Suction-piping checklist – Goulds Pumps 3355 - IOM User Manual
Page 24
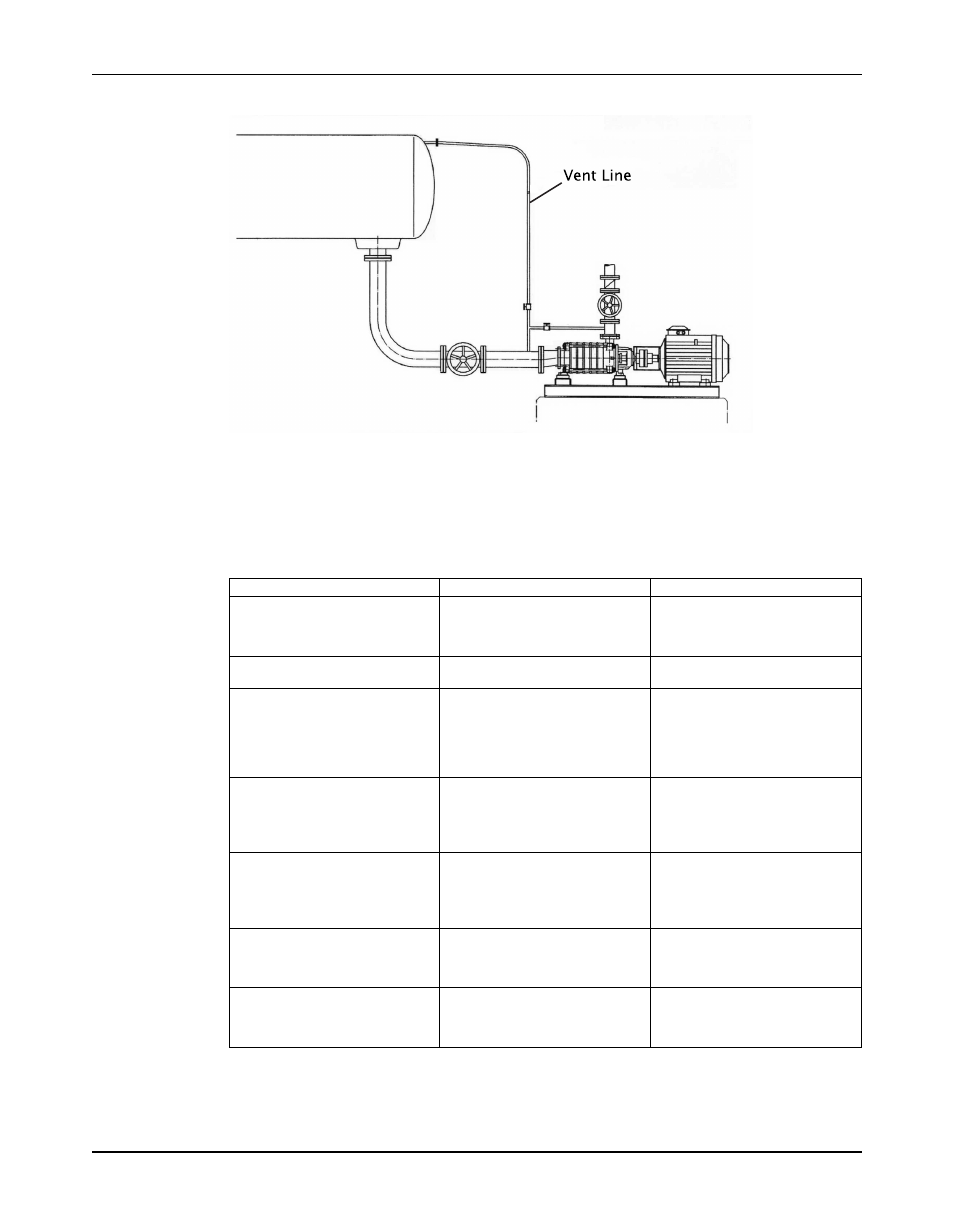
Installation
Example: Piping installation with a vent line
Suction-piping checklist
Performance curve reference
Net positive suction head available (NPSH
A
) must always exceed NPSH required (NPSH
R
) as
shown on the published performance curve of the pump.
Suction-piping checks
Check
Explanation/comment
Checked
Check that the distance between
This minimizes the risk of cavita-
the inlet flange of the pump and
tion in the suction inlet of the
the closest elbow is at least two
pump due to turbulence.
pipe diameters.
Check that elbows in general do
not have sharp bends.
Check that the suction piping is
The suction piping must never
one or two sizes larger than the
have a smaller diameter than the
suction inlet of the pump.
suction inlet of the pump.
Install an eccentric reducer be-
tween the pump inlet and the
suction piping.
Check that the eccentric reducer
at the suction flange of the pump
has the following properties:
• Sloping side down
• Horizontal side at the top
When suction strainers or suction Suction strainers help to prevent
bells are used, check that they are clogging.
at least three times the area of the Mesh holes with a minimum diam-
suction piping.
eter of 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) are
recommended.
If more than one pump operates
This recommendation helps you
from the same liquid source,
to achieve a higher pump perfor-
check that separate suction-piping mance.
lines are used for each pump.
If necessary, make sure that the
—
suction piping includes a drain
valve and that it is correctly in-
stalled.
22
Model 3355 Installation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual
