Bio-Rad Bio-Rex® Reactor Grade Resins User Manual
Page 7
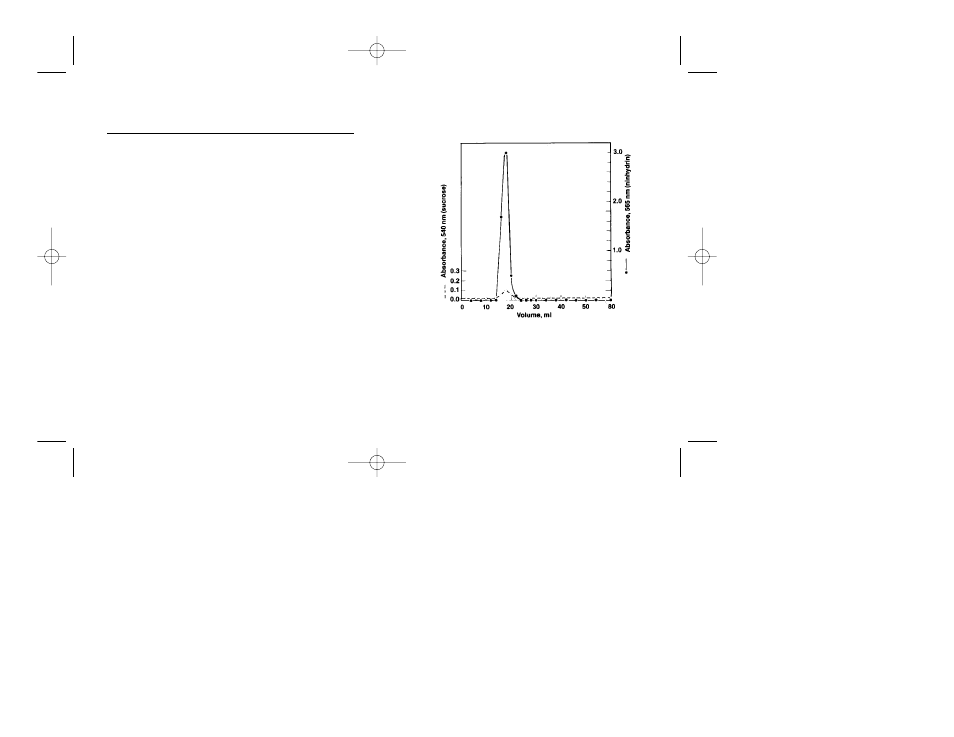
Fig. 2. Separation of hemoglobin from ampholytes
and sucrose on a mixed bed ion exchange column
(AG 501-X8 resin).
A hemoglobin blank in the sucrose
determination gives an absorbance of about 0.1. Neither
sucrose nor ampholyte emerged from the column in the
total volume tested.
3
AG 501-X8 resin has also been shown to be useful
for separating peptides of greater than 4,000 daltons from
ampholytes.
11
Table 3. Deionization of Urea by Batch and
Column Methods
Batch
Column
Sample
100 ml 6 M urea
100 ml 6 M urea
Starting conductivity
70 µmho/cm
70 µmho/cm
Amount of mixed bed resin
5 grams
5 grams (~8 ml)
Final conductivity
5.0 µmho/cm
0.2 µmho/cm
Time
~5 hours
~10 minutes
Ampholyte Removal
Carrier ampholytes may be quantitatively removed
from protein fractions derived from isoelectric focusing
using mixed bed resin. Mixed bed ion exchange chro-
matography represents a method for the quantitative
removal of carrier ampholytes. Figure 2 illustrates the
separation of proteins from ampholytes and sucrose. A 3
ml sample was applied to a 0.9 x 25 cm column of AG
501-X8 resin. AG 501-X8 resin has also been shown to be
useful for separating peptides of greater than 4,000 dal-
tons from ampholytes.
10
LIT205B 6/17/98 12:15 PM Page 10
