Accelerating and decelerating with constant path, Application examples, 3 accelerating and decelerating with constant path – Lenze EVF9383 User Manual
Page 175
Application examples
Accelerating and decelerating with constant path
3−5
l
EDSVF9383V−EXT EN 2.0
3.3
Accelerating and decelerating with constant path
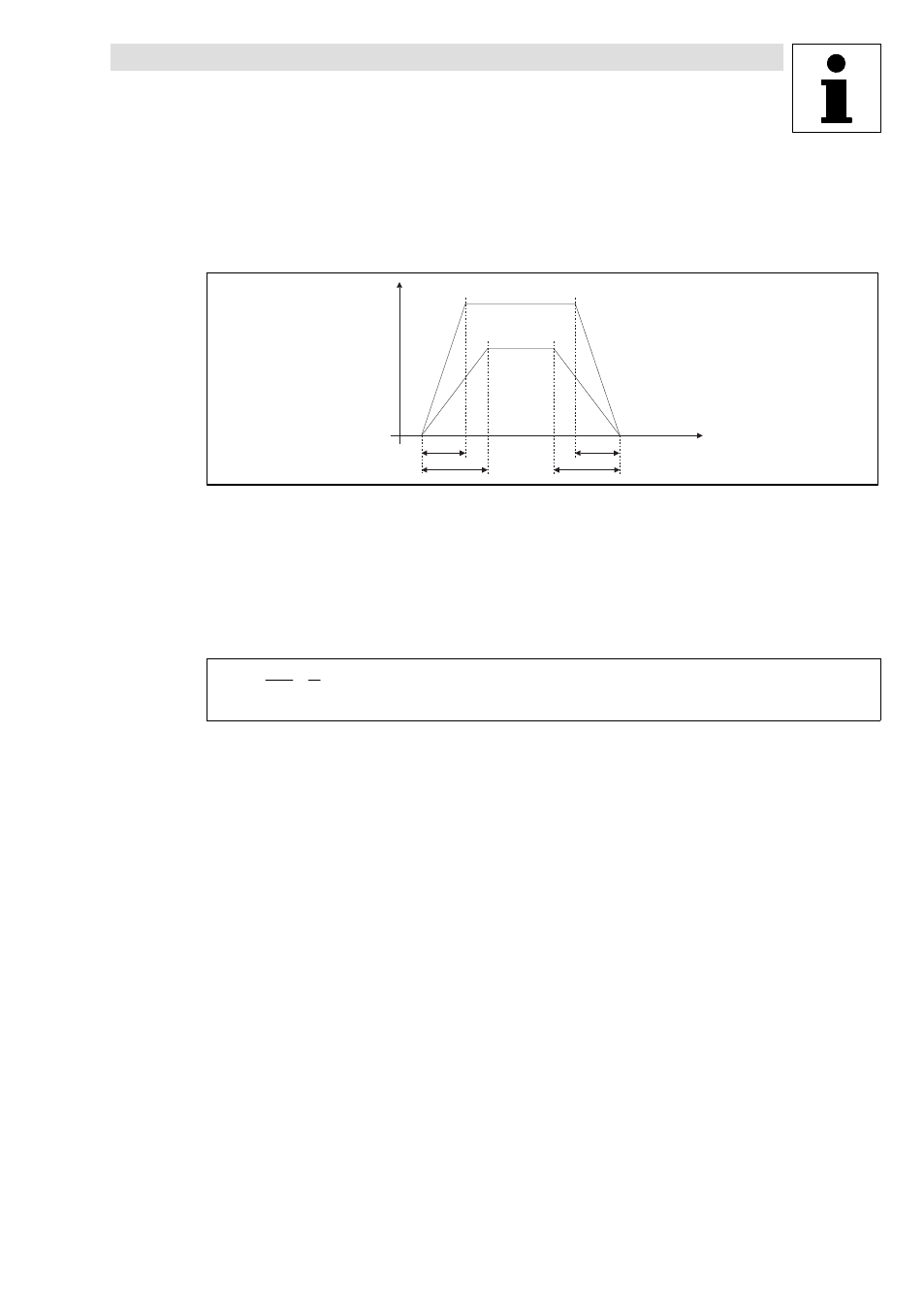
Use the basic configuration C0005 = 1000 with the changes shown in Fig. 3−2. However, set
C0104 = 2.
t
T
if
T
if
T
ir
T
ir
n
Fig. 3−3
Accelerating and decelerating with constant path (C0104 = 2)
n
Setpoint 1
Setpoint 2
Speed
T
ir
T
if
Acceleration time
Deceleration time
The distance is proportional to the number of motor revolutions. The distances are selected by
setting the Ti times (C0012, C0013).
l
The number of motor revolutions during acceleration or deceleration are calculated according
to the following formula:
N
+
n
max
60
@
T
i
2
N
Number of motor revolutions
n
max
Maximum speed (value in C0011)
T
i
Acceleration time T
ir
(value in C0012) or deceleration time T
if
(value in
C0013)
