3 0 applications information – Rainbow Electronics ADC10158 User Manual
Page 19
3 0 Applications Information
(Continued)
3 2 REFERENCE CONSIDERATIONS
The voltage difference between the V
REF
a
and V
REF
b
in-
puts defines the analog input voltage span (the difference
between V
IN
(Max) and V
IN
(Min)) over which the 2
n
(where n
is the programmed resolution) possible output codes apply
In the pseudo-differential and differential modes the actual
voltage applied to V
REF
a
and V
REF
b
can lie anywhere be-
tween the AV
a
and V
b
Only the difference voltage is of
importance When using the single-ended multiplexer mode
the voltage at V
REF
b
has a dual function It simultaneously
determines the ‘‘zero’’ reference voltage and with V
REF
a
the analog voltage span
The value of the voltage on the V
REF
a
or V
REF
b
inputs
can be anywhere between AV
a
a
50 mV and V
b
b
50 mV so long as V
REF
a
is greater than V
REF
b
The
ADC10154 and ADC10158 can be used in either ratiometric
applications or in systems requiring absolute accuracy The
reference pins must be connected to a voltage source capa-
ble of driving the minimum reference input resistance of
4 5 kX
The internal 2 5V bandgap reference in the ADC10154 and
ADC10158 is available as an output on the V
REF
Out pin To
ensure optimum performance this output needs to be by-
passed to ground with 330 mF aluminum electrolytic or tan-
talum capacitor The reference output is unstable with ca-
pacitive loads greater than 100 pF and less than 100 mF
Any capacitive loads
s
100 pF or
t
100 mF will not cause
the reference to oscillate Lower output noise can be ob-
tained by increasing the output capacitance The 330 mF
capacitor will yield a typical noise floor of 200 nVrms
0Hz
The 2 5V reference output is referred to the negative supply
pin (V
b
) Therefore the voltage at V
REF
Out will always
be 2 5V greater than the voltage applied to V
b
Applying
this voltage to V
REF
a
with V
REF
b
tied to V
b
will yield an
analog voltage span of 2 5V In bipolar operation the volt-
age at V
REF
Out will be at b2 5V when V
b
is tied to b5V
For the single-ended multiplexer mode the analog input volt-
age range will be from b5V to b2 5V The pseudo-differen-
tial and differential multiplexer modes allow for more flexibil-
ity in the analog input voltage range since the ‘‘zero’’ refer-
ence voltage is set by the actual voltage applied to the as-
signed negative input pin The drawback of using the inter-
nal reference in the bipolar mode is that any noise on the
b
5V tied to the V
b
pin will affect the conversion result The
bandgap reference is specified and tested in unipolar opera-
tion with V
b
tied to the system ground
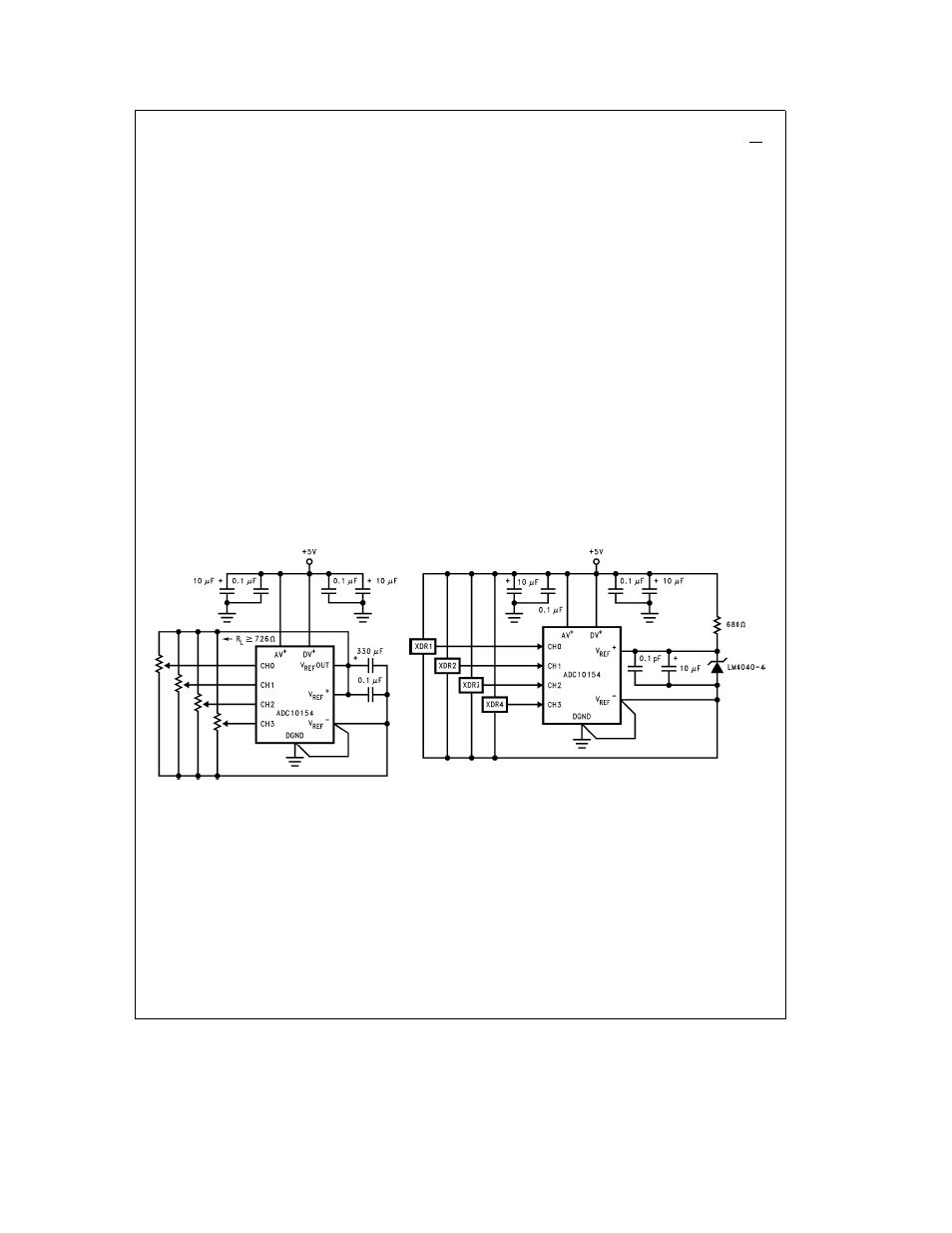
In a ratiometric system
(Figure 4a)
the analog input voltage
is proportional to the voltage used for the A D reference
This voltage may also be the system power supply so
V
REF
a
can also be tied to AV
a
This technique relaxes the
stablity requirements of the system reference as the analog
input and A D reference move together maintaining the
same output code for a given input condition
For absolute accuracy
(Figure 4b)
where the analog input
varies between very specific voltage limits the reference pin
can be biased with a time- and temperature-stable voltage
source that has excellent initial accuracy The LM4040 and
LM185 references are suitable for use with the ADC10154
and ADC10158
TL H 11225 – 21
a Ratiometric Using the Internal Reference
TL H 11225 – 22
b Absolute Using a 4 096V Span
FIGURE 4 Different Reference Configurations
19
