Abridged data sheet – Rainbow Electronics MAX66040 User Manual
Page 19
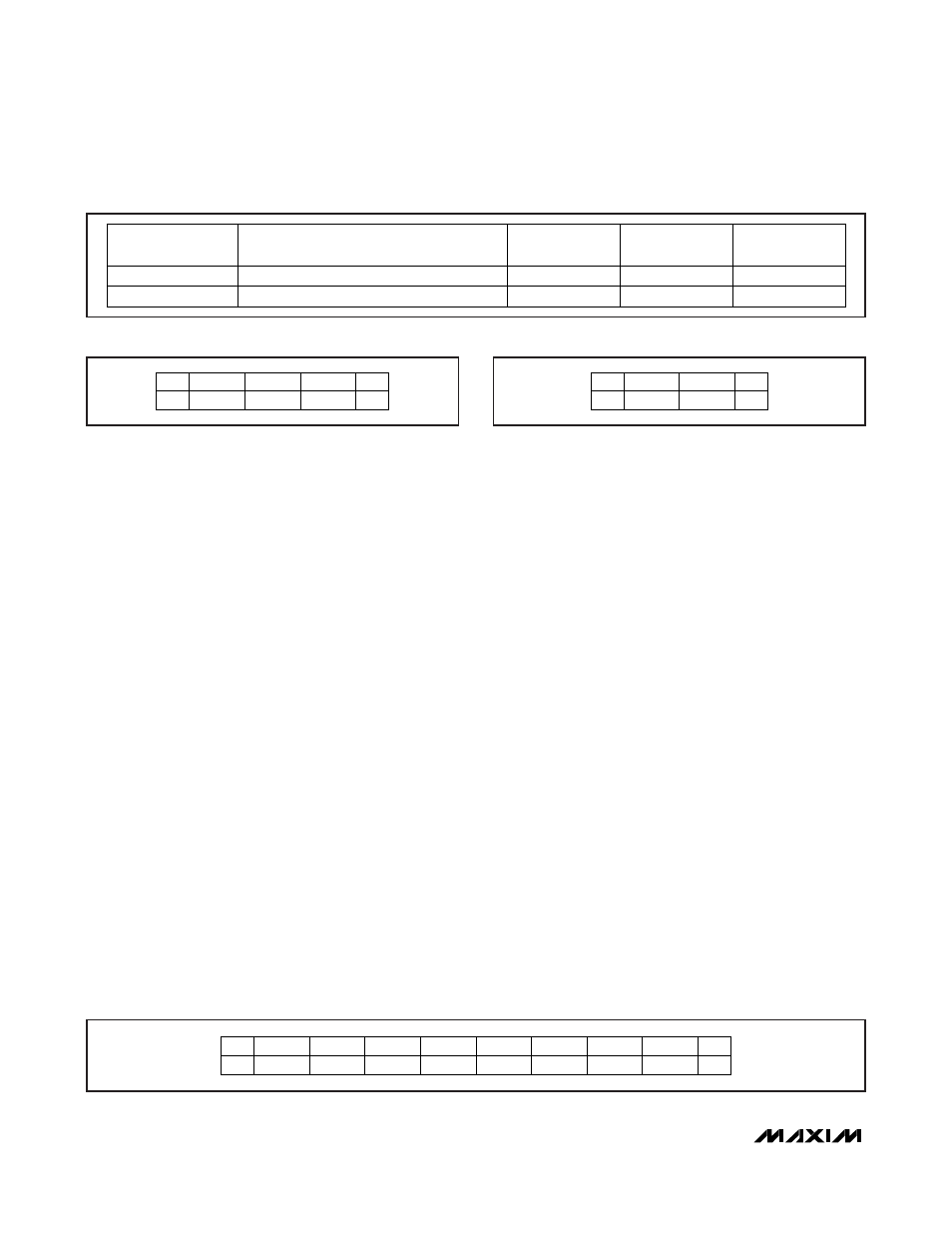
MAX66040
shows where this information is located in the protocol
info field and what the values are.
The bit-rate capability of the MAX66040 ranges from
105.9kbps to 847.5kbps in both directions (request and
response); request and response bit rate need not be
the same. The maximum frame size (upper nibble of the
2nd byte) of any request/response specifies 32 bytes.
The largest frame that occurs with the MAX66040 is 26
bytes (copy buffer request, compute page MAC
response). The protocol type (lower nibble of the 2nd
byte) specifies that the MAX66040 supports the
ISO/IEC 14443-4 block transmission protocol. The FWI
code 0111b specifies a frame waiting time of 38.7ms,
which is long enough to generate a computed secret.
Note that a slave may respond long before the maxi-
mum frame waiting time is expired. The ADC code 00b
specifies that the MAX66040 uses proprietary coding
for the application data field. The FO code 01b implies
that the MAX66040 supports CID, but does not support
the NAD field in the ISO/IEC 14443-4 block transmis-
sion protocol.
HLTB Command
The HLTB command is the only network function com-
mand to silence a slave by parking it in the HALT state.
If, based on the ATQB response, the master does not
want to further communicate with the slave, the master
issues the HLTB command. Figures 23 and 24 show
the format of the HLTB request frame and the corre-
sponding response frame. The data to be used in the
PUPI field must match the PUPI information that the
slave has transmitted in the ATQB response. While in
the HALT state, the slave only responds to the WUPB
request.
ATTRIB Command
The ATTRIB command is the only way to select a slave
and make it process commands that are transmitted
according to the ISO/IEC 14443 block transmission pro-
tocol. If, based on the ATQB response, the master
wants to communicate with the slave, the master must
put the slave into the ACTIVE state using the slave
selection command ATTRIB. The normal way for the
master to move a slave out of the ACTIVE state is by
sending a DESELECT command, which uses an
S-block to convey a network function command.
Figure 25 shows the format of the ATTRIB request
frame. The data to be used in the PUPI field must
match the PUPI information that the slave has transmit-
ted in the ATQB response. Param 1 tells the slave how
much time the master needs to switch from transmit to
receive (TR0), how much time the master needs to syn-
chronize to the slave’s subcarrier (TR1), and whether
the master is capable of receiving response frames
without SOF and/or EOF.
The MAX66040 ignores the data of Param 1. To ease
requirements for ISO/IEC 14443 Type B readers, the
MAX66040 has TR0 and TR1 fixed at 128/fs (151µs; fs
is the subcarrier frequency of 847.5kHz) and always
begins and ends its responses with SOF and EOF,
respectively.
ISO/IEC 14443 Type B-Compliant
Secure Memory
28
______________________________________________________________________________________
ABRIDGED DATA SHEET
1ST BYTE
2ND BYTE
3RD BYTE,
UPPER NIBBLE
3RD BYTE,
BIT 4, BIT 3
3RD BYTE,
BIT 2, BIT 1
BIT RATE CABILITY MAXIMUM FRAME SIZE, PROTOCOL TYPE
FWI
ADC
FO
77h 21h
0111b
00b
01b
Figure 22. Protocol Info Field Details
COMMAND
SOF
CRC
EOF
1Dh
(2 BYTES)
PUPI
(4 BYTES)
PARAM 1
(1 BYTE)
PARAM 2
(1 BYTE)
PARAM 3
01h
PARAM 4
(1 BYTE)
HLINF
(
≥ 0 BYTES)
Figure 25. ATTRIB Request Frame
COMMAND
SOF
CRC
EOF
50h
(2 BYTES)
PUPI
(4 BYTES)
Figure 23. HLTB Request Frame
INDICATOR
SOF
CRC
EOF
00h
(2 BYTES)
Figure 24. HLTB Response Frame
