Raid 1 (mirroring), Raid 5 (striping with parity), 3 raid 1 (mirroring) – chiliGREEN Home Server: Intel Rapid Storage Technology User Manual
Page 9: 4 raid 5 (striping with parity)
2.3
RAID 1 (Mirroring)
A RAID 1 array contains two hard drives where the data between the two is mirrored in real time to provide
good data reliability in the case of a single disk failure; when one disk drive fails, all data is immediately available
on the other without any impact to the integrity of the data.
The following table provides an overview of the advantages, the level of fault-tolerance provided and the typical
usage of RAID 1.
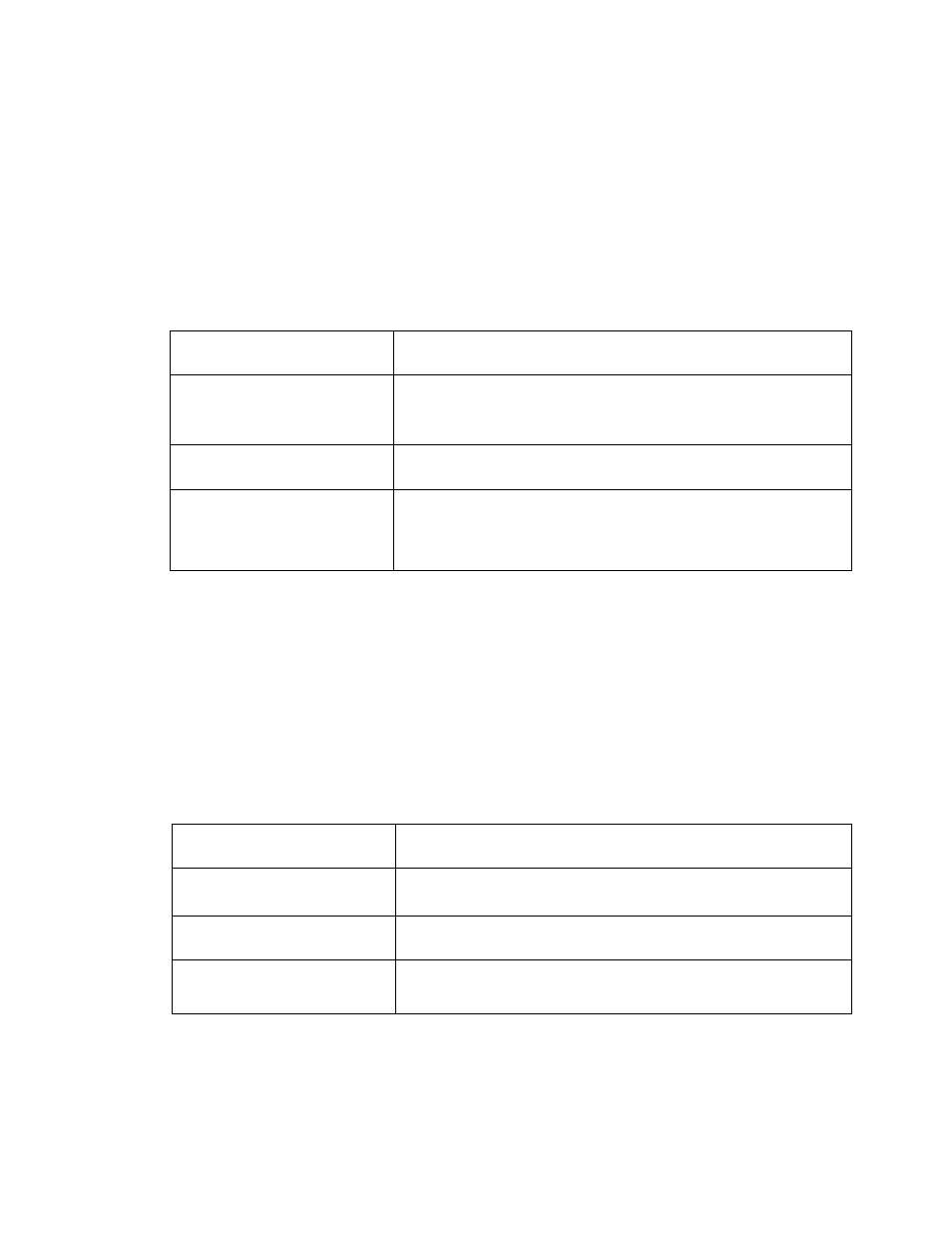
RAID 1 Overview
Hard Drives Required:
2
Advantage:
100% redundancy of data. One disk may fail, but data will
continue to be accessible. A rebuild to a new disk is
recommended to maintain data redundancy.
Fault- tolerance:
Excellent – disk mirroring means that all data on one disk is
duplicated on another disk.
Application:
Typically used for smaller systems where capacity of one disk
is sufficient and for any application(s) requiring very high
availability. Available in specific mobile configurations.
2.4
RAID 5 (Striping with Parity)
A RAID 5 array contains three or more hard drives where the data and parity are striped across all the hard
drives in the array. Parity is a mathematical method for recreating data that was lost from a single drive, which
increases fault-tolerance.
The following table provides an overview of the advantages, the level of fault-tolerance provided and the
typical usage of RAID 5.
RAID 5 Overview
Hard Drives Required:
3-6
Advantage:
Higher percentage of usable capacity and high read performance
as well as fault-tolerance.
Fault- tolerance:
Excellent - parity information allows data to be rebuilt after
replacing a failed hard drive with a new drive.
Application:
Storage of large amounts of critical data. Not available
in mobile configurations.
