Fortinet FortiDB User Manual
Page 21
System Views
Oracle System Views
FortiDB Version 3.2 Privilege Monitor User Guide
15-32000-81364-20081219
19
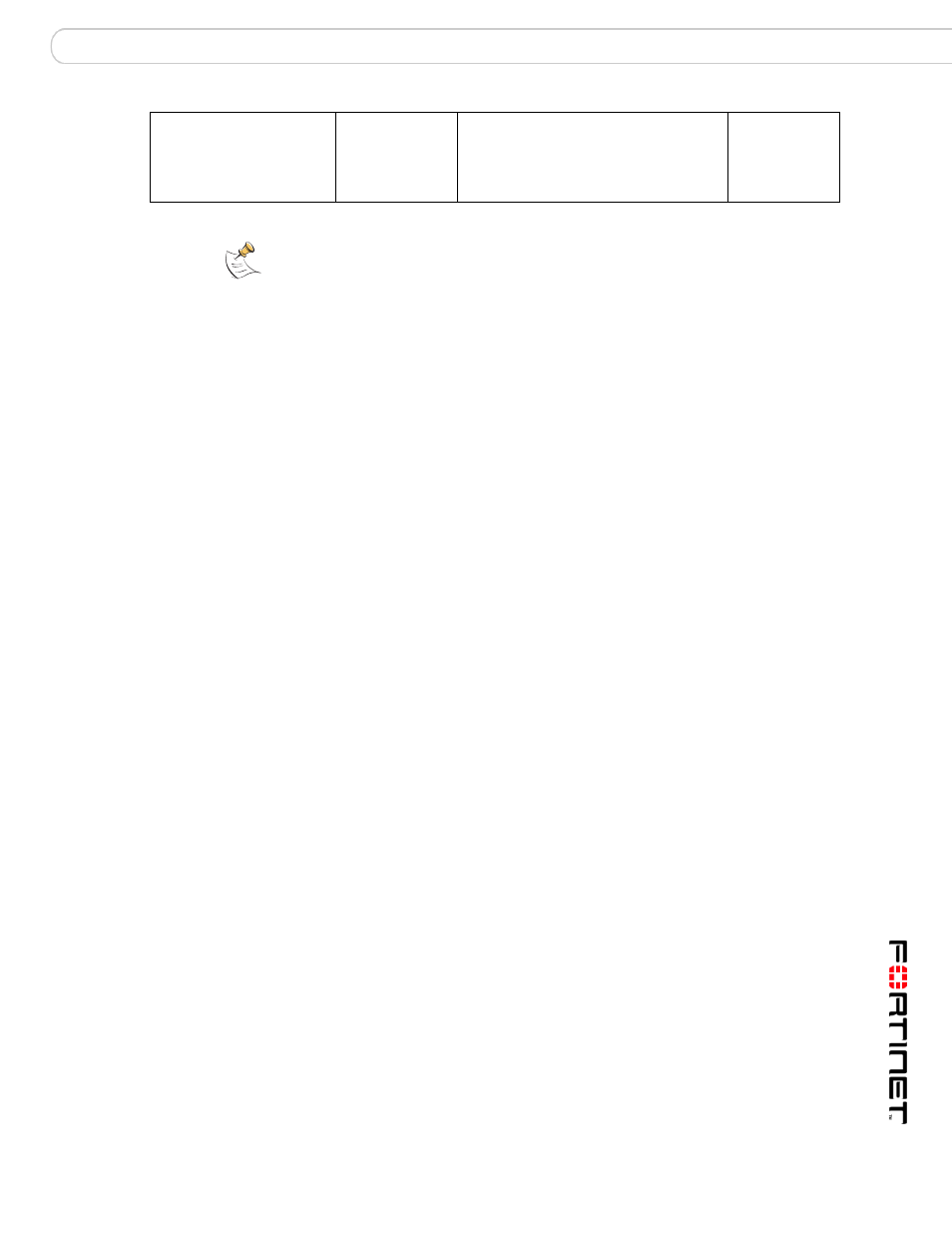
SYS.PROXY_USERS
Users who can
assume the
identity of
other users
Contains information about which
user can assume the identity of
another. Proxy users are typically
employed in an environment with a
middle tier, such as a firewall.
Note: SYS.DBA_TS_QUOTAS and SYS.PROXY_USERS always run with the
snapshot (or No Audit) Data Retrieval Method, even if the database connection
was defined with the Data Retrieval Method set to Audit. However, changing
Tablespace quotas and changing proxy users are activities that can be monitored
and can generate alerts. Both are monitored by SYS.DBA_USERS, which, in turn,
monitors the use of the ALTER USER command. As a result, you will see two
alerts generated for a single activity.
The two alerts come about in this manner. With the Audit method, when
SYS.DBA_USERS is enabled, FortiDB MA issues an AUDIT USER command
which causes CREATE/ALTER/DROP USER commands to be audited. In
addition, these commands are used to not only manage database users but
also Tablespace quotas and proxy users.
Consider, for example:
ALTER USER scott QUOTA UNLIMITED ON SYSTEM
This command generates an audit record whose action is ALTER USER
because of AUDIT USER. This causes the PM Schema View,
SYS.DBA_USERS, to generate the first of the two alerts. The ALTER USER
command also causes a record to be added to the Oracle's dictionary view,
SYS.DBA_TS_QUOTAS, in the target database. The PM Schema View,
SYS.DBA_TS_QUOTAS, monitors the dictionary view (using the No
Audit/snapshot method), detects this new record, and generates the second
alert.
The CREATE USER and DROP USER commands may also add or remove
records from the SYS.DBA_TS_QUOTAS and SYS.PROXY_USERS views. Like
ALTER USER, those commands also allow you to specify Tablespace and
proxy-user specifications.
