7 serial ports, 2) transmitter holding register (thr), 3) interrupt enable register (ier) – Acrosser AR-B1320 User Manual
Page 13: 4) interrupt identification register (iir), Serial ports -5
A
A
R
R
-
-
B
B
1
1
3
3
2
2
0
0
U
U
s
s
e
e
r
r
’
’
s
s
G
G
u
u
i
i
d
d
e
e
2.7 SERIAL
PORTS
The ACEs (Asynchronous Communication Elements ACE1 and ACE2) are used to convert the
parallel data to a serial format on the transmit side and convert the serial data to parallel on the
receiver side. The serial format, in order of transmission and reception, is a start bit, followed by
five to eight data bits, a parity bit (if programmed) and one, one and half (five-bit format only) or
two stop bits. The ACEs are capable of handling divisors of 1 to 65535, and produce a 16x clock
for driving the internal transmitter logic.
Provisions are also included to use this 16x clock to drive the receiver logic. Also included in the
ACE are a complete MODEM control capability, and a processor interrupt system that may be
software tailored to the computing time required to handle the communications link. The following
is a summary of each ACE accessible registers.
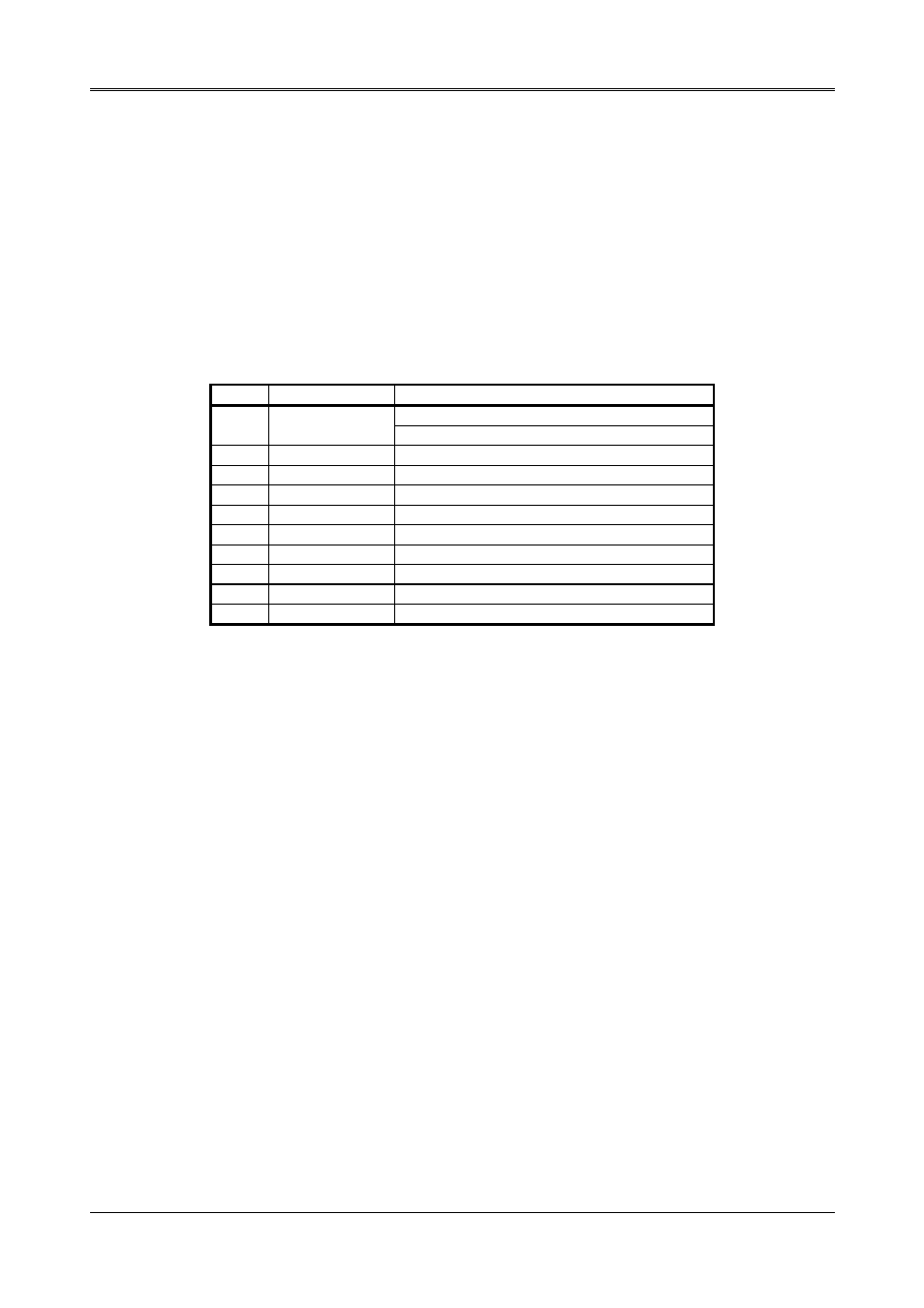
DLAB Port
Address
Register
Receiver buffer (RBR, read)
0
base + 0
Transmitter holding register (THR, write)
0
base + 1
Interrupt enable (IER)
X
base + 2
Interrupt identification (IIR, read only)
X
base + 3
Line control (LCR)
X
base + 4
MODEM control (MCR)
X
base + 5
Line status (LSR)
X
base + 6
MODEM status (MSR)
X
base + 7
Scratched register
1
base + 0
Divisor latch (least significant byte) (LS)
1
base + 1
Divisor latch (most significant byte) (MS)
Table 2-3 ACE Accessible Register
(1)
Receiver Buffer Register (RBR)
Bit 0-7: Received data byte (Read Only)
(2)
Transmitter Holding Register (THR)
Bit 0-7: Transmitter holding data byte (Write Only)
(3)
Interrupt Enable Register (IER)
Bit 0: Enable Received Data Available Interrupt (ERBFI)
Bit 1: Enable Transmitter Holding Empty Interrupt (ETBEI)
Bit 2: Enable Receiver Line Status Interrupt (ELSI)
Bit 3: Enable MODEM Status Interrupt (EDSSI)
Bit 4: Must be 0
Bit 5: Must be 0
Bit 6: Must be 0
Bit 7: Must be 0
(4)
Interrupt Identification Register (IIR)
Bit 0: “0” if Interrupt Pending
Bit 1: Interrupt ID Bit 0
Bit 2: Interrupt ID Bit 1
Bit 3: Must be 0
Bit 4: Must be 0
Bit 5: Must be 0
Bit 6: Must be 0
Bit 7: Must be 0
2-5
