Xantrex Technology 10 User Manual
Page 49
Batteries
975-0251-01-01
3–11
To calculate amp-hour consumption, first look at the rating plate on your AC
appliances. Each appliance will be rated in either AC amps or AC watts or AC VA
(volt-amps) apparent power. Use one of the following formulas to calculate the
DC amp-hour draw for a 12-volt system:
(AC amps Ч 10) Ч 1.1 Ч hours of operation = DC amp hours *
(AC watts ч 12) Ч 1.1 Ч hours of operation = DC amp hours *
(AC VA ч 12) Ч 1.1 Ч hours of operation = DC amp hours *
In all formulas, 1.1 is the factor for inverter efficiency.
* Divide amp hours by 2 for 24-volt systems.
** Batteries are frequently charged to 85% of full charge when charging with
alternators without 3-stage regulators.
Calculate the above for every AC appliance you intend to use on your inverter.
This will give you the total number of amp hours used between recharges. Size
your battery bank using this number as a guideline. A good rule to follow is to size
the battery bank about two times larger than your total amp hour load requirement.
Plan on recharging when 50% discharged.
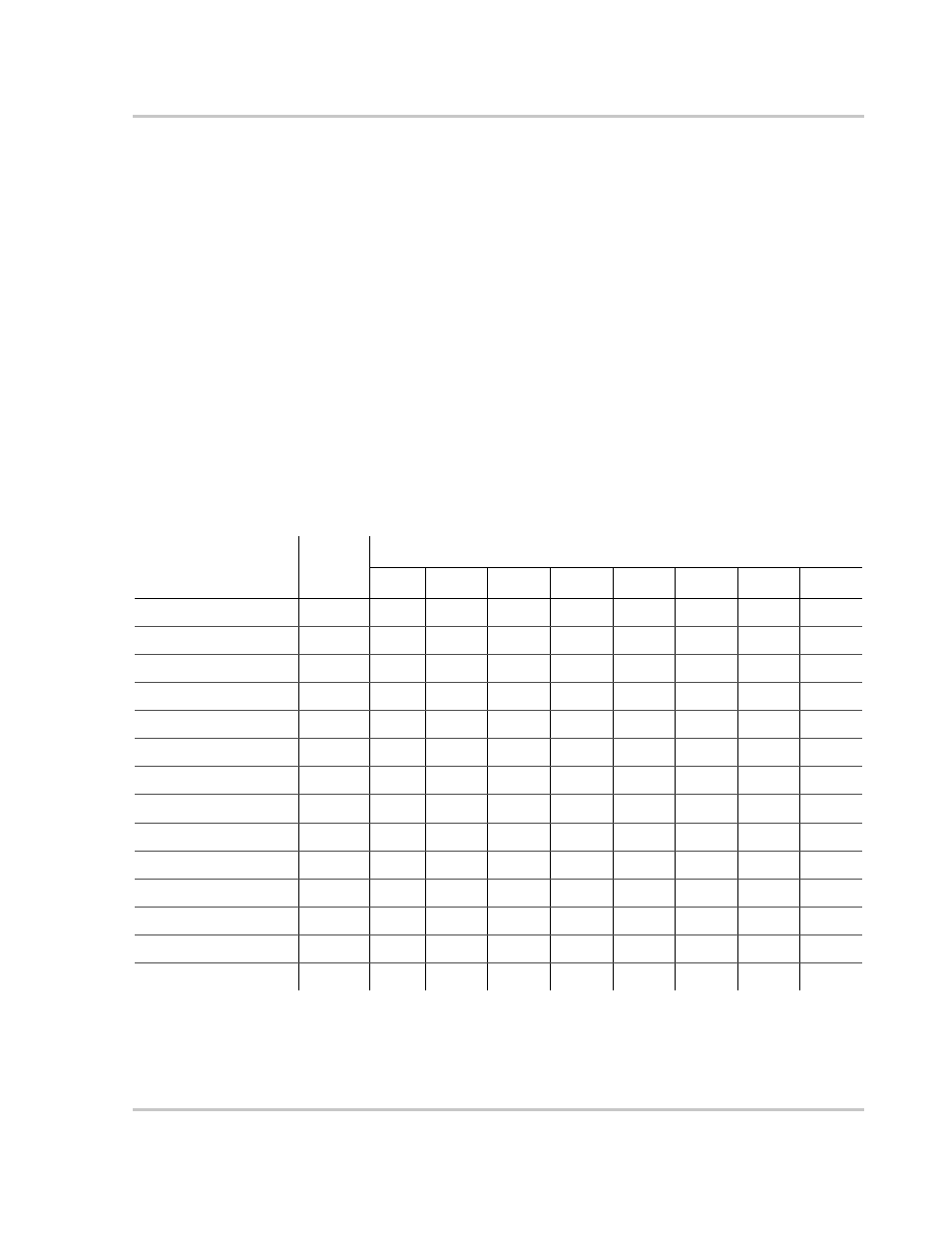
The number in each box represents the amp hours used (at 12 volts DC) based on
various continuous run times.
* Note: refrigeration is typically calculated using a 1/3 duty cycle.
Table 3-4 Typical Power Consumption
Appliance
Typical
Wattage
Appliance Run Times/Amp Hours*
5 min 15 min 30 min 1 hr.
2 hr.
3 hr.
8 hr.
24 hr.
13" color TV
50
0.33
1
2
4
8
12
32
96
19" color TV
100
0.66
2
4
8
16
24
64
192
VCR
50
0.33
1
2
4
8
12
32
96
Lamp
100
0.66
2
4
8
16
24
64
192
Blender
300
2
6
12
Curling iron
50
0.33
1
2
3/8" power drill
500
3.3
10
20
Icemaker*
200
2.6
5.2
10.4
15.6
41.6
83.2
Coffee maker
1000
6.6
20
40
80
160
3 cu. foot refrigerator*
150
2
4
8
12
32
96
20 cu. foot refrigerator*
750
21
42
84
126
336
672
Compact microwave
750
5
15
30
60
120
180
Full-size microwave
1500
10
30
60
120
240
360
Vacuum
1100
7.3
22
44
88
176
264
