5 automatic gateway configuration, 6 switch meshing (lan aggregation) – HP 2424M User Manual
Page 14
HP ProCurve Switch 4000M / 8000M / 2424M / 1600M Reviewer’s Guide
• To prevent broadcast storms, the switch provides broadcast throttling, a filter defined on each
port that allows only a user-specified level of broadcast traffic from entering the switch from
that port (default is 40%).
Actual packet forwarding is handled at layer 2 where high speed and low latency can be economically
provided.
More details on ABC can be found in the paper “HP Switches - Controlling Network Traffic” in the
technical library on HP’s networking web site at
http://www.hp.com/rnd/products/solutions/techlib/techlib.htm
.
2.5 Automatic Gateway Configuration
If the HP ProCurve Switch 4000M/8000M/2424M/1600M will be replacing an existing router with
multiple subnets, the default gateway in end nodes connected to the switch need to be set to their own
IP address, or, if the stack supports it, 0.0.0.0. This will force each end node to ARP whenever a packet
is sent to a destination not previously known. Once changing the default gateway is done, no other
administrative action is needed in the future when moving end-nodes around the network.
In DHCP environments the HP ProCurve Switch 4000M/8000M/2424M/1600M can set the end node
default gateway setting to the same IP address as the end node. The switches do this by changing the
default gateway field of the DHCP packets as they travel through the switch.
Any end nodes that are on the same switch segment as the DHCP server will not be modified since
those packets do not travel through the switch. It is recommended when using the Automatic Gateway
Configuration feature that DHCP servers be located on switch segments without any end nodes.
If the DHCP server itself allows setting the default gateway to the end node address it is better to use the
DHCP server this way rather than the Automatic Gateway Configuration in the switch. Microsoft
Windows NT
®
8
2000, when released, will allow this directly. Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 can also do this
with a registry change. For details see:
http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/q167/6/86.asp
.
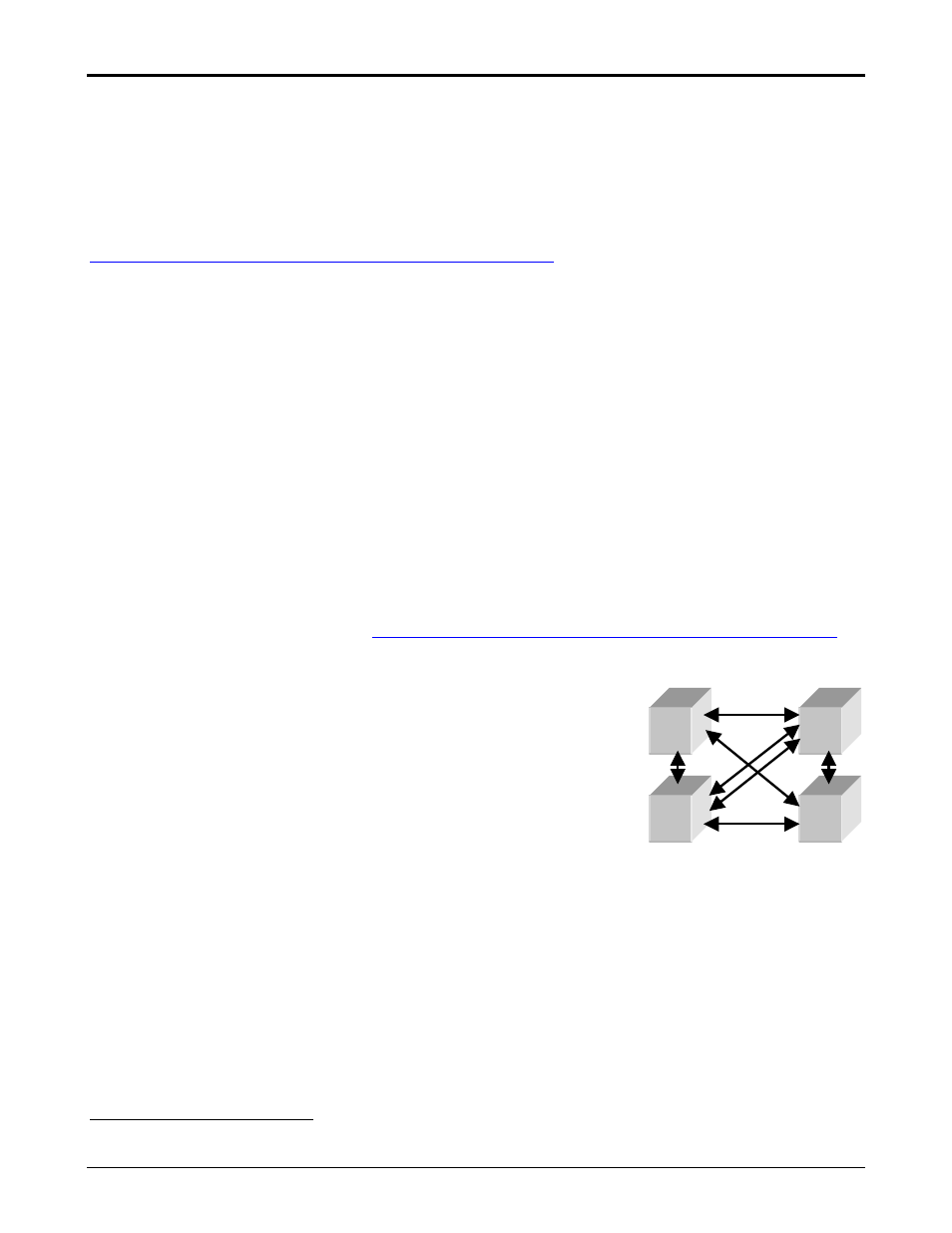
2.6 Switch Meshing (LAN Aggregation)
The HP ProCurve Switch 4000M/8000M/2424M/1600M support Switch
Meshing, a way to interconnect these switches in a meshed topology.
Meshed switch-to-switch links can all be used simultaneously to their full
advantage, with traffic being load balanced through redundant links
based on dynamically determined latency in the different possible paths
between switches. High availability, fault tolerant networks can be easily
built with very low network administration required.
In traditional switched environments, meshed topologies are not allowed
A
D
C
B
without the use of the Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1D). Spanning Tree detects loops in the
topology and logically blocks as many links as necessary to avoid traffic loops. If one of the active links
fails, Spanning Tree enables another link to re-establish the path, if possible. Unfortunately, Spanning
Tree requires links to be available that are not being used for data, letting available bandwidth go
unused.
Although Spanning Tree Protocol is supported by the 4000M/8000M/2424M/1600M (allowing them to
participate in pre-existing switch/router environments), Switch Meshing is superior in that it provides a
way for the switches to use all the available links between switches. With Switch Meshing, the switch
selects the best traffic path for each new destination end-node it learns based on dynamically
determined latency in each of the possible paths to the node. Recalculation of path latency in each
switch is done every 30 seconds and is based on link speeds, input and output buffer queue lengths, and
knowledge of any dropped packets on particular ports.
8
Microsoft and Windows NT are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
©1998, 1999, 2000 Hewlett-Packard Co
Revision 3.2b – 1/15/2000
Page 14 of 36
