Recursive sequences – Texas Instruments TI-83 PLUS User Manual
Page 186
TI-83 Plus
Sequence Graphing
183
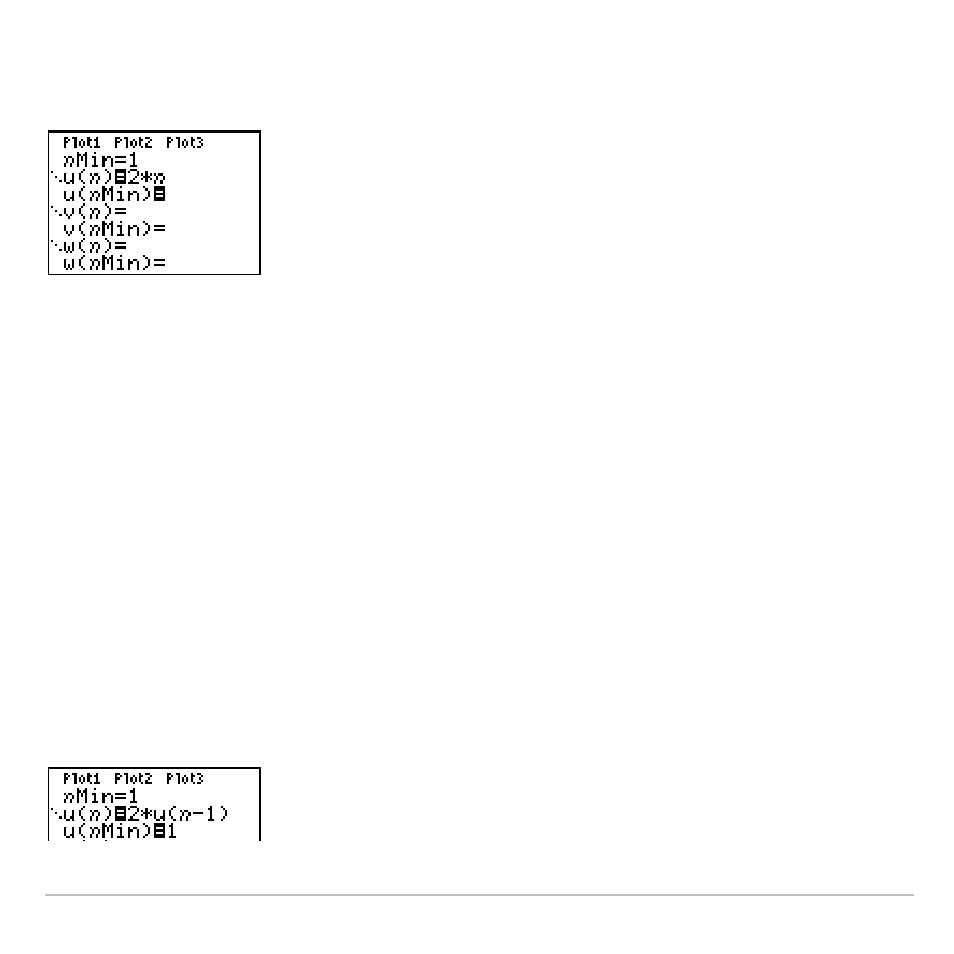
For example, in the nonrecursive sequence below, you can calculate
u(5)
directly, without first calculating
u(1)
or any previous term.
The sequence equation above returns the sequence
2
,
4
,
6
,
8
,
10
, …for
n
=
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
,
… .
Note: You may leave blank the initial value
u(nMin)
when calculating
nonrecursive sequences.
Recursive Sequences
In a recursive sequence, the
n
th term in the sequence is defined in
relation to the previous term or the term that precedes the previous term,
represented by
u(
n
N
1)
and
u(
n
N
2)
. A recursive sequence may also be
defined in relation to
n
, as in
u(
n)=u(n
N
1)+
n.
For example, in the sequence below you cannot calculate
u(5)
without
first calculating
u(1)
,
u(2)
,
u(3)
, and
u(4)
.
This manual is related to the following products:
