Avcs gyro – Futaba GY611 User Manual
Page 9
9
B
EFORE
U
SE
Differences Between AVCS Gyro and Conventional Gyro
Compared to a convention gyro, the AVCS gyro has a substantially
improved tail control capacity. Gyro operation also differs from that
of conventional systems in a number of ways.
The following sequentially describes the conventional gyro and the
AVCS gyro.
AVCS Gyro
Conventional gyro
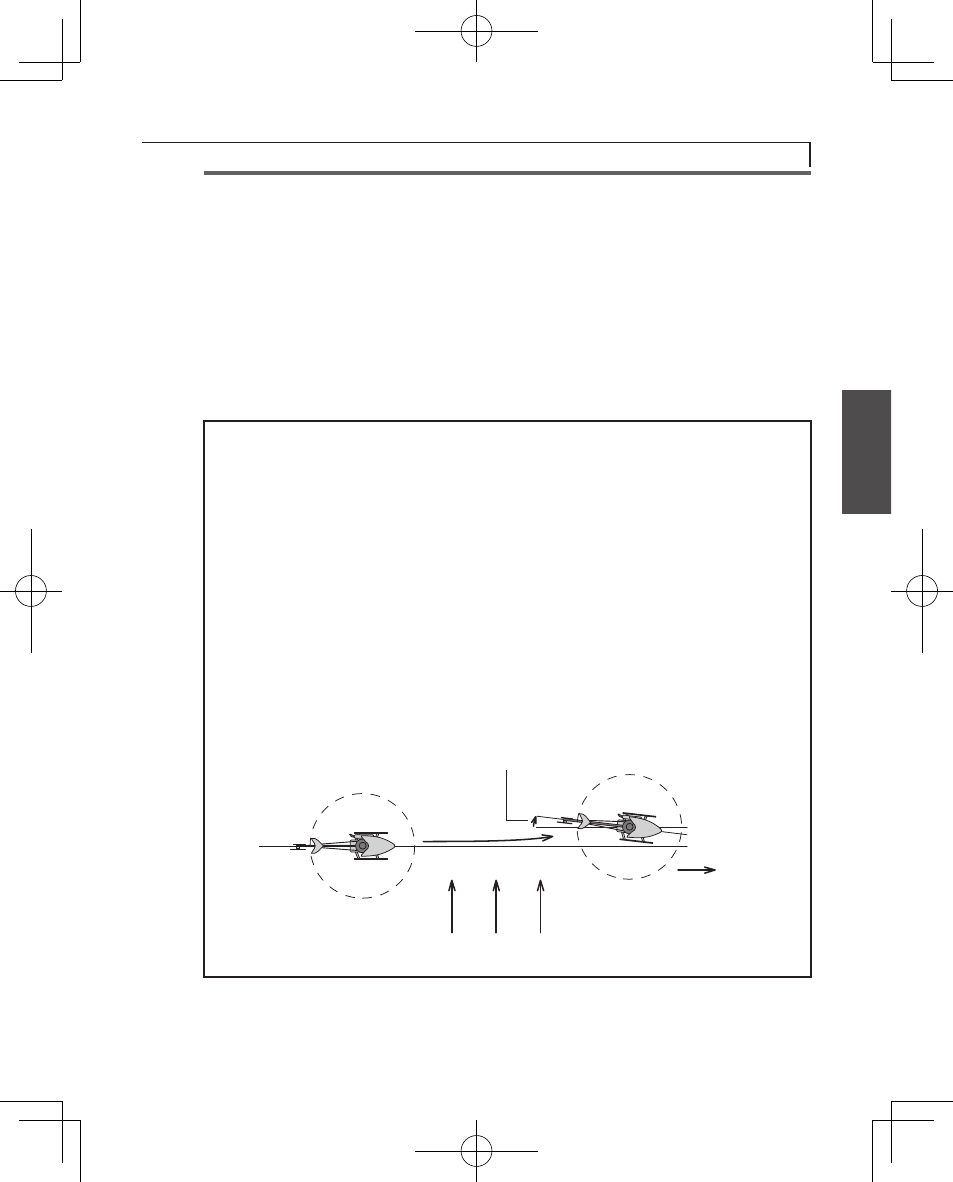
The conventional gyro detects movement of the helicopter's tail and controls
the rudder servo so that movement of the tail stops.
Now, consider hovering when the helicopter is exposed to a side wind, the
tail drifts. When the tail drifts, the gyro detects the tail rotation angular veloc-
ity and operates the servo in the direction that stops the tail from moving.
Drifting of the tail is stopped by control from the gyro. When the tail stops
drifting, the control amount from the gyro becomes zero. Since the helicop-
ter is always exposed to side wind, even in this state, the tail starts to drift
again. When the tail drifts, the gyro tries to stop it again. The "drifting stop"
operation is repeated and the tail continues to drift in the wind direction in
this manner. The higher the gyro sensitivity, the smaller the amount of this
drift. However, if the sensitivity is high, hunting will occur and, therefore, the
sensitivity amp has a limit.
• Drifting stop
Forward
Side wind
