Elenco Basic Electricity User Manual
Basic electricity, Model scp-10, 1a 5v
If you have any problems, contact Elenco
®
Copyright © 2014 Elenco
®
Electronics, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ● 150 Carpenter Ave. ● Wheeling, IL 60090
(800) 533-2441 Fax: (847) 520-0085 ● e-mail: [email protected] ● Website: www.elenco.com or www.snapcircuits.net
WARNING: SHOCK HAZARD
-
Never connect Snap Circuits
®
to the electrical outlets in your
home in any way!
WARNING:
Always check your wiring before
turning on a circuit. Never leave a circuit
unattended while the batteries are installed.
Never connect additional batteries or any other
power sources to your circuits.
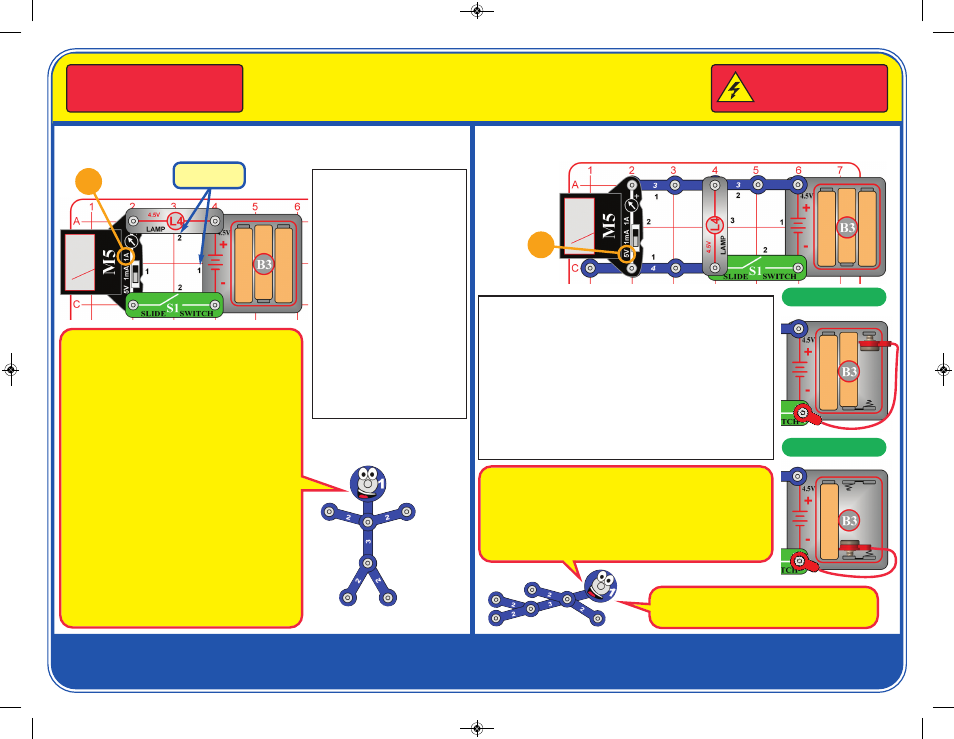
Basic Electricity
Model SCP-10
753159
Snap Circuits
®
uses electronic
blocks that snap onto a base
grid to build different circuits.
These blocks have different
colors and numbers on them so
that you can easily identify
them. Build the circuit shown by
placing all the parts with a black
1 next to them on the clear base
grid first. Then, assemble parts
marked with a 2. Install three (3)
“AA” batteries (not included)
into the battery holder (B3).
Set the meter (M5) to the 1A
setting.
Turn on the slide switch (S1).
The lamp (L4) comes on, and
the meter measures how much
electric current is flowing.
Project 1
Lamp Current
Project 2
Batteries in Series
Electricity is the movement of sub-atomic charged
particles through a material due to electrical pressure
across the material, such as from a battery. Power
sources, like batteries, push electricity through a circuit,
like a pump pushes water through pipes. Wires carry
electricity, like pipes carry water. Devices like lamps use
the energy in electricity to do things. Switches control the
flow of electricity like valves and faucets control water.
The electrical pressure exerted by a battery or other
power source is called voltage and is measured in volts
(V). The “+” and “–” signs on a battery indicate which
direction it will “pump” electricity.
The electric current is a measure of how fast electricity
is flowing in a wire, just as the water current describes
how fast water is flowing in a pipe. It is expressed in
amperes (A) or milliamps (mA = 1/1,000 of an ampere).
The “power” of electricity is a measure of how fast energy
is moving through a wire. It is a combination of the voltage
and current (Power = Voltage x Current). It is expressed in
watts (W).
The resistance of a component or circuit represents how
much it resists the electrical pressure (voltage) and limits the
flow of electric current. The relationship is Voltage = Current
x Resistance. When resistance increases, less current flows.
Resistance is measured in ohms (W).
If desired, use the voltage measured here (with 3 batteries) and the
current measured in project 1 to calculate the resistance and power of
the lamp:
Resistance equals Voltage divided by Current, and should be about 15
ohms. Power equals Voltage times Current, and should be about 1 Watt.
Your results may be different, because M5 is a simple meter with low
accuracy, and your battery voltage can vary.
1A
5V
Set the meter (M5) to the 5V setting, and turn on the slide
switch (S1). The lamp (L4) comes on, and the meter measures
the voltage from the 3 batteries.
Part B: Remove the left battery from the holder (B3), then snap
one side of the red jumper jumper on as shown, and touch
metal on the other end to the left spring in the battery holder.
Read the voltage on the meter, measuring 2 batteries, and
notice how the lamp is dimmer.
Part C: Now also remove the center battery from the holder and
touch metal on the end of the red jumper wire to the center
spring in the holder. Read the voltage on the meter, measuring
1 battery, and notice how the lamp is dimmer.
Placement
Level Numbers
Quiz answers:
1. B
2
. B
3
. C
4
. A
5
. B
Batteries are like electrical pressure, pushing electricity
through a circuit. Adding more batteries increases the
flow of electricity, making the lamp brighter.
Part B:
Part C:
SCP-10_021714.qxp_SCP-10_Instructions 3/7/14 2:35 PM Page 1
