TE Technology TC-24-10 User Manual
Page 7
7
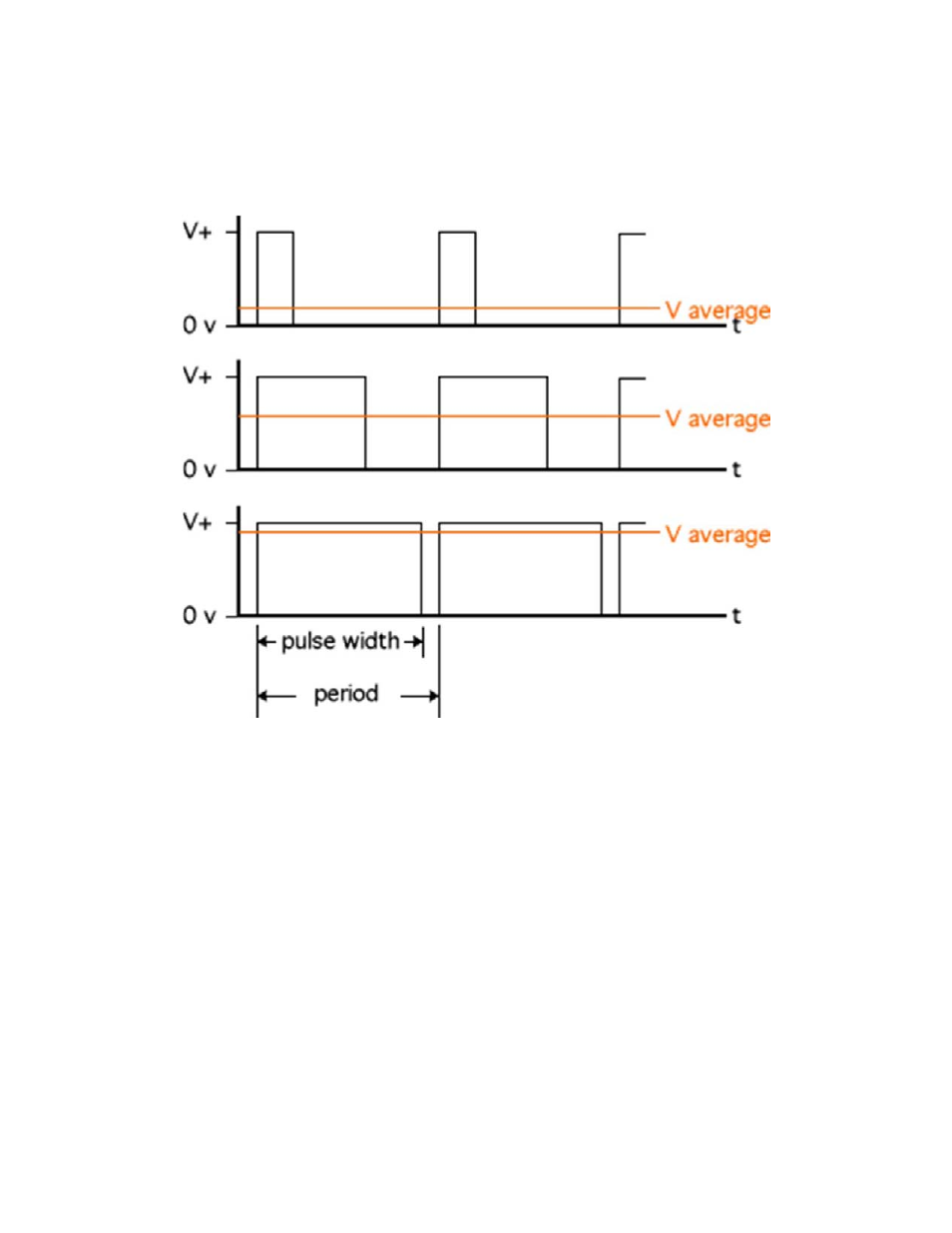
Pulse‐width modulated power output
The controller regulates the output power to the TE using a method called pulse‐width modulation (PWM). With
PWM, power to the TE device is switched quickly “ON” and “OFF” at a constant frequency (1000 Hz for this
controller). This creates a square wave “pulse” of power with a constant time period. The “ON” time, or pulse
width, can be varied to create an average output voltage (Vaverage) that is required by the TE device to maintain
the set temperature.
The important advantage to PWM is that it does not cause the extreme temperature excursions that are
experienced with a thermostatic control system. This helps to extend the life and reliability of the TE devices. An
added benefit is that the controller does not generate a large amount of waste heat, so a large heat sink is not
usually required.
Multiple Control Configurations
The controller can be used with either one power supply for powering the controller electronics and the TE device
together or with two power supplies for powering the controller electronics and TE device independently.
Whether the controller is configured to use one or two power supplies, the TE device should not be allowed to
draw more than 10 A at its rated voltage.
When using one power supply, the input voltage is passed directly through the controller to the TE device during
“ON” pulse. The controller electronics operate within a (9 to 26) V range, so the TE device must likewise be rated
for at least 9 V, but no more than 26 V.
If the TE device operates on less than 9 V, the TC‐24‐10 can be configured to use two power supplies. The power
supply for the controller electronics must be able to provide (9 to 26) V at 150 mA current minimum. The power
supply for the TE device can then be selected to provide the appropriate voltage ranging from (0 to 40) V.
