Schneider Electric Modbus Plus Network Bridge Multiplexer none User Manual
Page 33
Device Addressing and Message Routing
31007492
23
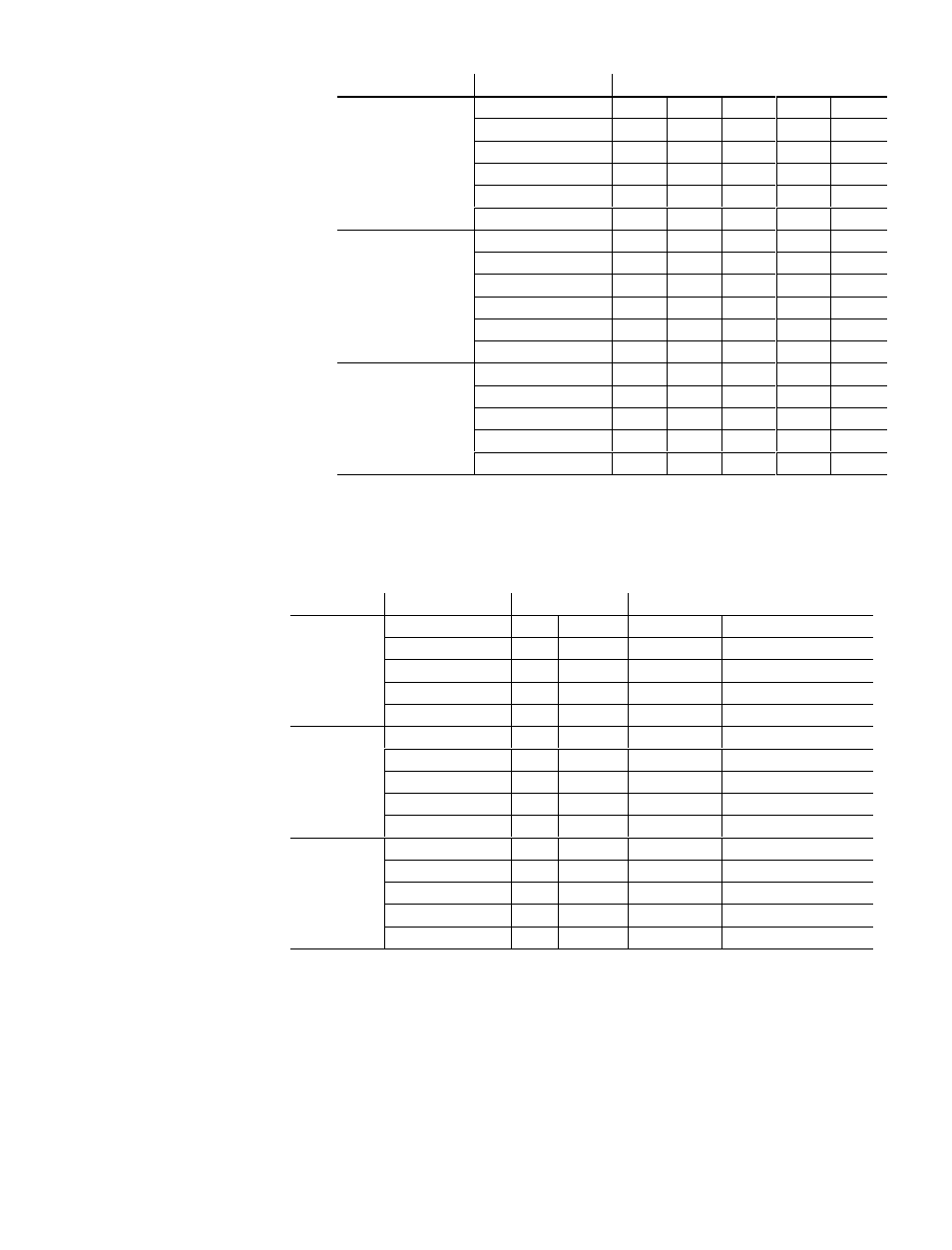
Here are examples of routing between peer, master, and slave devices.
From
To
Routing Path
CPU A (Primary)
Slave A
5
2
0
0
0
50
5
3
50
0
0
CPU C
25
2
0
0
0
SA85 (Task 1)
25
30
1
0
0
Slave B
25
4
2
0
0
200
25
4
3
200
0
CPU C
SA85 (Task 2)
30
2
0
0
0
Slave B
4
2
0
0
0
200
4
3
200
0
0
CPU A (Primary)
24
8
0
0
0
CPU B (Standby)
24
40
0
0
0
100
24
5
3
100
0
SA85
Slave B
4
2
0
0
0
150
4
3
150
0
0
CPU C
2
0
0
0
0
CPU A (Primary)
24
8
0
0
0
50
24
5
3
50
0
If Masters A, B, and C are programming panels such as the Modicon
P230, they can attach to various devices using Direct, Implicit, or MUX
addressing, or mapped routing:
From
To
Address
Routing Method
Master A
CPU A (Primary)
8
Attach
Direct
8 0 0 0 0
Slave A
72
Attach
MUX
Internal Path
CPU C
252
Attach
Implicit
252/10 = 25 2 0 0 0
50
50
Attach
Mapped
0 3 50 0 0
200
200
Attach
Mapped
25 4 3 200 0
Master B
CPU C
2
Attach
Direct
2 0 0 0 0
Slave B
72
Attach
MUX
Internal Path
CPU A (Primary)
248
Attach
Implicit
248/10 = 24 8 0 0 0
200
200
Attach
Mapped
0 3 200 0 0
50
100
Attach
Mapped
24 5 3 50 0
Master C
CPU A (Primary)
248
Attach
Implicit
248/10 = 24 8 0 0 0
CPU B (Standby)
71
Attach
Mapped
24 40 0 0 0
Slave A
72
Attach
Mapped
24 5 2 0 0
Slave B
73
Attach
Mapped
4 2 0 0 0
150
74
Attach
Mapped
4 3 150 0 0
