RKI Instruments GX-2009 Manual User Manual
Page 26
21 • Operation
GX-2009 Operator’s Manual
•
The GX-2009 provides the combustible sensor with some protection
against exposure to high levels of combustible gas. It does this by
turning off the combustible sensor power temporarily when it
determines that an over scale (more than 100% LEL) concentration of
combustible gas is present that may damage the sensor. Nevertheless,
concentrations of combustible gas of more than 100% LEL can still
affect the zero level or calibration of the combustible sensor if the
concentration is high enough.
CAUTION: Do not expose the combustible sensor to high concentrations
of combustible gas such as that from a butane lighter.
Exposure to high concentrations of combustible gas may
adversely affect the performance of the sensor.
CAUTION: Any rapid increase in the combustible gas reading followed by
a declining or erratic reading may indicate a gas concentration
above the LEL which may be hazardous.
•
Some gases such as silicone vapors, chlorinated hydrocarbons, and
sulphur compounds can contaminate the detection elements inside the
combustible sensor damaging the sensor and resulting in reduced
response to combustible gas. Make every effort to avoid these gases.
The H
2
S scrubber disks protect the combustible sensor from H
2
S, but
you should avoid other sulphur compounds.
Alarms
This section covers alarm indications. It also describes the two types of
alarm logic, how to reset the GX-2009 after an alarm has occurred, and
how to respond to an alarm condition.
NOTE: False alarms may be caused by radio frequency (RF) or
electromagnetic (EMI) interference. Keep the GX-2009 away from
RF and EMI sources such as radio transmitters or large motors.
Hydrogen
1.00
Xylene
0.93
IPA
2.50
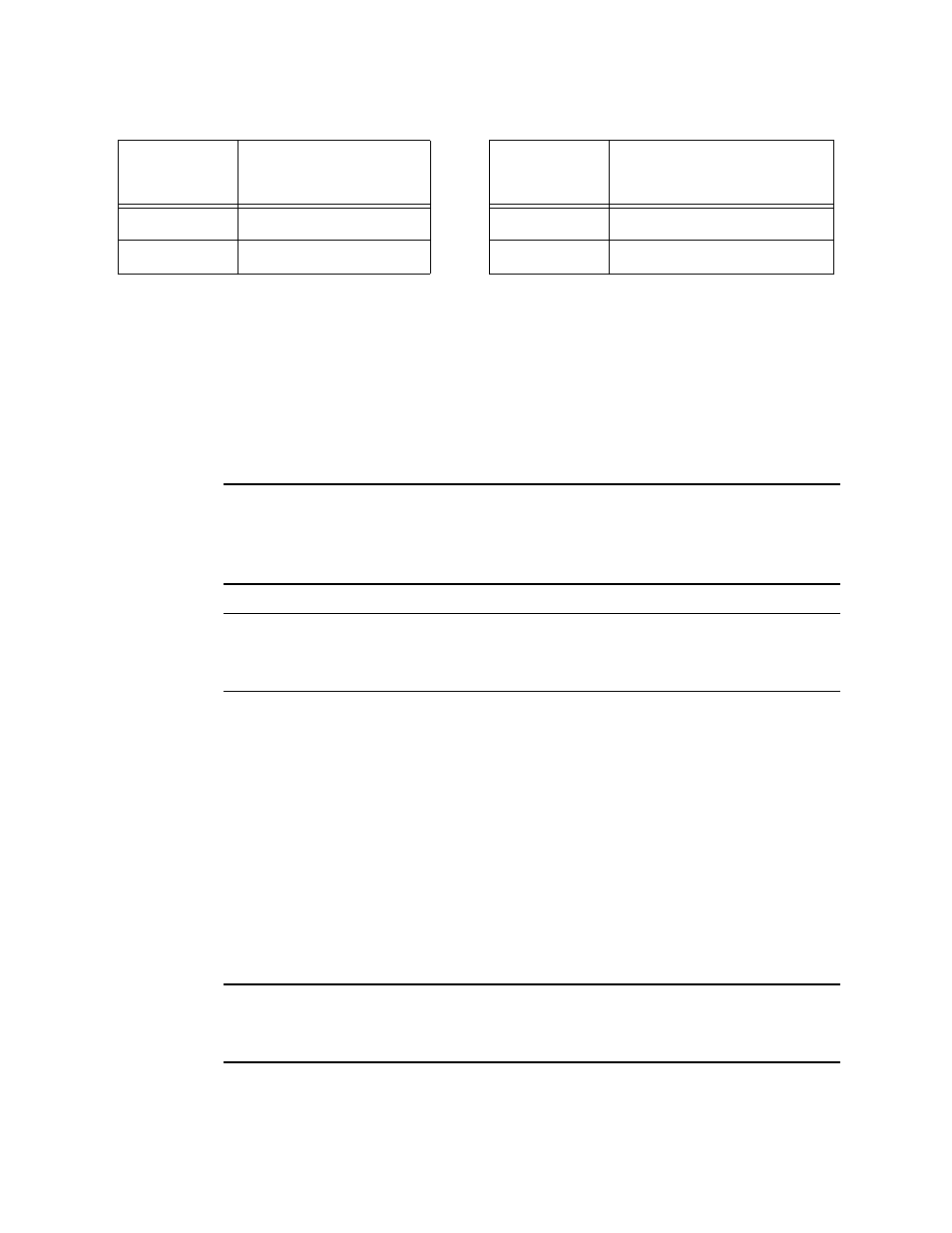
Table 3: LEL Hydrocarbon Conversions
Gas
LEL Conversion
Factor (CH
4
Cal.)
Gas
LEL Conversion Factor
(CH
4
Cal.)
