Operation, Continued product features, Continued product features - continued – Transition Networks CBFTF10XX-15X User Manual
Page 4
6
CBFTF10xx-15x
Tech Support: 800-260-1312 International: 952-941-7600 7am-6pm CST (GMT-6:00)
OPERATION
- Continued
Product Features
Auto-Negotiation
The Auto-Negotiation feature allows the Media Converter to be used with
10Base-T and 100Base-TX twisted-pair ports. Using Auto-Negotiation, the
Media Converter brings up the copper links in the highest speed and mode
possible for all the attached network devices.
If selected, Auto-Negotiation allows a twisted-pair link to become operational
only after the Auto-Negotiation function matches network speed capabilities
at both ends of the twisted-pair copper segment.
Autocross
The AutoCross™ feature, when selected, allows either straight-through (MDI)
or crossover (MDI-X) cables to be used when connecting to 10Base-TX or
100Base-TX devices, such as hubs, transceivers, or network interface cards
(NICs). AutoCross determines the characteristics of the cable connection and
automatically configures the unit to link up, regardless of the cable
configuration. (This feature does not require operator intervention.)
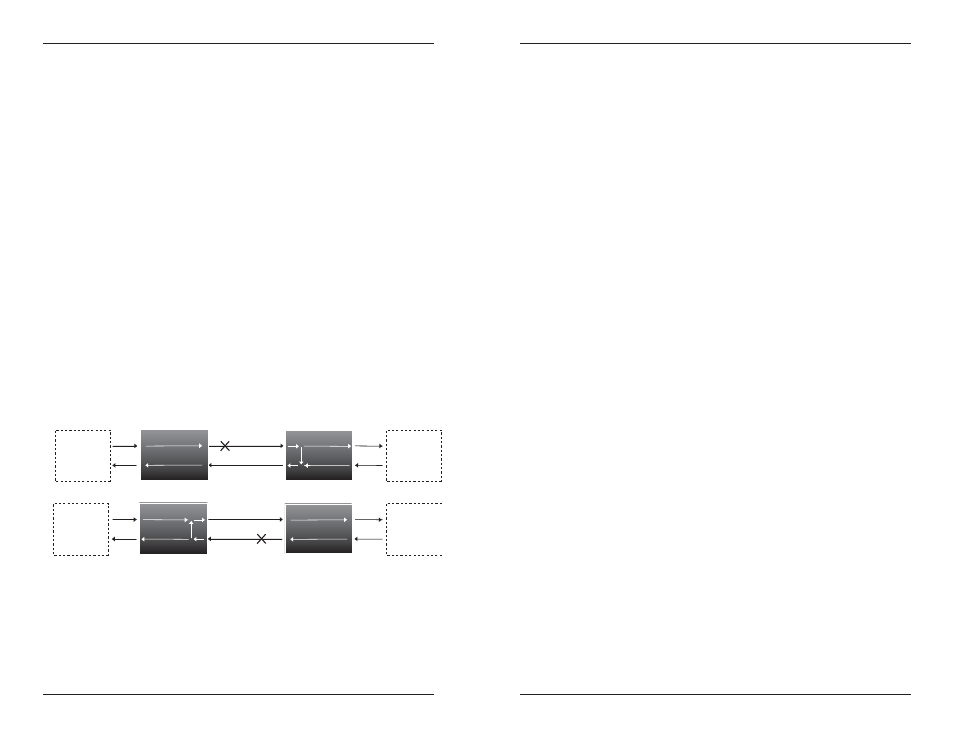
Far-End Fault
When the Far-End Fault feature is activated, a fault on an incoming fiber link
causes the Media Converter to transmit a Far-End Fault signal on the outgoing
fiber link. In addition the Far-End Fault signal also activates the Link Pass-
Through, which, in turn, disables the link on the copper portion of the
network.
Fiber
Copper
Copper
(Sends a Far-End
Fault)
Media Converter
Media Converter
Fiber
Copper
Copper
Media Converter
(Sends a Far-End
Fault)
Media Converter
100Base-TX
Device
100Base-TX
Device
100Base-FX
Device
100Base-FX
Device
[email protected] -- Select the “Transition Now” Link for a Live Web Chat
7
OPERATION
- Continued
Product Features - Continued
Full-Duplex Network
In a full-duplex network, maximum cable lengths are determined by the type
of cables that are used. See page 1 (front cover) for the cable specifications
for the different CBFTF10xx-15x models.
The 512-Bit Rule does not apply in a full-duplex network.
Half-Duplex Network (512-Bit Rule)
In a half-duplex network, the maximum cable lengths are determined by the
round trip delay limitations of each Fast Ethernet collision domain. (A
collision domain is the longest path between any two terminal devices, e.g. a
terminal, switch, or router.)
The 512-Bit Rule determines the maximum length of cable permitted by
calculating the round-trip delay in bit-times (BT) of a particular collision
domain. If the result is less than or equal to 512 BT, the path is good.
For more information on the 512-Bit Rule, see the white paper titled “Collision
Domains” on the Transition Networks website at:
http://www.transition.com/learning/whitepapers/colldom_wp.htm
Using SNMP
See the on-line documentation that comes with Transition Networks
FocalPoint™ software for applicable commands and usage.
Use SNMP at an attached terminal or at a remote location to monitor the
Media Converter by monitoring:
•
Media Converter power
•
Copper and f
iber link status
•
Copper and fiber duplex mode
•
Copper port speed
•
Hardware switch setting
Also, use SNMP to enter network commands that:
•
Enable/disable Auto-Negotiation on copper
•
Force 10Mb/s or 100Mb/s on copper
•
Force full-duplex or half-duplex on copper
•
Force full-duplex or half-duplex on fiber
•
Enable/disable Far-End Fault on fiber
