Carrier 50HG014-028 User Manual
Page 10
10
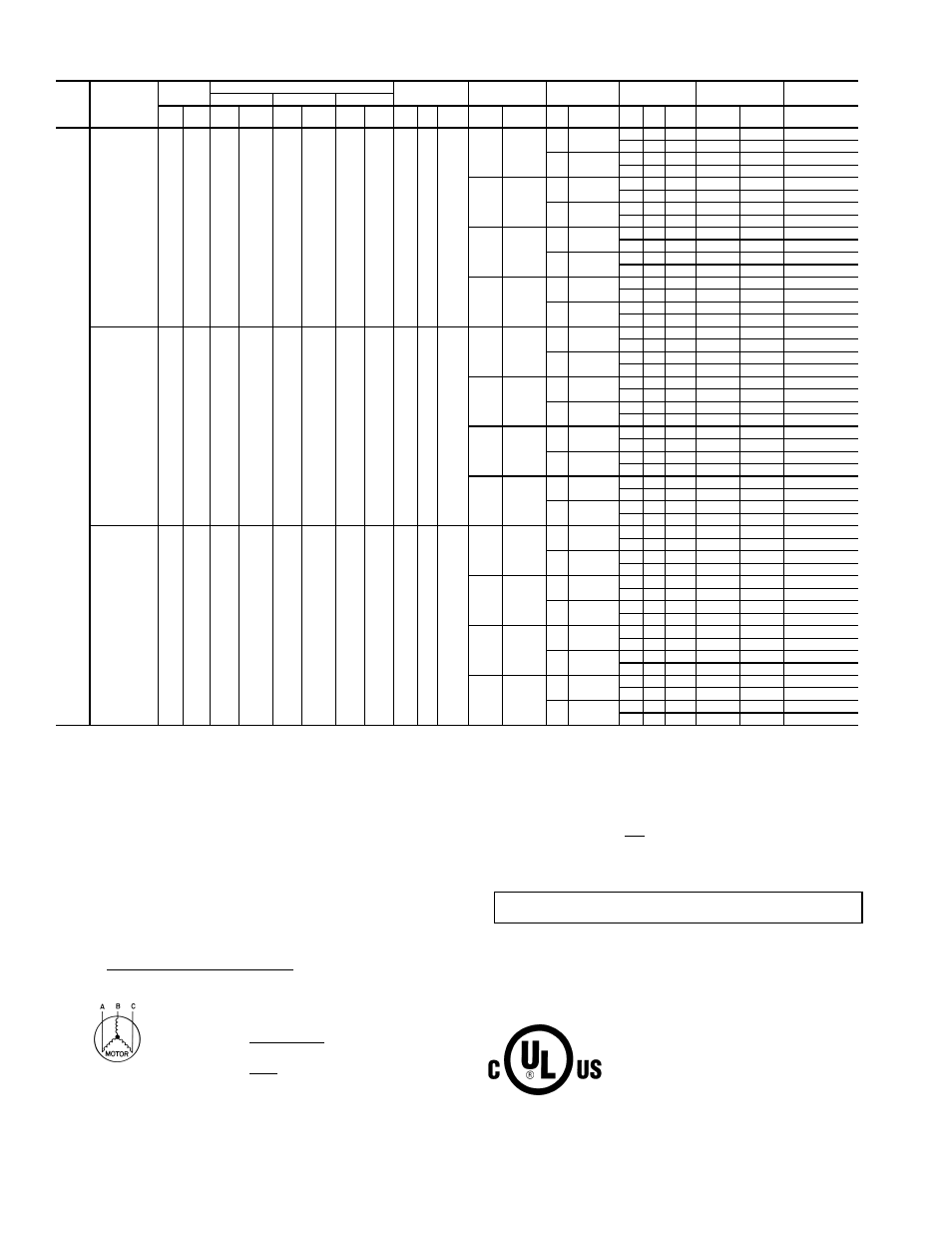
Table 2A — Electrical Data (Units Without Optional Convenience Outlet)
LEGEND AND NOTES FOR TABLES 2A AND 2B
LEGEND
*Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
†208/230 v 75-kW Electric Heat units must use dual-point wiring. The main table lists the
branch circuit values for the refrigeration part of the system. The following two tables list
the branch circuit values for the electric heat and values for a feeder circuit for both branch
circuits.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements for multimotor and combination load equipment
(refer to NEC Articles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective device for the unit shall
be fuse or HACR breaker. Canadian units may be fuse or circuit breaker.
2. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than 2%.
Use the following formula to determine the percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance
Example: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457 – 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 – 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 – 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum allowable
2%.
3. The 75-kW 208/240-v electric heat can be factory installed but it must be wired sepa-
rately in the field.
4. The convenience outlet full load amps (FLA) are 5, 3 and 3 for 208/230, 460, 575-v
units, respectively.
5. The FLA load amps provided in the table for electric heaters are based on 208/240, 480
and 600 v.
6. MCA calculation for 50HG014-028 units with electric heaters over 50 kW is = 1.25 x
(IFM + Power Exhaust + Convenience Outlet FLA amps) + 1.00 x (Electric Heater FLA).
UNIT
SIZE
50HG
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
(3 Ph, 60 Hz)
VOLTAGE
RANGE
COMPRESSOR
OFM
ELECTRIC
HEAT
IFM
POWER
EXHAUST
POWER
SUPPLY
DISCONNECT
SIZE
No. 1
No. 2
No. 3
Min
Max
RLA
LRA
RLA
LRA
RLA
LRA
Qty Hp
FLA
(ea)
kW
FLA
Hp
FLA
Qty
Hp
FLA
(ea)
MCA
MOCP*
FLA
014
208/230
187
253
19.2
146.0
19.2
146.0
—
—
4.0
1
/
4
1.5
—
—
3.7
10.6/ 9.6
—
—
—
60/ 59
70/ 70
70/ 70
2
1.0
5.9
72/ 71
90/ 80
80/ 80
5.0
16.7/15.2
—
—
—
66/ 64
80/ 80
80/ 70
2
1.0
5.9
78/ 76
90/ 90
90/ 90
12/16
33/ 38
3.7
10.6/ 9.6
—
—
—
60/ 60
70/ 70
70/ 70
2
1.0
5.9
72/ 74
90/ 80
80/ 80
5.0
16.7/15.2
—
—
—
66/ 67
80/ 80
80/ 70
2
1.0
5.9
78/ 81
90/ 90
90/ 90
19/25
52/ 60
3.7
10.6 /9.6
—
—
—
78/ 87
80/ 90
80/ 90
2
1.0
5.9
93/102
100/110
90/100
5.0
16.7/15.2
—
—
—
86/ 94
90/100
80/ 90
2
1.0
5.9
101/109
110/110
100/110
38/50
104/120
3.7
10.6/ 9.6
—
—
—
143/132
150/150
150/150
2
1.0
5.9
158/147
175/150
150/175
5.0
16.7/15.2
—
—
—
151/139
175/150
150/175
2
1.0
5.9
166/154
175/175
175/175
460
414
506
9.5
73.0
9.5
73.0
—
—
4.0
1
/
4
0.7
—
—
3.7
4.8
—
—
—
29
35
35
2
1.0
3.1
35
40
40
5.0
7.6
—
—
—
32
40
35
2
1.0
3.1
38
45
45
15
18
3.7
4.8
—
—
—
29
35
35
2
1.0
3.1
36
40
40
5.0
7.6
—
—
—
32
40
35
2
1.0
3.1
40
45
45
25
30
3.7
4.8
—
—
—
44
45
45
2
1.0
3.1
51
60
50
5.0
7.6
—
—
—
47
50
45
2
1.0
3.1
55
60
60
50
60
3.7
4.8
—
—
—
66
80
80
2
1.0
3.1
74
80
90
5.0
7.6
—
—
—
70
80
80
2
1.0
3.1
77
80
90
575
518
633
7.6
58.4
7.6
58.4
—
—
4.0
1
/
4
0.7
—
—
3.0
3.9
—
—
—
24
30
30
2
1.0
3.1
30
35
35
5.0
6.1
—
—
—
26
30
30
2
1.0
3.1
32
35
35
16
15
3.0
3.9
—
—
—
24
30
30
2
1.0
3.1
31
35
35
5.0
6.1
—
—
—
26
30
30
2
1.0
3.1
34
35
35
25
24
3.0
3.9
—
—
—
35
35
35
2
1.0
3.1
43
45
40
5.0
6.1
—
—
—
38
40
35
2
1.0
3.1
45
50
45
48
46
3.0
3.9
—
—
—
62
70
60
2
1.0
3.1
70
80
70
5.0
6.1
—
—
—
65
70
60
2
1.0
3.1
73
80
70
FLA
— Full Load Amps
MCA
— Minimum Circuit Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
Refrigeration
NEC
— National Electrical Code
IFM
— Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor OFM
— Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
LRA
— Locked Rotor Amps
RLA
— Rated Load Amps
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Average Voltage =
452 + 464 + 455
3
=
1371
3
= 457
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%, contact your
local electric utility company immediately.
7
457
