Dell PowerVault MD3000i User Manual
Page 20
Dell™ PowerVault MD3000 and MD3000i Array Tuning Best Practices
December 2008 – Revision A01
Page 20
RMW, or Read-Modify-Write, is the second-best write algorithm available for
RAID 5 and 6. A RMW occurs when a quantity of bits, smaller or equal to an
individual segment are modified. This constitutes a two-read operation in RAID 5
and a three-read operation in RAID 6, with one of the segments being modified,
and the parity drive(s) are read in. Then parity for the affected region is
recalculated and then the data and parity in the stripe are re-written to disk. In
small transactional processing, an extremely large number of RMWs should be
expected. These RMW writes can cause a significant loss of performance;
however this impact can be lessened by proper tuning of virtual disk stripe size. .
RMW2 is used to differentiate Write-to-cache RMWs and Write-Through RMWs,
with RMW2 being the latter, these statistics were consolidated in the second
generation firmware. RMW2’s also specifically happen when cache is disabled
by force, failed mirroring controller (if policy is active) or failed cache battery.
Additionally, the second generation firmware discretely tracks Full Stripe Write-
Through conditions, and both generations track data on Number of Parity stripes
re-calculated.
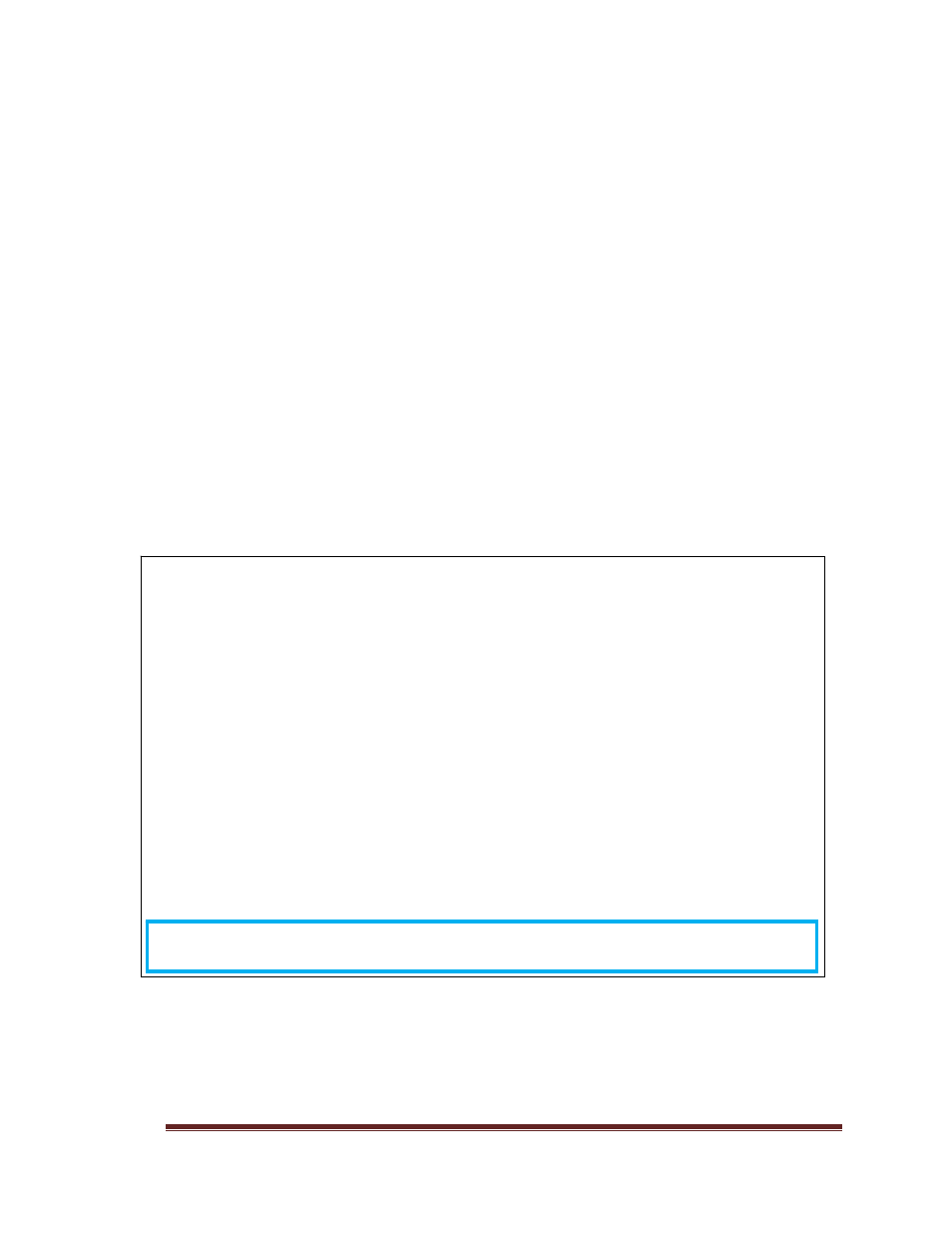
Figure 9: First Generation Firmware - Write Algorithms
Virtual Disk Unit 0 Configuration
Volume Type: 13+1 RAID 5
User Label: MyRAID5_1
Block Size: 512 bytes
Large IO: 4096 blocks
Segment Size: 256 blocks
Stripe Size: 3328 blocks
...
IO Statistics:
small small large large cache
reads writes reads writes total hits
requests 2028332119 147699066 0 0 2176031185 1289775370
blocks 3091968111 2518067526 0 0 1315068341 4019884678
avg blocks 4 17 0 0 0 3
IO pct. 93.21% 6.78% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 59.27%
IOs stripes /IO clusters /IO
reads 2028332119 2034477363 1.00 2107869128 1.03
writes 147699066 148449472 1.00 157404718 1.06
write Full Partial RMW No Parity RMW2 FSWT
algorithms 1105611 12598366 32120072 0 0 0
