Dell PowerVault MD3000i User Manual
Page 10
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices
December 2008 – Revision A01
Page 10
traffic virtual disks share a disk group, even with purely sequential usage models,
the disk group I/O behavior becomes increasingly random, lowering overall
performance. Additionally, when a disk group must be shared, the most heavily
trafficked virtual disk always should be located at the beginning of a disk group.
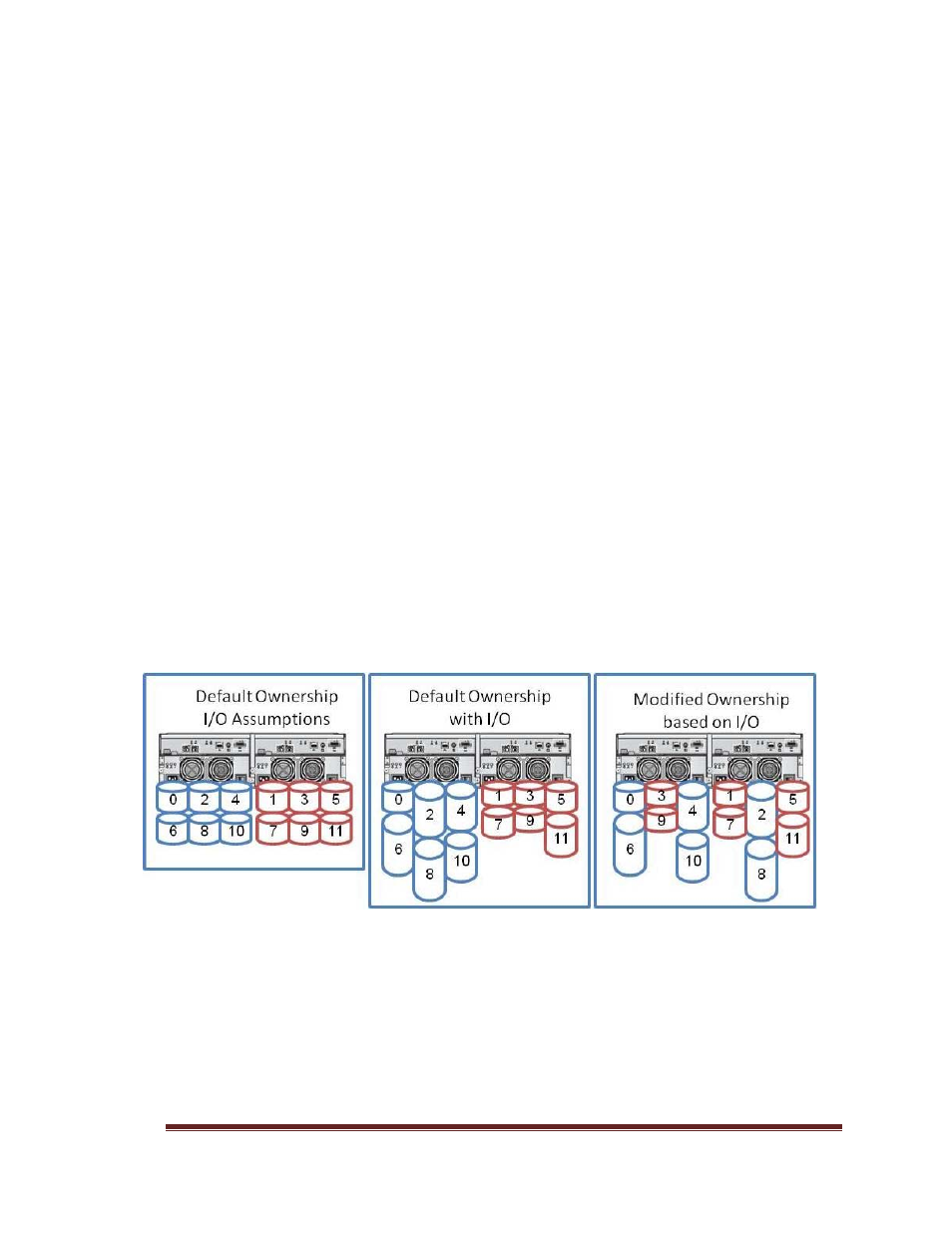
4.4 Virtual Disk Ownership
The Dell™ MDSM can be used to automatically build and view virtual disks. It
uses optimal settings to stripe the disk group. Virtual disks are assigned to
alternating RAID controllers when they are created. This default assignation
provides a simple means for load balancing the workload of the RAID controllers.
Ownership can later be modified to balance workload according to actual usage. If
virtual disk ownership is not manually balanced, it is possible for one controller to
have the majority of the work, while the other controller is idle.
Limit the number of virtual disks in a disk group. If multiple virtual disks are in a
disk group, consider the following information:
• Consider the impact each virtual disk has on other virtual disks in the
same disk group.
• Understand the patterns of usage for each virtual disk.
• Different virtual disks have higher usage at different times of day.
Figure 1: Virtual disk ownership balance.
4.5 Calculating Optimal Segment and Stripe Size
The choice of a segment size can have a major influence on performance in both
IOPS and data transfer rate.
The term segment size refers to the amount of data written to one drive in a
virtual disk group before writing data to the next drive in the virtual disk group. A
set of contiguous segments spanning across member drives creates a stripe. For
example, in a RAID 5, 4 + 1 virtual disk group with a segment size of 128KiB, the
