K absolute value and argument calculation, K rectangular form ↔ polar form display – Casio fx-3650P User Manual
Page 20
E-18
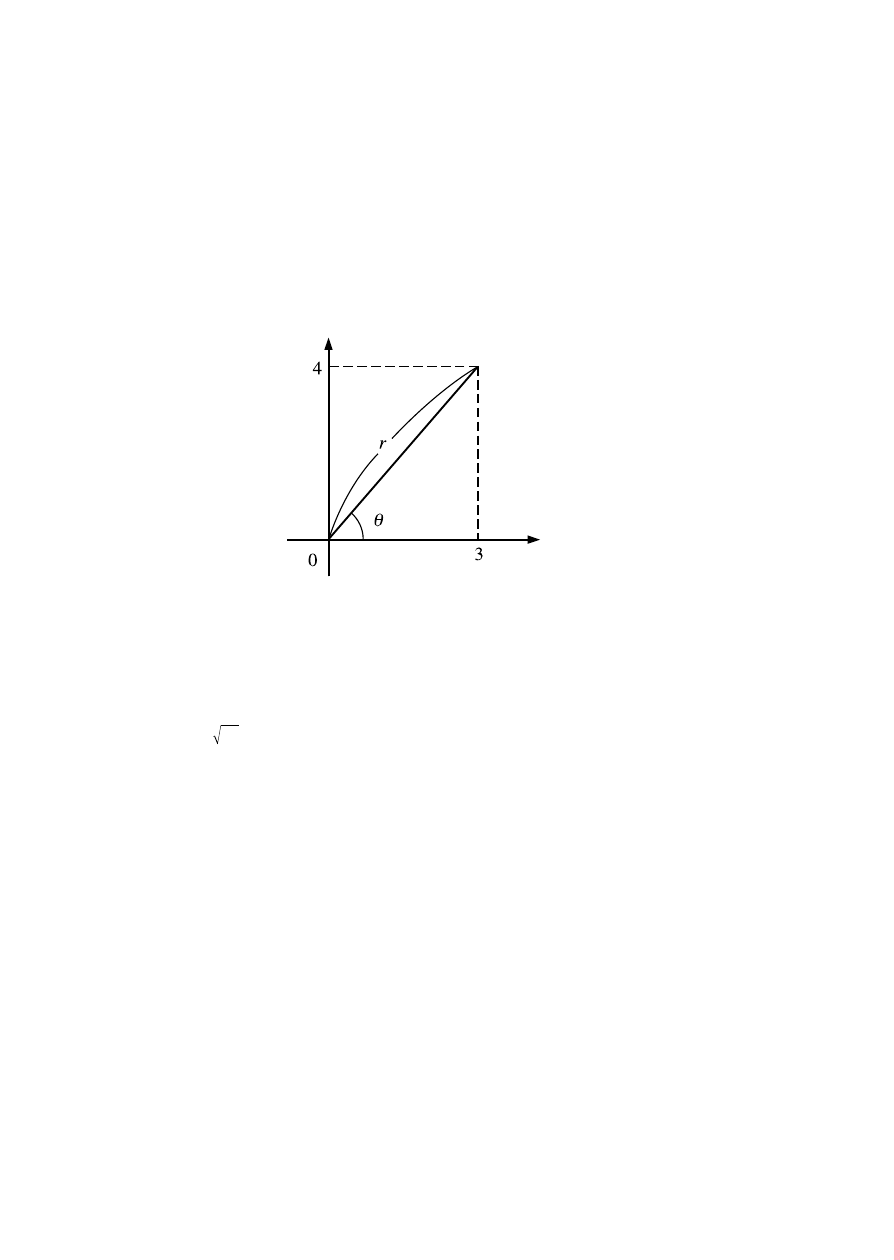
kAbsolute Value and Argument Calculation
Supposing the imaginary number expressed by the rectangular form
z
=
a
+
bi
is represented as a point in the Gaussian plane, you can
determine the absolute value (
r
) and argument (
) of the complex
number. The polar form is
r
Є
.
• Example 1: To determine the absolute value (
r
) and argument (
) of
3 + 4
i
(Angle unit: Deg)
(
r
=
5
,
=
53.13010235
°)
(
r
҃
5
)
A
A
R
3
+
4
i
T
<
(
҃
53.13010235
°)
A
a
R
3
+
4
i
T
<
• The complex number can also be input using the polar form
r
Є
.
• Example 2:
2
Є 45 ҃
1
ѿ
i
(Angle unit: Deg)
L
2
A
Q
45
<
A
r
kRectangular Form ↔ Polar Form Display
You can use the operation described below to convert a rectangular form
complex number to its polar form, and a polar form complex number to its
rectangular form. Press
A
r
to toggle the display between the absolute
value (
r
) and argument (
).
• Example: 1
ѿ
i
↔
1.414213562
Є 45
(Angle unit: Deg)
1
+
i
A
Y
<
A
r
L
2
A
Q
45
A
Z
<
A
r
Imaginary axis
Real axis
