Ivoclar Vivadent CosmoPost User Manual
Page 4
4
Contraindication
CosmoPost
– Notes for dentists
and dental technicians
Indication
Since CosmoPost is a ceramic post system, the main
indication is the aesthetically important anterior region, both
in the maxilla and the mandible.
l Anterior region
– 1.4-mm CosmoPost
Use:
1. In the maxilla: only for the lateral incisors, ie, teeth 12 and
22 (FDI); teeth 7 and 10 (ADA).
2. In the mandible: for the central and lateral incisors, ie,
teeth 32 to 42 (FDI); teeth 23 to 26 (ADA).
Any other application is contraindicated and may
compromise the success of the prosthetic restoration.
– 1.7-mm CosmoPost
Use:
The 1.7-mm CosmoPost is used for those teeth, for which
the diameter of the coronal part of the root or the coronal
endodontium clinically indicates a 1.7-mm root canal post.
These teeth are usually the four canines and the central
incisors in the maxilla.
II Posterior region
– Depending on the clinical situation, both the 1.7-mm and
1.4-mm CosmoPost can be used in the posterior region.
Generally, the 1.4-mm post is used for maxillary and
mandibular premolars, while the 1.7-mm post is used for
molars (distal canal in the mandible, palatal canal in the
maxilla).
Important
– The indications and working parameters must be
observed at all times
– The CosmoPost must not be adjusted by grinding,
tapered, or provided with retention grooves, since such
measures may result in predetermined breaking points
on the post.
– The post must not be blasted with aluminium oxide
(Al
2
O
3
). The surface of the post has already been
roughened.
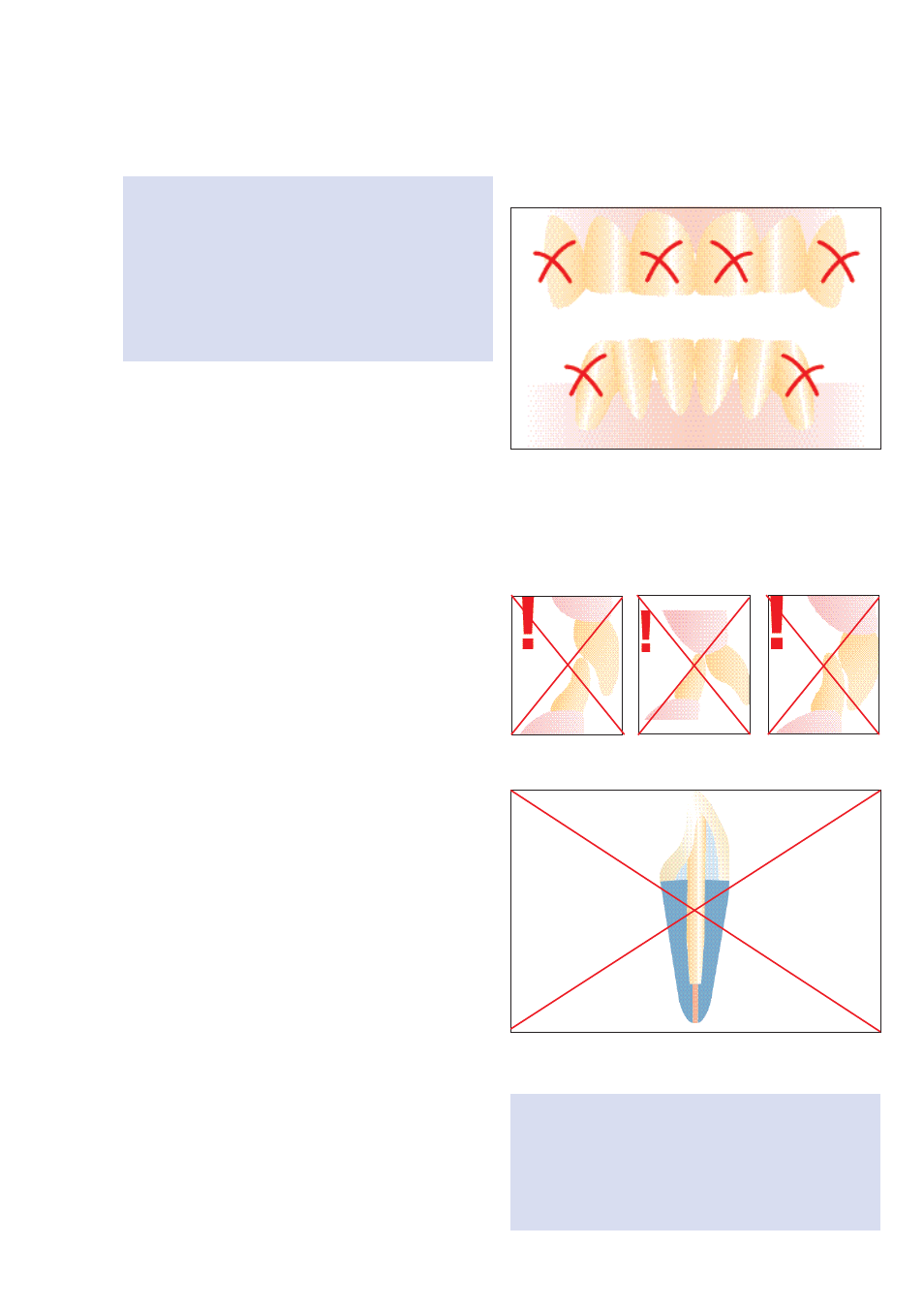
The use of the 1.4-mm CosmoPost is absolutely contra-
indicated for the marked teeth (FDI: 13, 11, 21, 23, 33,
43) (ADA: 6, 8, 9, 11, 22, 27).
Additional contraindications are as follows:
– Use of the CosmoPost for patients suffering from bruxism
or suspected bruxism
– Deep overbite
Important
If the defined preparation (residual dentin) is not possible
or one of the above contraindications is present, a metal
post must be used, since the risk of a post fracture is
clearly increased. A fractured post most often results in
the extraction of the root, since the post is virtually
impossible to remove.
– Less than 2–3 mm supergingival dental hard tissue
– Circular isogingival damage
– Allergy to any of the ingredients
!
