EXFO EXpert IPTV Test Tools (FTB-200v2) User Manual
Page 50
50
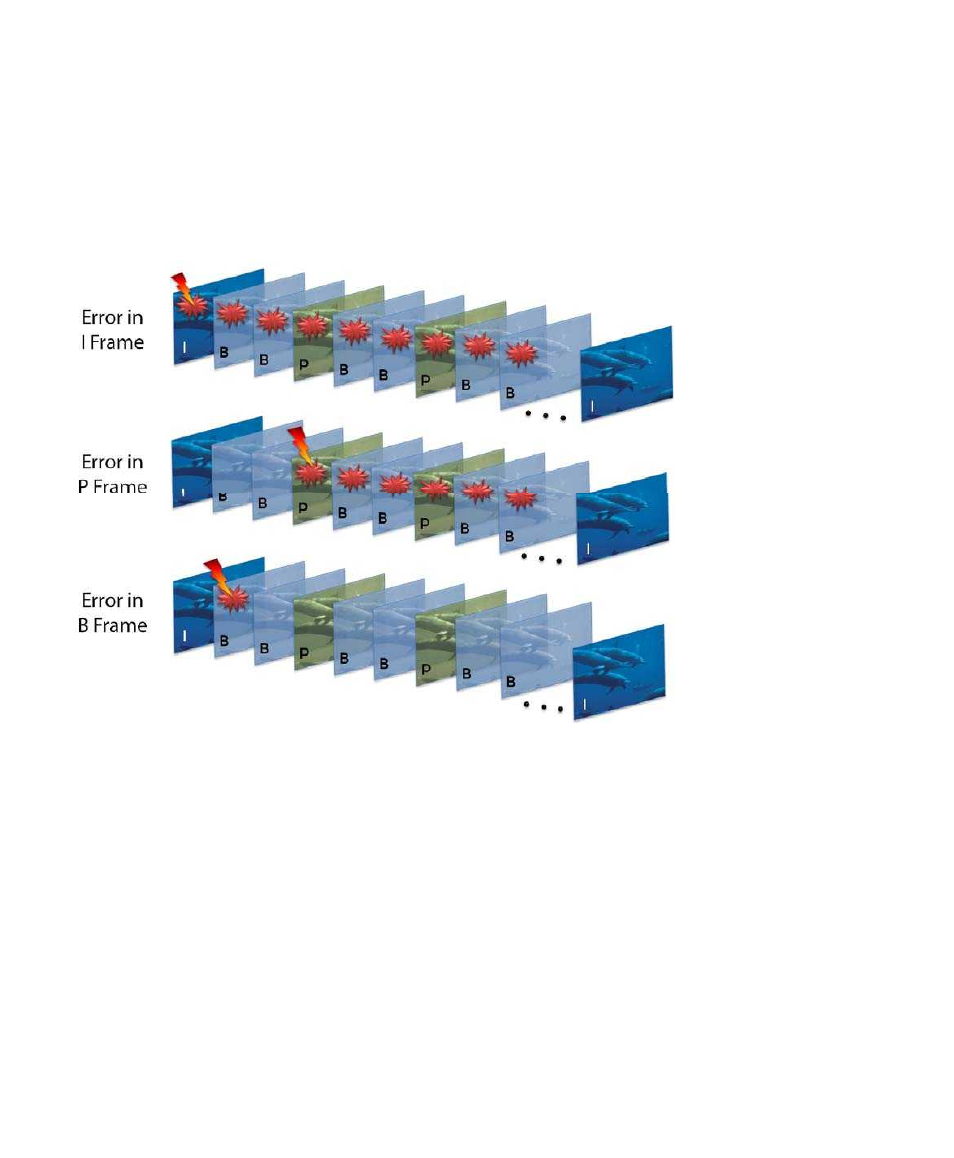
For inter‐frame or motion‐based coding (P and B frames), motion vectors are determined for
each block and encoded. As for intra‐frame coding, errors can render a whole slice or frame
unusable. In simple inter‐frame coding systems, the loss of one I or P frame can make all
subsequent frames unusable until the next I frame is received—resulting in a significant
period of degraded, frozen, or blank video.
Note: the H.264
(MPEG‐4 AVC) codec
standard introduces
two new frame types,
Figure 2‐2. Error
propagation through
frames in a typical
GOP
“Switching I” (SI) and
“Switching P” (SP), which are designed to enable the decoder to more easily switch between
video streams with different bitrates. VQmon/HD reports SI and SP frame metrics when
H.264 is used.
Figure 2‐2 shows the impact of encoding errors on various frame types (I, B, and P) in a typical
Group of Pictures (GOP).
In most cases, the standards for video coding provide considerable flexibility to both the
encoder and decoder, allowing a range of cost/performance tradeoffs to be made. This can
make it difficult to precisely assess the impact of network impairments without knowledge of
the exact implementation.
