3 pilot operated valve, 4 bellows valve, Value calculation – Bronkhorst IN-FLOW User Manual
Page 14: 1 for gases
BRONKHORST HIGH-TECH B.V.
page 14
9.17.022
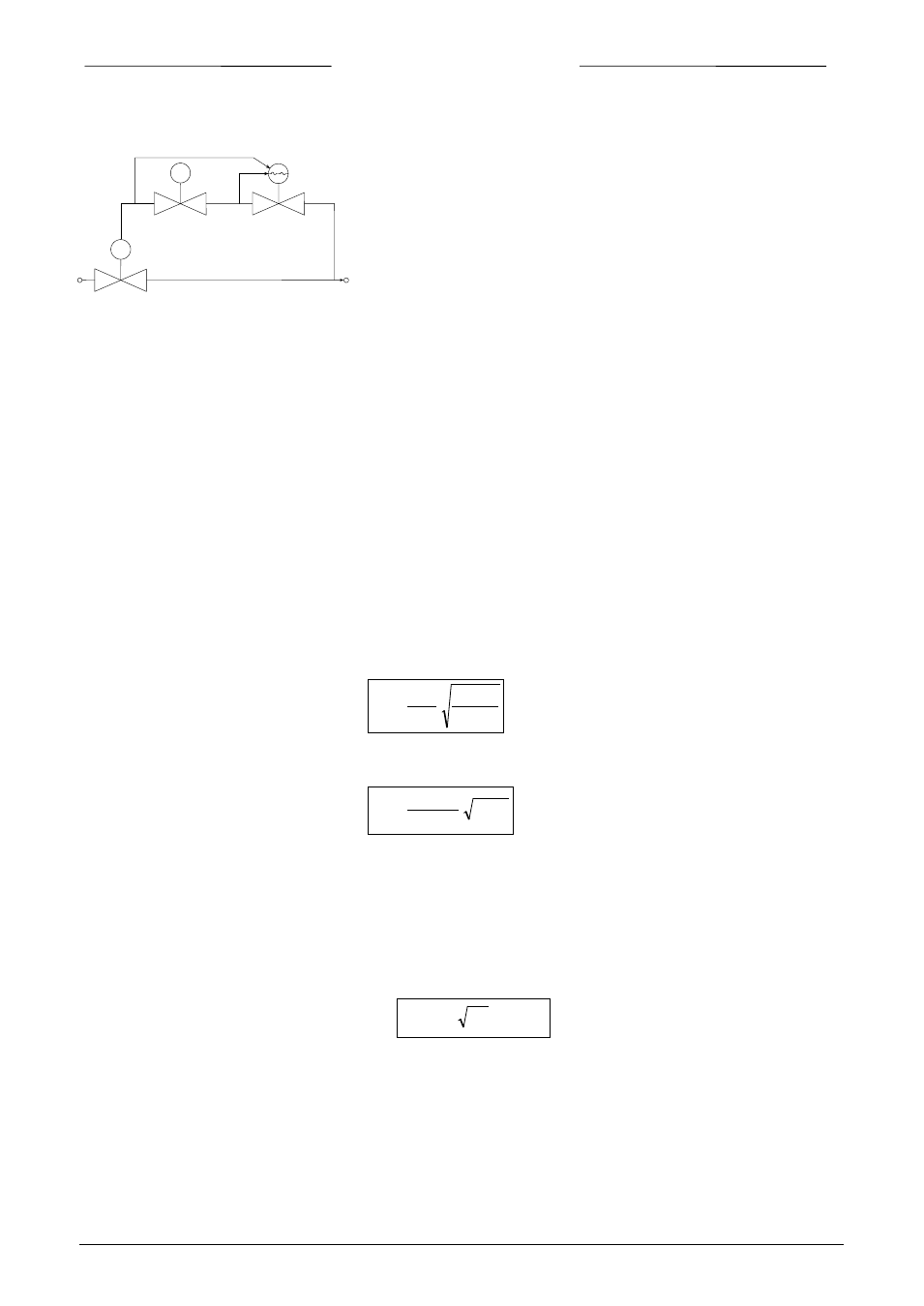
1.3.3 Pilot operated valve
For high flow rates the pilot operated valve has been designed. A
solenoid driven control valve controls the pressure difference
across a piston, which lifts the main plunger.
1.3.4 Bellows valve
This valve type is a direct driven, low power, solenoid operated control valve. A special design, incorporating
a metal bellows allows for a relatively large orifice opening to be controlled. The design is suited for low
pressure or vacuum applications.
1.4
K
v
-value calculation
This calculation method can be used to determine the K
v
-value of the main orifice of a control valve.
1.4.1 For gases
Determine desired ∆p across valve.
∆
p must be at least 20% of supply pressure, or in closed loop systems, of total pressure difference in loop.
If ∆p is 20-50% of supply pressure, use formula:
K
T
p p
v
vn
n
=
⋅
⋅
Φ
∆
514
2
ρ
undercritical
If ∆P is 50-100% of supply pressure, use formula:
K
p
T
v
vn
n
=
⋅
⋅
Φ
257
1
ρ
overcritical
Units:
Φ
vn
= flow [m
n
3
/h]
p
1
= supply pressure [bara]
p
2
= downstream pressure [bara]
∆
p = pressure difference (p
1
- p
2
) [bara]
T = temperature [K]
ρ
n
= density [kg/m
n
3
]
The orifice diameter can be determined by: d= 7.6
K
v
[mm]
P1
pilot valve
pressure
compensating
valve
P2
flowcontrol valve
