5 voltage clamp circuit, 1 clamp overpower protection, 7 quasi-resonant second stage – Cirrus Logic CS1613A User Manual
Page 11: Figure 15)
CS1610A/11A
CS1612A/13A
DS976F1
11
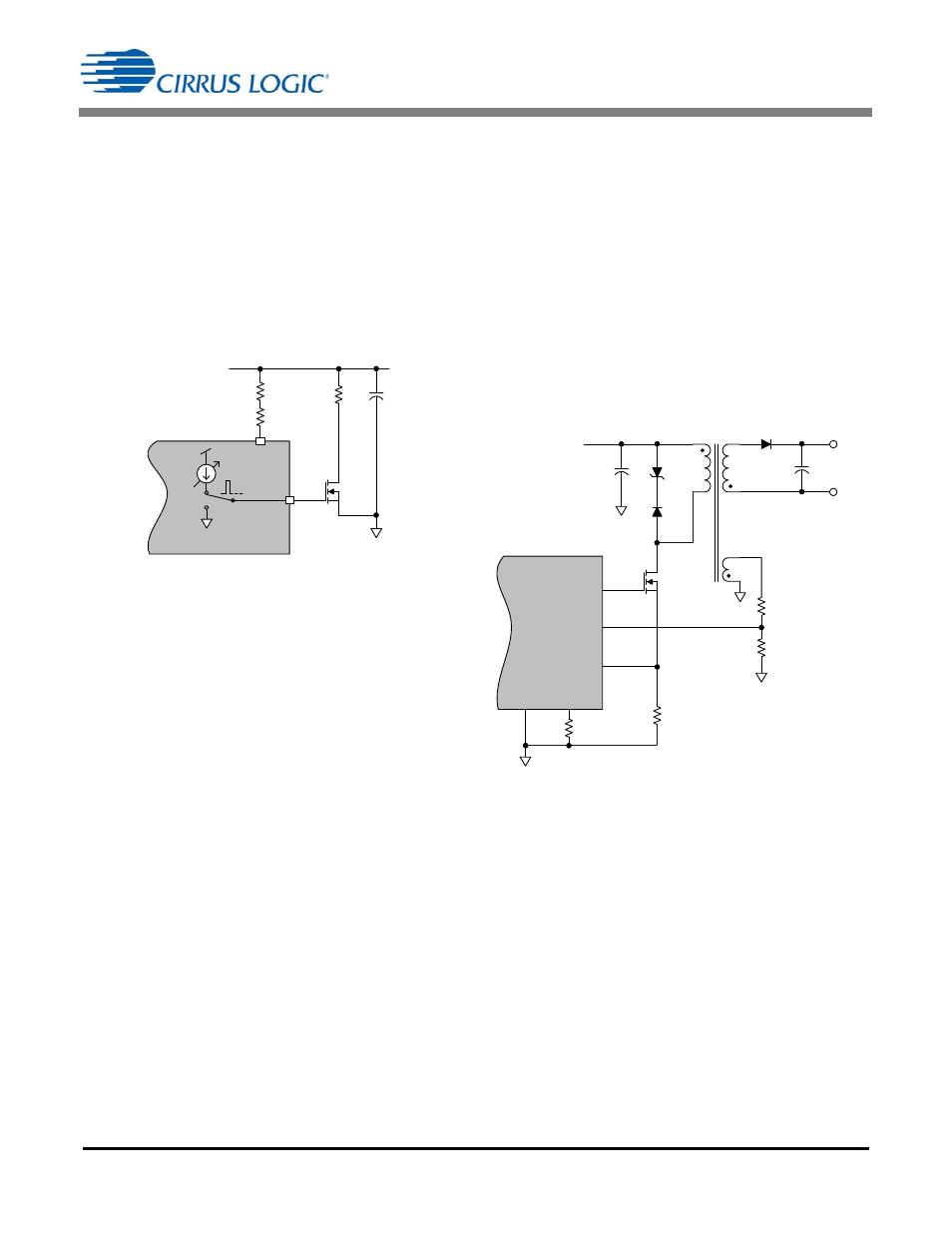
5.5 Voltage Clamp Circuit
To keep dimmers conducting and prevent them from misfiring,
a minimum power needs to be delivered from the dimmer to
the load. This power is nominally around 2W for 230V and
120V TRIAC dimmers. At low dim angles (
90°), this excess
power cannot be converted into light by the second output
stage due to the dim mapping at light loads. Boost stage
output voltage V
BST
can rise above the safe operating voltage
of the primary-side bulk capacitor C8.
The CS1610A/11A/12A/13A provides active clamp circuitry on
the CLAMP pin, as shown in Figure 14.
A PWM control loop ensures that boost output voltage V
BST
does not exceed 227V for 120VAC applications or 432V for
230VAC applications. This control turns on the MOSFET of
the voltage clamp circuit, allowing the clamp circuit to sink
current through the load resistor R10, preventing boost output
voltage V
BST
from exceeding the maximum safe voltage.
5.5.1
Clamp Overpower Protection
The CS1610A/11A/12A/13A clamp overpower protection
(COP) digital controlled timer clocks the turn-on time of the
clamp circuit over a one second period. If within a given one
second period the clamp circuit turn-on time exceeds 51.2ms
for a CS1610A/12A or 76.8ms for a CS1611A/13A, a COP
fault condition occurs and the system shuts down. If after any
given one second period a COP event does not occur, the
timer is reset to zero. The COP fault state is not cleared until
the power to the IC is recycled.
5.6 Dimming Signal Extraction and the Dim
Mapping Algorithm
When operating with a dimmer, the dimming signal is
extracted in the time domain and is proportional to the
conduction angle of the dimmer. A control variable is passed
to the quasi-resonant second stage to achieve 2% to 100%
output currents.
5.7 Quasi-resonant Second Stage
The second stage is a quasi-resonant current-regulated
DC-DC converter capable of flyback or buck operation,
delivering the highest possible efficiency at a constant current
while minimizing line frequency ripple. Primary-side control is
used to simplify system design and reduce system cost and
complexity.
The digital algorithm ensures monotonic dimming from 2% to
100% of the dimming range with a linear relationship between
the dimming signal and the LED current. The flyback stage is
controlled by sensing current in the transformer primary.
CLAMP
3
I
CLA MP
S1
CS1610 A/ 11A/ 12A/13A
V DD
C8
R8
BSTOUT
R10
R9
V
B S T
16
Q3
Figure 14. CLAMP Pin Model
13
11
T1
D8
C9
LED +
LED -
D7
R12
Z2
C8
R11
R13
R
FB GA IN
Q4
FBGAIN
FBAUX
GND
GD
FBSENSE
15
9
12
CS1610A/11A
V
B S T
Figure 15. Flyback Model
