Moog Music MF-107 FreqBox User Manual
Page 11
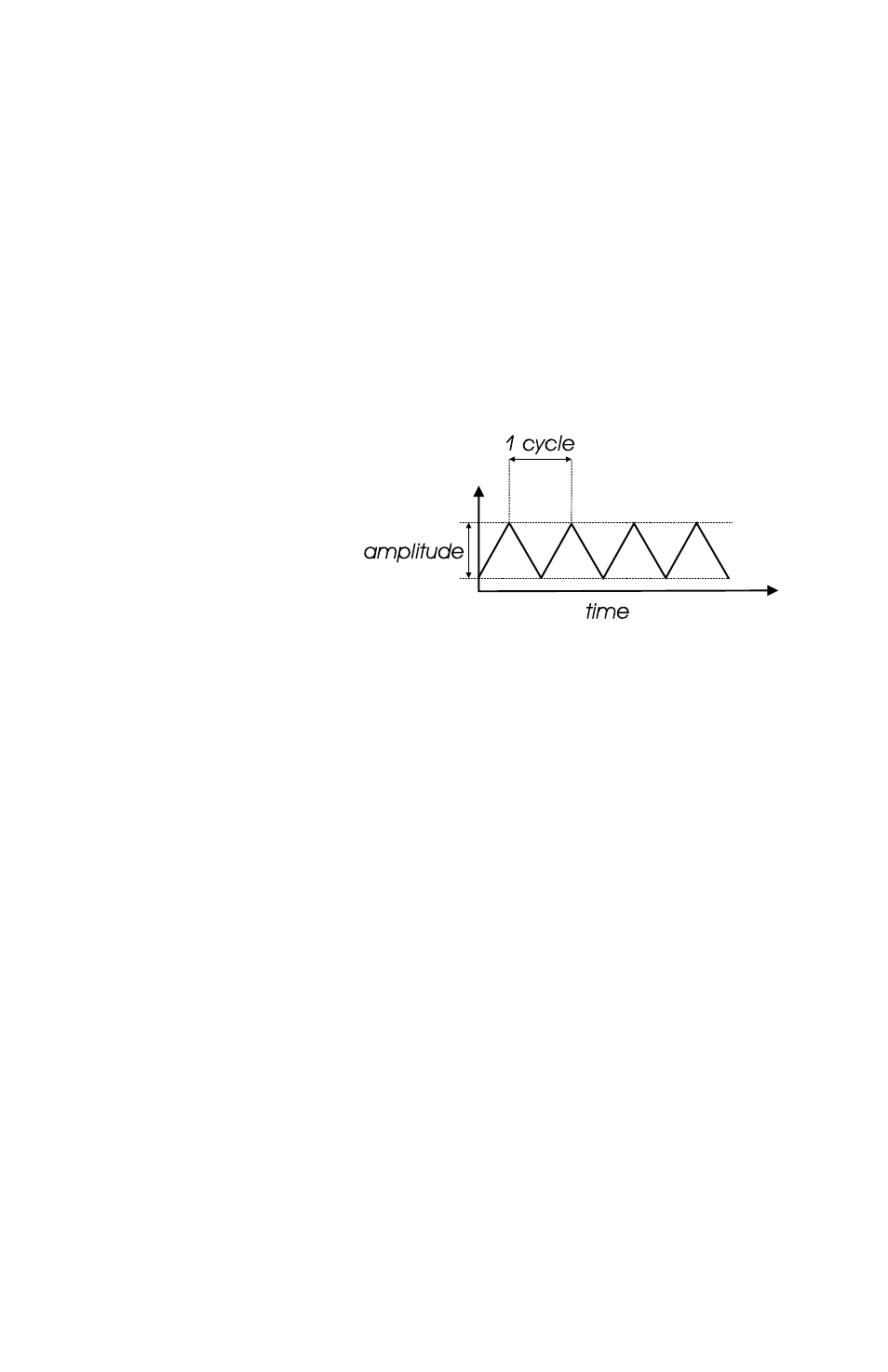
11
the vibration in the sound.
Different instruments playing the same pitch sound different, like
an oboe and a violin playing A440. That’s because musical sounds
generally have many frequency components. They're called harmonics,
or overtones, or partials. The harmonics of a pitched musical sound
are related to the pitch we hear, called the fundamental, by simple
relationships, 1X (fundamental, or first harmonic) 2X(2nd harmonic), 3X
(3rd harmonic), 4X (4
th
harmonic), 5X (5
th
harmonic), 6X (6
th
harmonic),
and so on. These relationships define what we call the harmonic series.
The presence and strength of different harmonics is what gives a sound
its characteristic tone color, or timbre. We can represent a musical sound
as a waveform. The waveform is a time graph of the actual shape of the
Figure 11: a basic waveform graph
vibration. See Figure 11.
The waveform of a single
harmonic is called a sine
wave. It is the simplest type
of periodic vibration there
is. If you listen to a 500 Hz
sine wave, you hear a pitch
nearly an octave above
middle C, with a mellow, muted quality, like a flute or a whistle. A 100
Hz sine wave also sounds mellow and muted, but its pitch is more than
an octave below middle C.
VCOs
The heart of the FreqBox is a Voltage Controlled Oscillator, or VCO.
The FreqBox VCO is a descendant of the same oscillators used in the
Moog Voyager and Little Phatty® synthesizers. An oscillator is a type
of circuit that vibrates electronically such that the changes in voltage
(electrical potential) can be used as a sound source. An oscillator circuit
doesn’t produce sound until it is changed from an electrical signal to
a mechanical signal, usually by the means of loudspeakers. The sound
made by an analog oscillator circuit is most often a very simple signal
because it has very simple vibrations.
The "voltage controlled" part of a VCO refers to the fact that in this
circuit a control voltage (CV) determines the frequency of the oscillator.
A steady CV will result in a steady pitch, while a changing CV will cause
a change in frequency. The FreqBox has a front panel Frequency control
changing that generates a voltage that increases as the control is turned
clockwise. This causes the frequency of the FreqBox VCO to rise.
