Main logic loop, Slc processor not in run, Backplane data transfer – ProSoft Technology MVI46-GSC User Manual
Page 42
MVI46-GSC ♦ SLC Platform
Reference
Generic Serial Communication Module
Page 42 of 78
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
December 5, 2007
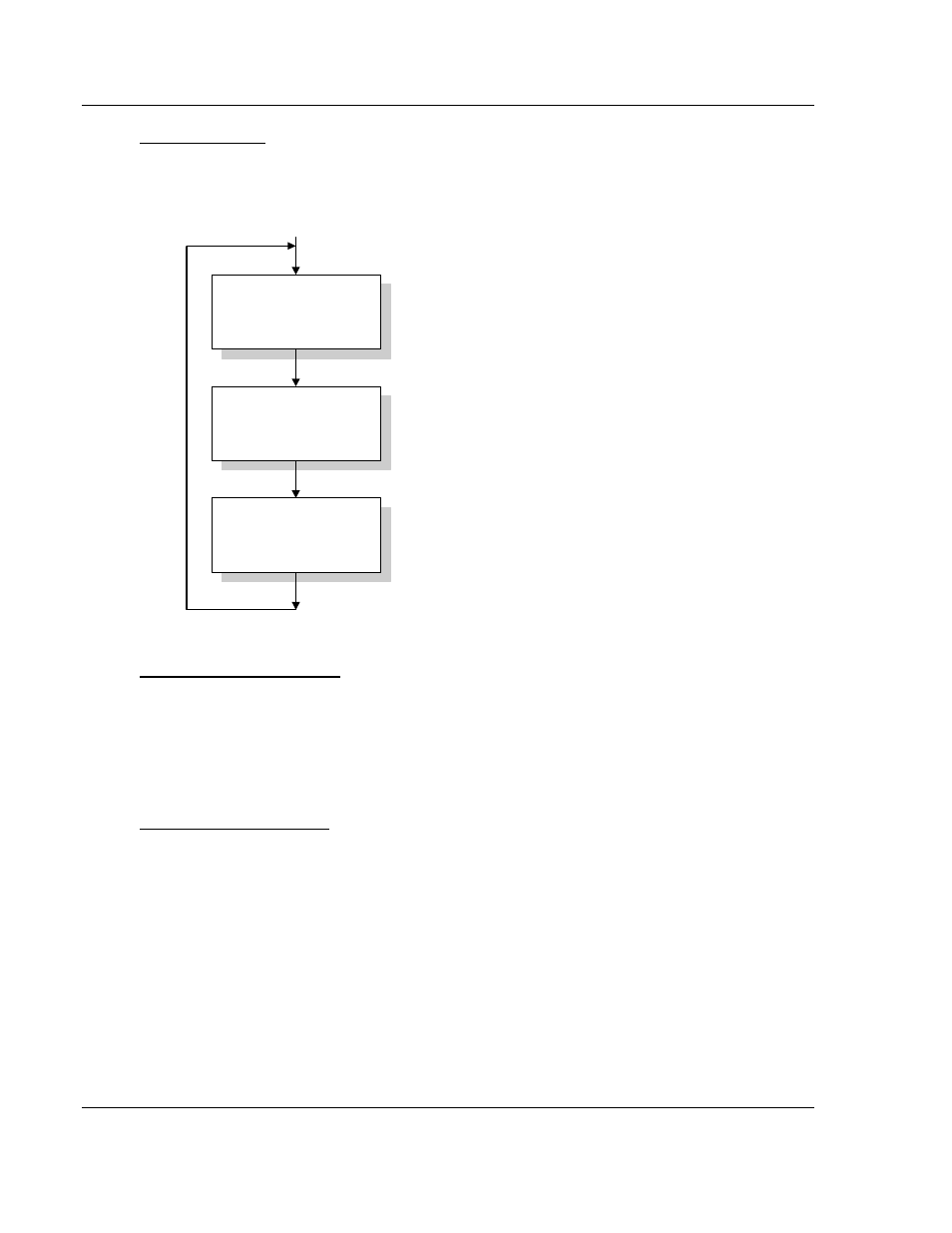
Main Logic Loop
Upon completing the power up configuration process, the module enters an
infinite loop that performs the following functions:
Call I/O Handler
Call CFG/DEBUG Port
Driver
Call Network Server
Drivers
Call I/O Handler
Transfers data between the module and processor
(user, status, etc.)
Call Serial Port Driver
Rx and Tx buffer routines are interrupt driven. Call to
serial port routines check to see if there is any data
in the buffer, and depending on the value, will either
service the buffer or wait for more characters.
Call Serial Port Driver
(Configuration/Debug Port)
Rx and Tx buffer routines are interrupt driven. Call to
Cfg/Dbg port routines check to see if there is any
data in the buffer, and depending on the value, will
either service the buffer or immediately return.
From Power Up Logic
SLC Processor Not in Run
Whenever the module detects that the processor has gone out of the Run mode
(that is, Fault or PGM), the application ports can be shut down as prescribed in
the user configuration. When the processor is returned to a running state, the
module will resume communications on the serial networks. Data transfer will not
occur across the backplane when the processor is not in run mode.
Backplane Data Transfer
The MVI46-GSC module communicates directly over the SLC backplane. Data
travels between the module and the SLC processor across the backplane using
the module's M-Files coordinated using bits in the input and output image of the
module. The update frequency of the images is determined by the scan rate of
the ladder logic.
Data received on the application ports is placed in the module's M1 file. This data
is processed by the ladder logic in the SLC processor. Each port has a reserved
data area of 128 words (256 bytes) to hold this data (4096 bytes maximum per
message). This large data area permits fast throughput of data between the
module and the processor.
