Performance figures, Handling errors, Exported functions – Sundance SMT6035 v.2.2 User Manual
Page 38: Exception mechanism, 21 performance figures, 22 handling errors
Version 2.2
Page 38 of 39
SMT6035 User Manual
21 Performance figures
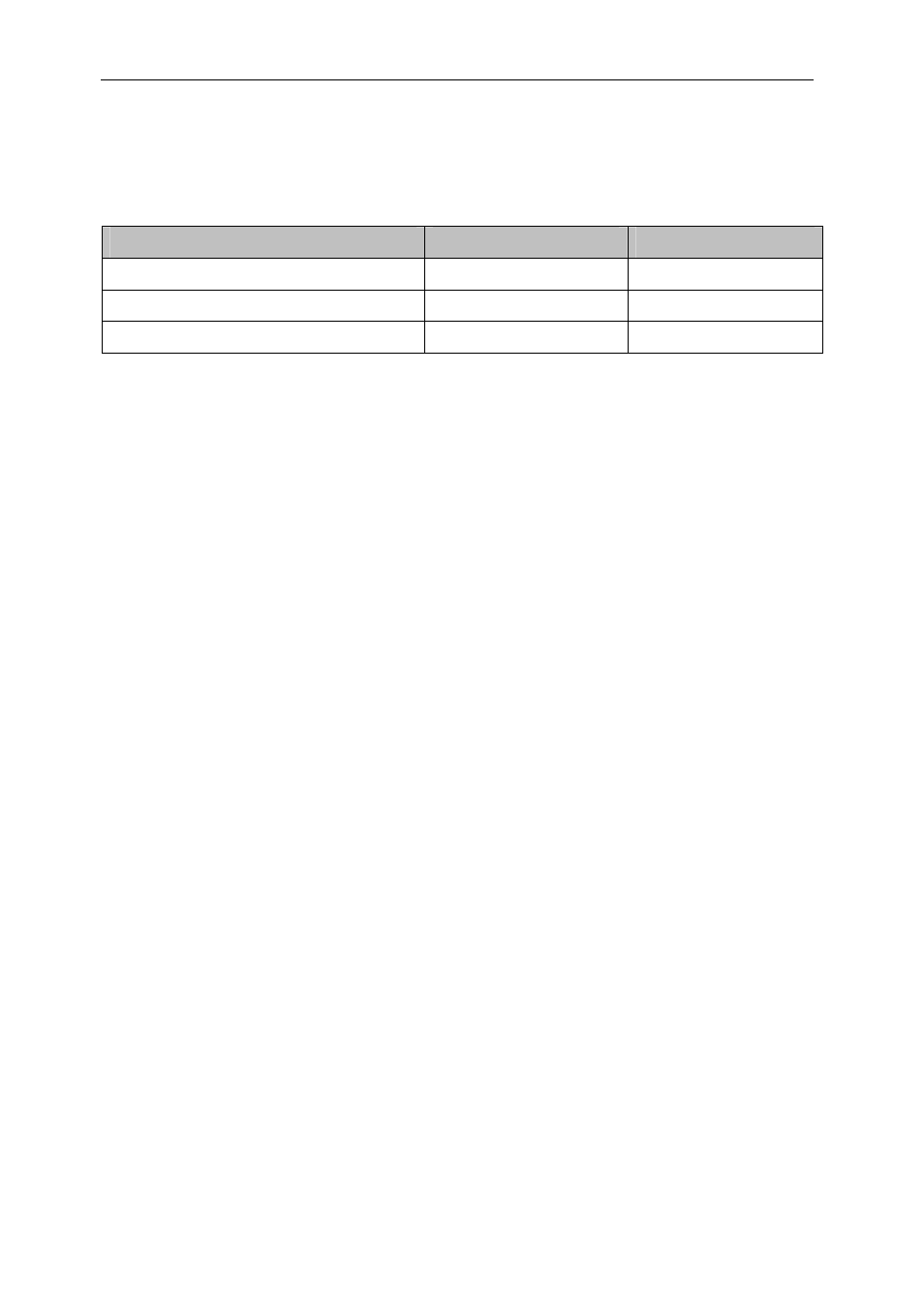
The table below shows typical performance figures obtained with the SMT6035.
Transfer type
Read [MB/s]
Write [MB/s]
HSC with contiguous memory.
46
40
HSC with Scatter/Gather memory.
40
32
Host comport
2
2
Table 3 - Typical performance figures for various transfer types
22 Handling errors
22.1 Exported functions
Most of the functions exported by libsmtdrv.so return status values. You should
always check the return values from these functions. SmtGetError() can be
used to translate the return values into text strings.
The following is an example code section to show you how to use the functions
exported by libsmtdrv.so.
// Open the library
SMTRet ret = SmtOpen();
if ( ret!=SMT_OK )
{
cout << "Could not open SmtDrv library. The error was ("
<< SmtGetError(ret)
<< ")"
<< endl;
return 0;
}
22.2 Exception mechanism
The functions accessed through the SmtOpenBoard() interface will signal errors
by throwing an exception of type SMTExc. Any of the functions provided by
IFHw may throw an exception of type SMTExc.
You have to surround your function accesses by a try-catch block as shown:
try
{
pB->ResetTIMs();
User Manual - Version 2.2, 04/01/07; © Sundance Italia S.R.L.
