L.p. and natural gas orifices, Orifice specifications chart – Whirlpool 4322452 User Manual
Page 22
Page 3-4
L.P. AND NATURAL GAS ORIFICES
The actual size and configuration of each orifice depends on several factors. The most important
factor, however, is the type of gas that will be used by the gas range system. The two most
frequently used types are:
liquefied petroleum (L.P.)
gas, and
natural
gas.
L.P. gas is generally heavier than natural gas and has a higher heat output.
For example, when one cubic foot of L.P. gas is burned, it gives off approximately 2,500 B.T.U. of
heat, while one cubic foot of natural gas will yield only 1,000 B.T.U. Since the heat density of L.P.
gas is higher than natural gas, it takes less cubic feet of L.P. gas to produce the same amount of
heat. An L.P. orifice will always be smaller than a natural gas orifice with an equivalent B.T.U. rating
(see the following “Orifice Specifications Chart” ). It is also important to remember that much more
air is needed with the L.P. gas system (24 cu. ft.) than with the natural gas system (10 cu. ft.). The
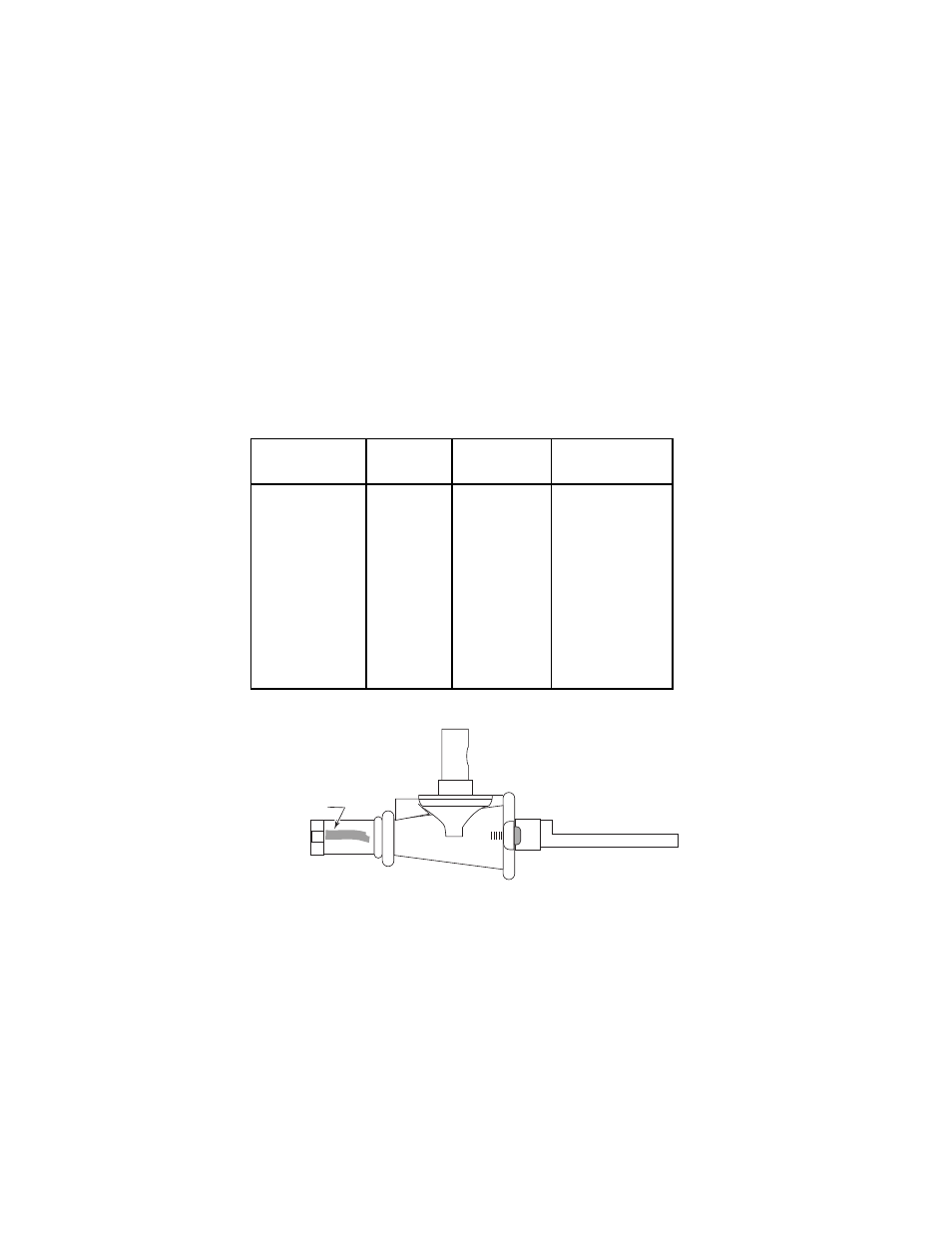
identification color location on the valve is shown in Figure 3-6.
SUGGESTED
IDENT.
DRILL SIZE
COLOR
STAMPING
BTU RATING
1.45 MM
BRASS
NAT
9,500
#65
BRASS
L.P.
8,500
#55
BLACK
NAT
7,500
#68
BLACK
L.P.
6,500
1.2 MM
NICKEL
NAT
6,500
.7 MM
NICKEL
L.P.
5,500
#54
BRASS
NAT
9,000
#66
BRASS
L.P.
8,000
1.85 MM
–
NAT
12,500
#60
–
L.P.
11,500
Identification
Color
Figure 3-6
Orifice Specifications Chart
