Energizer battery manufacturing version 1.2 – Energizer PP355 User Manual
Page 5
P a g e
| 5
ENERGIZER BATTERY MANUFACTURING
VERSION 1.2
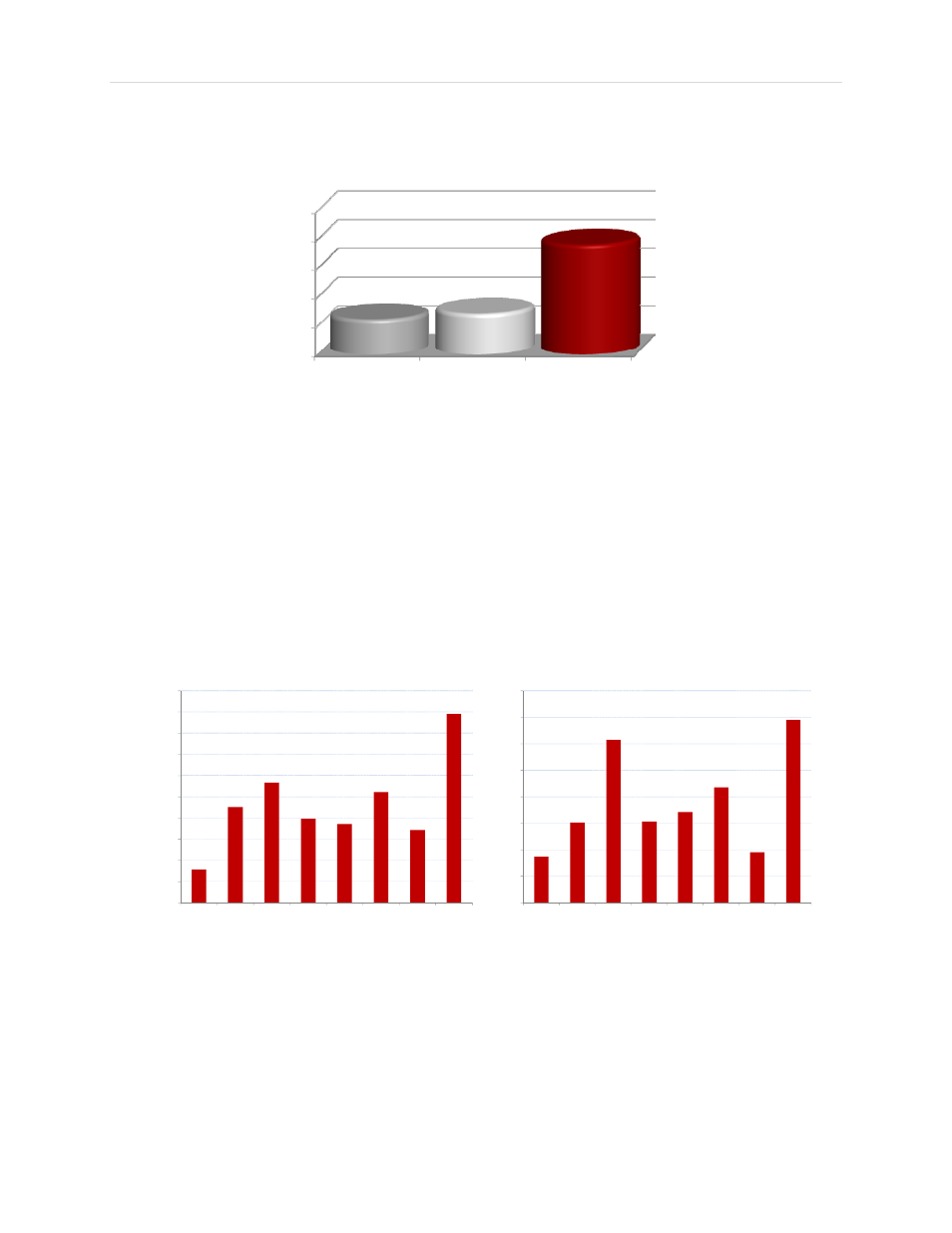
Figure 2: Runtime for Equivalent Volume AAAA Batteries in 50 mW Devices
0
10
20
30
40
50
AAAA Alkaline
Lithium Ion
ZAP PP355
12
14
38
The high energy density of Zinc Air is made possible by using a thin air electrode where the cathode
reaction takes place and by using atmospheric oxygen as the cathode reactant. The result is greater
internal volume for zinc, the active anode material. More zinc translates into longer runtime in similar
overall volume. Figure 3 demonstrates the higher energy density of Zinc Air compared to other
consumer battery systems. The chart on the left displays volumetric energy density in units of Wh/L,
and the chart on the right shows gravimetric energy density in units of Wh/kg. This data is based on the
volume of a AA sized battery for all systems and a continuous 50mA current drain to a 0.9 volt cutoff.
Figure 3: Comparison of Zinc Air versus Other Battery Technologies
156
450
565
396
371
522
343
890
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
Carbon
Zinc
Alkaline
Lithium
Li Ion
Lithium Ion
Polymer
Lithium
MnO2
NiMH
Zinc
Air
En
er
gy
De
ns
it
y
(W
h
/L
)
87
151
307
153
171
218
95
345
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
Carbon
Zinc
Alkaline
Lithium
Li Ion
Lithium Ion
Polymer
Lithium
MnO2
NiMH
Zinc
Air
Sp
ec
ific
En
e
rg
y
(Wh
/k
g)
Energizer Zinc Air Prismatic batteries have an operating voltage similar to Alkaline, which is between
1.10 and 1.30 volts depending on the drain rate of the device. The discharge profile however is
relatively flat similar to rechargeable Nickel Metal Hydride batteries. Figure 4 contains examples of
discharge curves for Zinc Air, Alkaline, Nickel Metal Hydride, and Lithium Iron Disulfide batteries. Even
though the Zinc Air PP355 battery has the same external volume as the AAAA battery, it delivers up to
3X the runtime at a 50 mW discharge.
