3 pc/104 channel signal description, Pc/104 channel signal description -11 – Acrosser AR-B1320 User Manual
Page 31
A
A
R
R
-
-
B
B
1
1
3
3
2
2
0
0
U
U
s
s
e
e
r
r
’
’
s
s
G
G
u
u
i
i
d
d
e
e
3.13.3
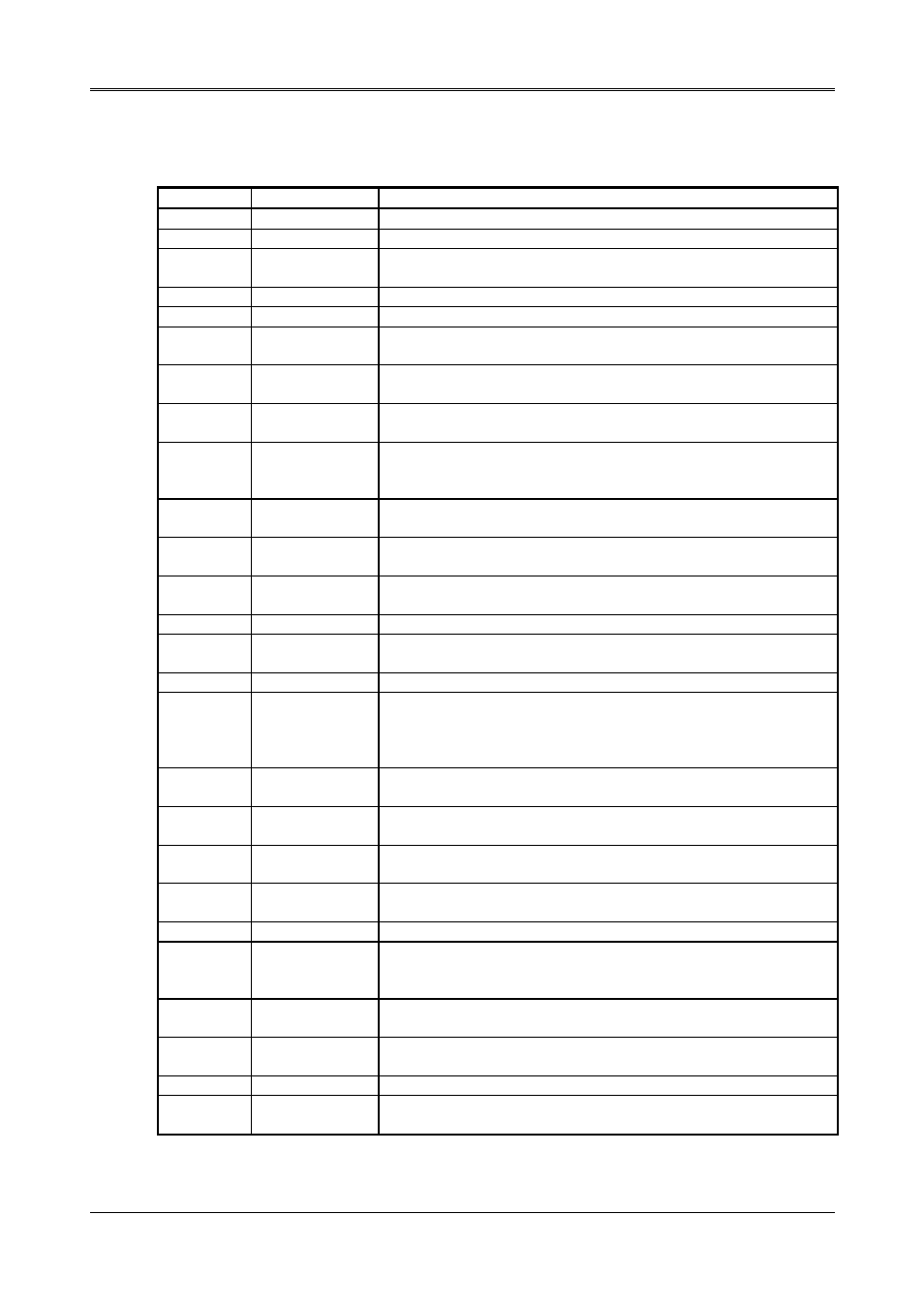
PC/104 CHANNEL SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
Name I/O
Description
BUSCLK
[Output]
The BUSCLK signal of the I/O channel is asynchronous to the CPU clock.
RSTDRV
[Output]
This signal goes high during power-up, low line-voltage or hardware reset
SA0 – SA19
[Input / Output]
The System Address lines run from bit 0 to 19. They are latched onto the falling
edge of "BALE"
LA17 - LA23
[Input / Output]
The Unlatched Address line run from bit 17 to 23
SD0 - SD15
[Input / Output]
System Data bit 0 to 15
BALE
[Output]
The Buffered Address Latch Enable is used to latch SA0 - SA19 onto the falling
edge. This signal is forced high during DMA cycles
-IOCHCK
[Input]
The I/O Channel Check is an active low signal which indicates that a parity error
exist on the I/O board
IOCHRDY [Input,
Open
collector]
This
signal lengthens the I/O, or memory read/write cycle, and should be held low
with a valid address
IRQ 3-7, 9-12,
14, 15
[Input]
The Interrupt Request signal indicates I/O service request attention. They are
prioritized in the following sequence : (Highest) IRQ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7 (Lowest)
-IOR
[Input / Output]
The I/O Read signal is an active low signal which instructs the I/O device to drive
its data onto the data bus
-IOW
[Input / Output]
The I/O write signal is an active low signal which instructs the I/O device to read
data from the data bus
-SMEMR
[Output]
The System Memory Read is low while any of the low 1 Mbytes of memory are
being used
-MEMR
[Input / Output]
The Memory Read signal is low while any memory location is being read
-SMEMW
[Output]
The System Memory Write is low while any of the low 1 Mbytes of memory is
being written
-MEMW
[Input / Output]
The Memory Write signal is low while any memory location is being written
DRQ 0-3, 5-7
[Input]
DMA Request channels 0 to 3 are for 8-bit data transfers. DMA Request channels
5 to 7 are for 16-bit data transfers. DMA request should be held high until the
corresponding DMA has been completed. DMA request priority is in the following
sequence:(Highest) DRQ 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7 (Lowest)
-DACK 0-3, 5-7 [Output]
The DMA Acknowledges 0 to 3, 5 to 7 are the corresponding acknowledge signals
for DRQ 0 to 3 and 5 to 7
AEN
[Output]
The DMA Address Enable is high when the DMA controller is driving the address
bus. It is low when the CPU is driving the address bus
-REFRESH
[Input / Output]
This signal is used to indicate a memory refresh cycle and can be driven by the
microprocessor on the I/O channel
TC
[Output]
Terminal Count provides a pulse when the terminal count for any DMA channel is
reached
SBHE
[Input / Output]
The System Bus High Enable indicates the high byte SD8 - SD15 on the data bus
-MASTER
[Input]
The MASTER is the signal from the I/O processor which gains control as the
master and should be held low for a maximum of 15 microseconds or system
memory may be lost due to the lack of refresh
-MEMCS16
[Input, Open collector] The Memory Chip Select 16 indicates that the present data transfer is a 1-wait
state, 16-bit data memory operation
-IOCS16
[Input, Open collector] The I/O Chip Select 16 indicates that the present data transfer is a 1-wait state,
16-bit data I/O operation
OSC
[Output]
The Oscillator is a 14.31818 MHz signal
-ZWS
[Input, Open collector] The Zero Wait State indicates to the microprocessor that the present bus cycle
can be completed without inserting additional wait cycle
Table 3-9 I/O Channel Signal Description
3-11
