Troubleshooting, 1 optical power loss, 2 fault conditions – CANOGA PERKINS 9145E Network Interface Device User Manual
Page 43: 1 remote fault (rmtf), Chapter 5 troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
9145E Ethernet Network Interface Device User’s Manual
Optical Power Loss
31
This chapter covers identifying fault conditions and determining corrective action. The front panel
LEDs provide both normal and fault information. To aid troubleshooting, Tables 5-1and 5-2 list all
LED functions and indications.
5.1 Optical Power Loss
Whenever there is a significant signal loss, the Rx indictor turns off. Check cable integrity, and
remove and inspect the cable connectors, being careful not to damage the fiber end-face surface
or the connector housing. Clean all optical connectors before reinstalling them.
5.2 Fault Conditions
The 9145E front panel and interface module LEDs show fault conditions. Additional information
about fault conditions appears on the System Alarms Log. Use the System Alarms Screen to
view alarms and faults on the 9145E (reference 6913303, 9145E NID Software Version 1.0 Users
Manual).
5.2.1 Remote Fault (RMTF)
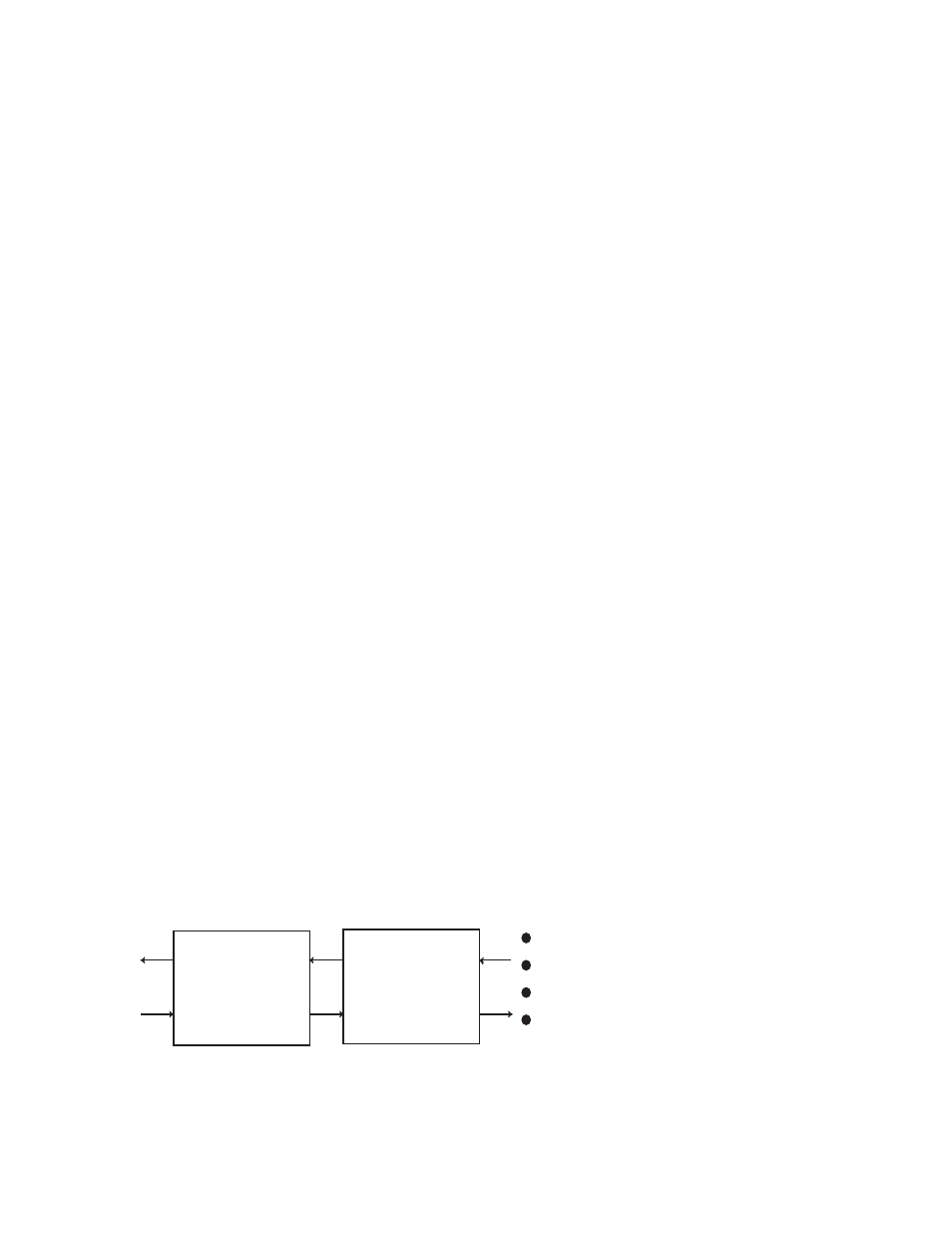
If an optical port loses the RX optical signal, it sends a Remote Fault (RMTF) signal on its Trans-
mit to the distant end on the optical link. The SPD LED is off, and an alarm flags the link loss on
the optical port. When an optical port receives a Remote Fault signal, the ACT/LNK LED lights
red and an alarm flags the remote side optical link failure. Both local and remote link partners
must be configured to the same RMTF enable/disable setting (See Figure 5-1).
Figure 5-1. Remote Fault Signal
Tx
Rx
Rx
Tx
x
RMTF
USER
PORT
NETWORK
PORT
LOCAL DEVICE
Tx
Rx
Rx
Tx
USER
PORT
NETWORK
PORT
REMOTE DEVICE
Local device ACT/LNK detects link loss
Tx transmits RMTF to remote device
Local device ACT/LNK turns OFF
Remote device ACT/LNK turns red
Chapter 5
Troubleshooting
