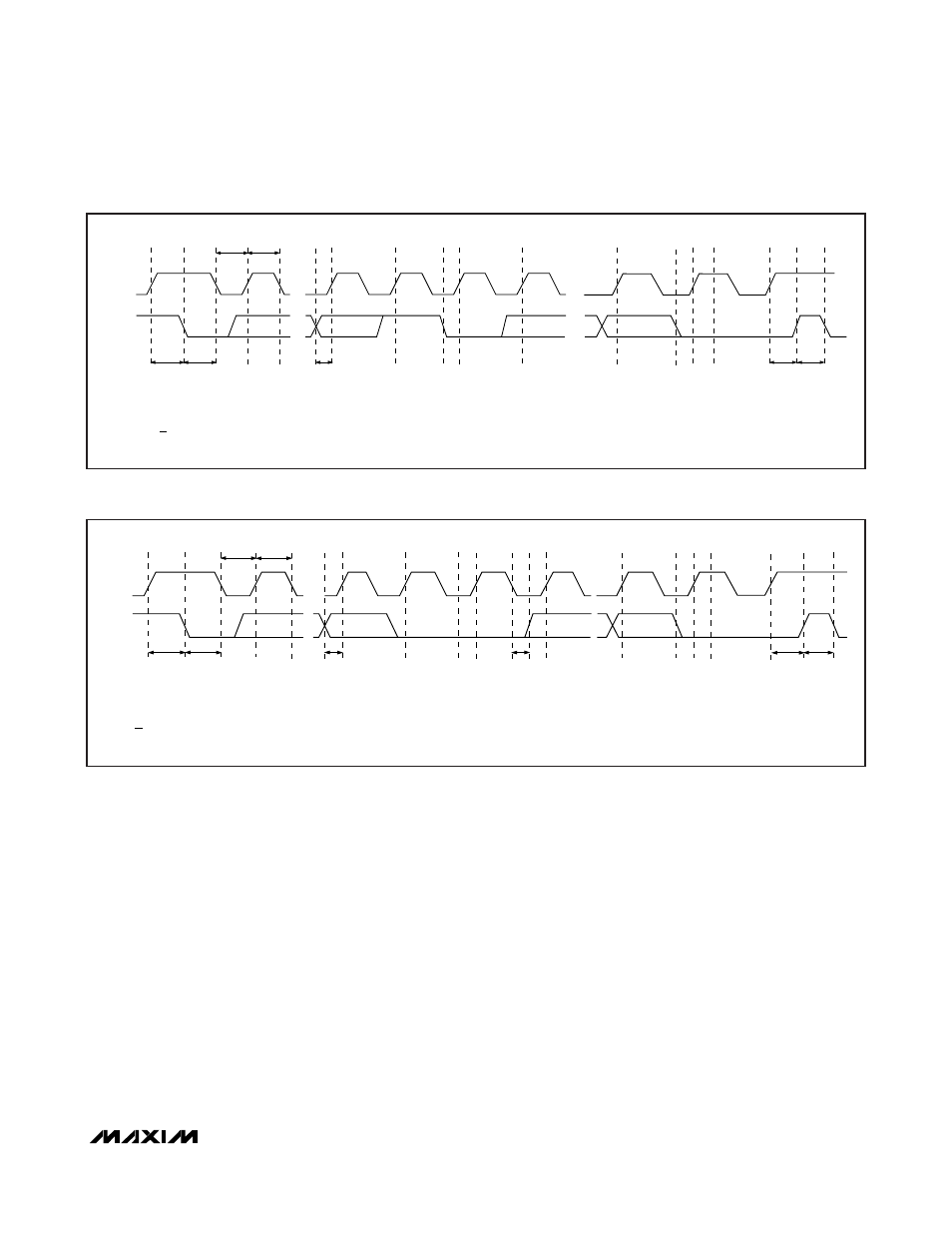
SMBCLK
A = START CONDITION.
B = MSB OF ADDRESS CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
C = LSB OF ADDRESS CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
D = R/W BIT CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
SMBDATA
t
SU:STA
t
HD:STA
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
SU:DAT
t
SU:STO
t
BUF
L
M
K
E = SLAVE PULLS SMBDATA LINE LOW.
F = ACKNOWLEDGE BIT CLOCKED INTO MASTER.
G = MSB OF DATA CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
H = LSB OF DATA CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
I = MASTER PULLS DATA LINE LOW.
J = ACKNOWLEDGE CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
K = ACKNOWLEDGE CLOCK PULSE.
L = STOP CONDITION.
M = NEW START CONDITION.
Figure 3. SMBus Write-Timing Diagram
SMBCLK
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
SMBDATA
t
SU:STA
t
HD:STA
t
LOW
t
HIGH
t
SU:DAT
t
HD:DAT
t
SU:STO
t
BUF
A = START CONDITION.
B = MSB OF ADDRESS CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
C = LSB OF ADDRESS CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
D = R/W BIT CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
E = SLAVE PULLS SMBDATA LINE LOW.
L
M
F = ACKNOWLEDGE BIT CLOCKED INTO MASTER.
G = MSB OF DATA CLOCKED INTO MASTER.
H = LSB OF DATA CLOCKED INTO MASTER.
I = MASTER PULLS DATA LINE LOW.
J = ACKNOWLEDGE CLOCKED INTO SLAVE.
K = ACKNOWLEDGE CLOCK PULSE.
L = STOP CONDITION.
M = NEW START CONDITION.
Figure 4. SMBus Read-Timing Diagram
