Dell PowerVault 114x User Manual
Page 4
4
LTFS allows m
ulti-
thread copies to and from the tape and saves the files in an interlaced
manner. Inter
lacing is the multi
- thread capa
bility of LTFS that allows the host system to
save data continuously from more than one save action. The resulting data on tape is
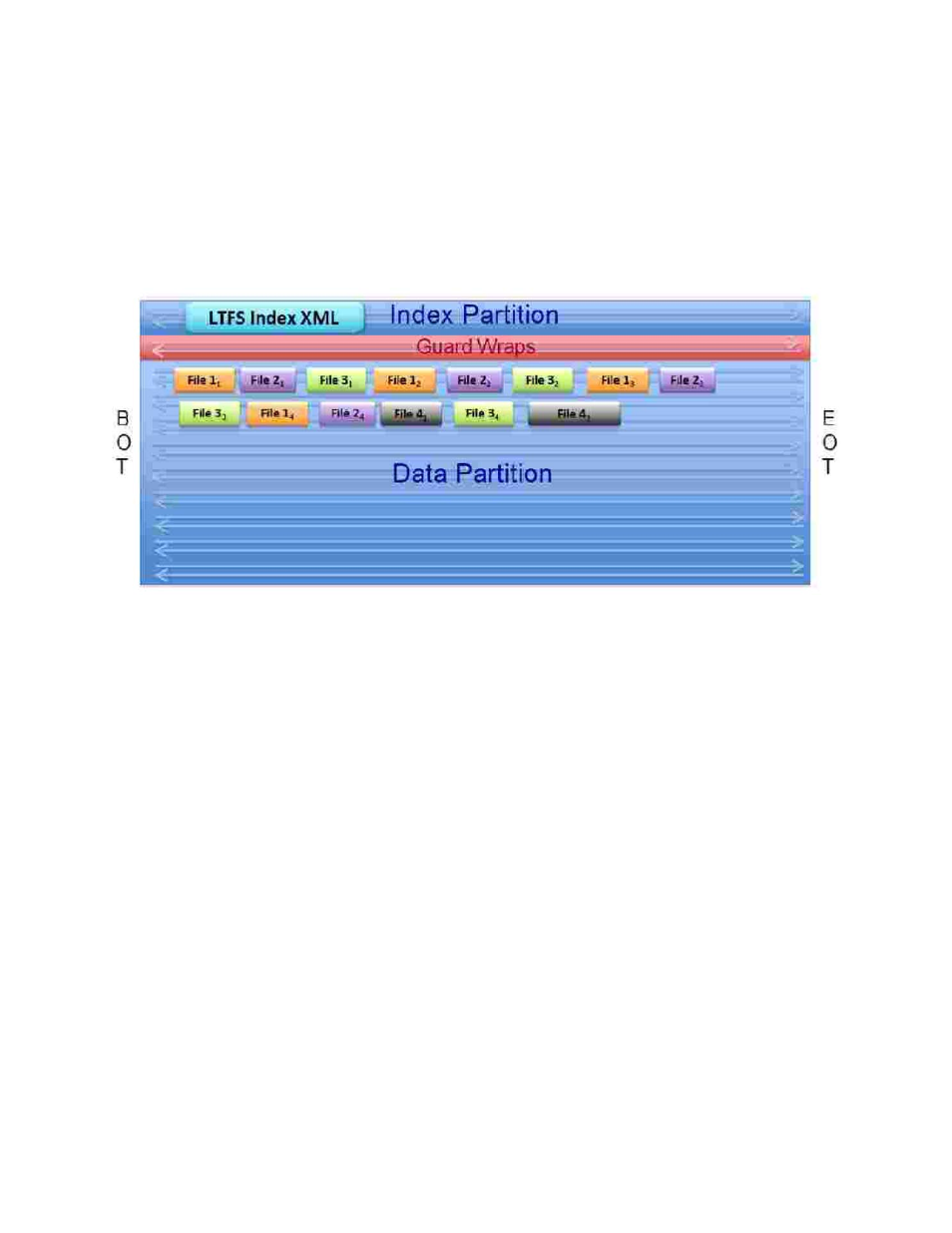
called interlaced and in contrast to the clean data blocks on tape demonstrated in Figure
2, the files are now in smaller separated chunks that can be spread across long
areas
of
tape depending on the files size interlaced to the tape. Figure 4
shows the
interlaced files
as they look logically on tape.
Figure 4 – Interlaced Files
Reads and Writes Using LTFS SDE
The time to gain access to the actual files in the file system is dependent on the location
of the data on the tape media and the time needed to seek to that portion of the media
and read the data.
Contiguous writes are file writes that are performed in a sequential manner. Sequential
writes are writes done in a single system thread. As an example, any copy command
execution is a single write. The copy command can be done as a single command to
copy entire directories or even multiple directories. It is not limited to a single file.
T
his same method is employed on drag
- and- d
rop operations. Any selection of multiple
files or directories in a GUI environment and executed as a single drag is considered a
single thread
ed copy.
Interlaced file writes are created when multiple threads are used simultaneously to write
data to tape. Multithread writes can be issued using multiple copy commands at the
same time, such as multiple command windows with copy commands issued from each
or
running batch copy files at the same time to the same tape.
Interlacing in a GUI environment is achieved by doing multiple drag
- and- drop
operations to the same tape simultaneously. This can be multiple or single files copied in
