Chapter 3 theory of operation, Circuitry of the gpib-120a, Figure 3-1. gpib-120a block diagram – National Instruments GPIB-120A User Manual
Page 15: Circuitry of the gpib-120a -1, Figure 3-1, Gpib-120a block diagram -1
© National Instruments Corporation
3-1
GPIB-120A User Manual
Chapter 3
Theory of Operation
This chapter describes the operational theory of the GPIB-120A. This chapter assumes that you
have a basic knowledge of the GPIB. If you are a first-time user or you would like to review the
basics, refer to Appendix A, Operation of the GPIB, for a history and the basic operation of the
GPIB.
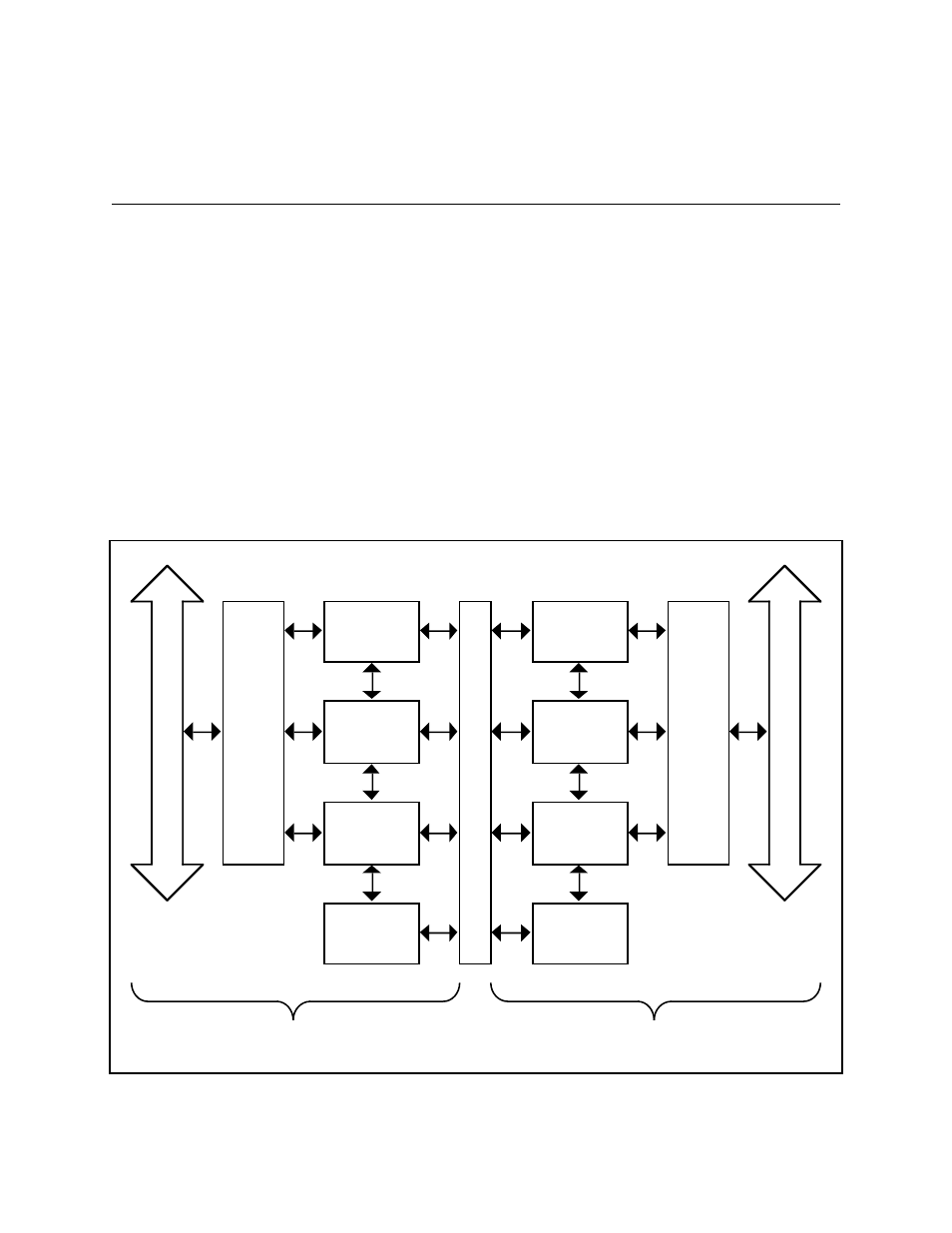
Circuitry of the GPIB-120A
The GPIB-120A consists of two sides: Bus A and Bus B. The circuitry for both sides is
logically identical and the two sides are electrically isolated from each other. The only
difference between the two sides is that logic ground on Bus A is connected to the chassis
ground while the logic ground for Bus B is not. Thus, Bus B is the isolated side of the
expansion. To reduce measurement problems caused by noise and ground loops, the
measurement instruments must be located on the isolated Bus B and all other devices must be
located on Bus A. A block diagram for the GPIB-120A is shown in Figure 3-1.
GPIB
Transceivers
Optoisolators
Controller
Detection
GPIB A
GPIB B
GPIB
Transceivers
Controller
Detection
Side B
Side A
Source
Handshake
Detection
Source
Handshake
Detection
Data
Direction
Control
Data
Direction
Control
Parallel
Poll
Detection
Parallel
Poll
Detection
Figure 3-1. GPIB-120A Block Diagram
