Sql server database instance parameters, Maximum degree of parallelism, Lightweight pooling – HP ProLiant DL980 G7 Server User Manual
Page 32: Priority boost
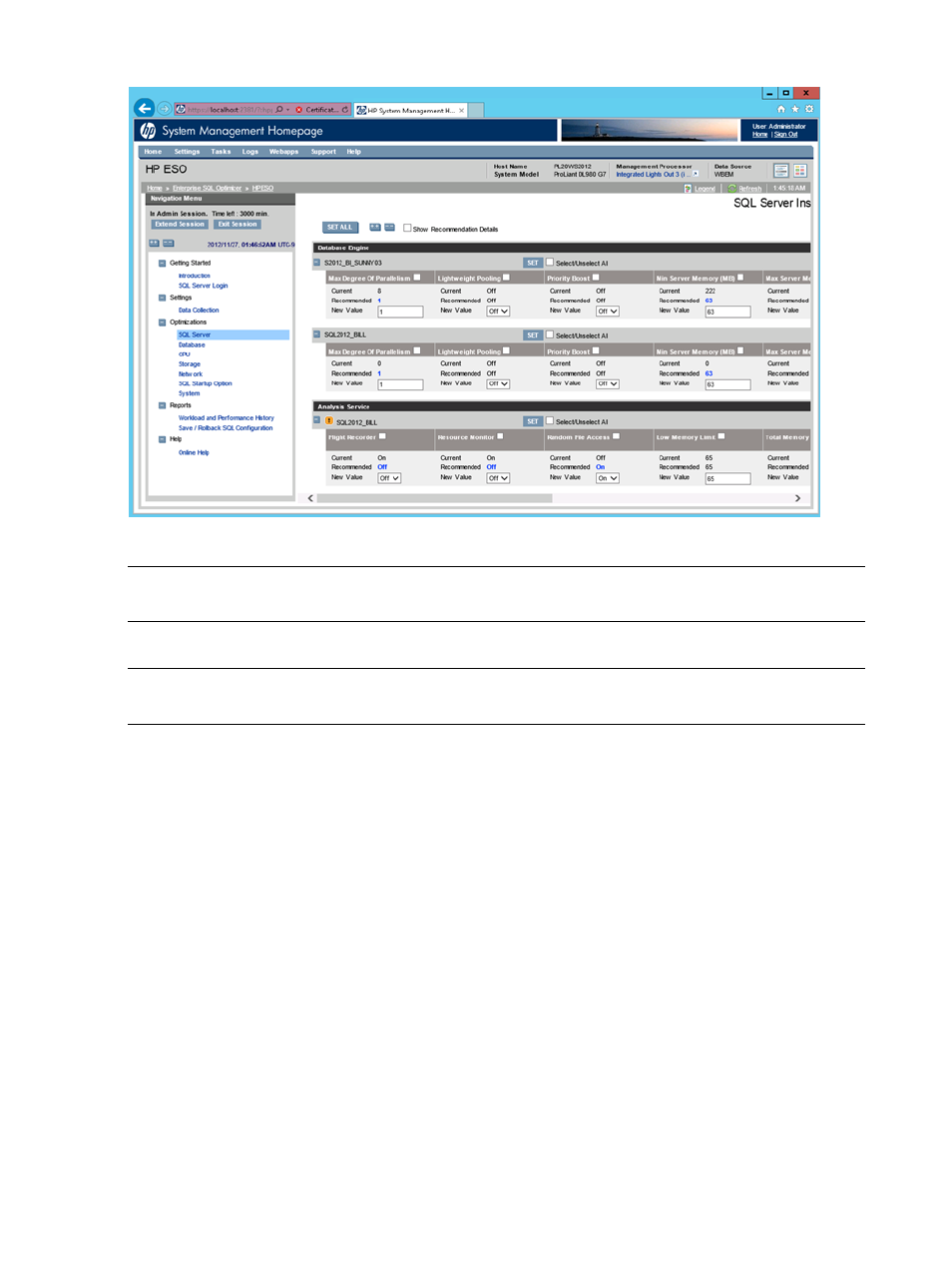
Figure 30 SQL Server page
The following subsections describe the parameters affecting SQL Server optimization.
NOTE:
For information about affinity settings, see
“CPU page: Viewing and enabling CPU
assignment optimization recommendations” (page 41)
SQL Server database instance parameters
NOTE:
Cluster-related parameters (Cluster Network Name, Computer Name, Status, and Computer
Role) are described in
“Clustered SQL Server instance” (page 40)
.
Maximum Degree of Parallelism
When SQL Server runs on a system with more than one microprocessor or CPU, it detects the best
degree of parallelism. Specifically, it recognizes the number of processors employed to run a single
statement, for each parallel plan execution. Use the Maximum Degree of Parallelism (MAXDOP)
option to limit the number of processors to use in parallel plan execution.
Lightweight Pooling
Use the Lightweight Pooling option to reduce system overhead associated with the excessive context
switching sometimes seen in symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) environments. When excessive
context switching is present, lightweight pooling can provide better throughput by performing the
context switching inline, thus helping to reduce user/kernel ring transitions.
Priority Boost
Use the Priority Boost option to specify whether Microsoft SQL Server should run at a higher
Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, or Windows Server
2008 R2 scheduling priority than other processes on the same system. If you set this option to 1,
SQL Server runs at a priority base of 13 in the Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows
Server 2008, or Windows Server 2008 R2 scheduler. The default is 0, which is a priority base
of 7.
32
Using HP ESO
