1 creating virtual cache partitions, About virtual cache partitions, Cache capacity for a clpr – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 4
1 Creating virtual cache partitions
This topic provides detailed instructions for dividing storage system cache memory into virtual
cache logical partitions (CLPRs) using Cache Partition software.
About virtual cache partitions
If one storage system is shared with multiple hosts, one host reading or writing a large amount of
data can require enough of the storage system’s cache memory to affect other users. The Cache
Partition function allows improved I/O performance by dividing storage system cache memory
into multiple virtual cache memories (cache logical partitions or CLPRs).
Partitioning cache matches data to appropriate storage resources based on availability,
performance, capacity, and cost. It improves flexibility by allowing dynamic changes to cache
partitions while in use.
Partitioning cache dedicates cache resources for exclusive use by specific applications to maintain
priority and quality of service for business-critical applications. Storage administrators can secure
and/or restrict access to storage resources to ensure confidentiality for specific applications. By
dedicating resources to each partition as needed, a high quality of service can be maintained for
all users.
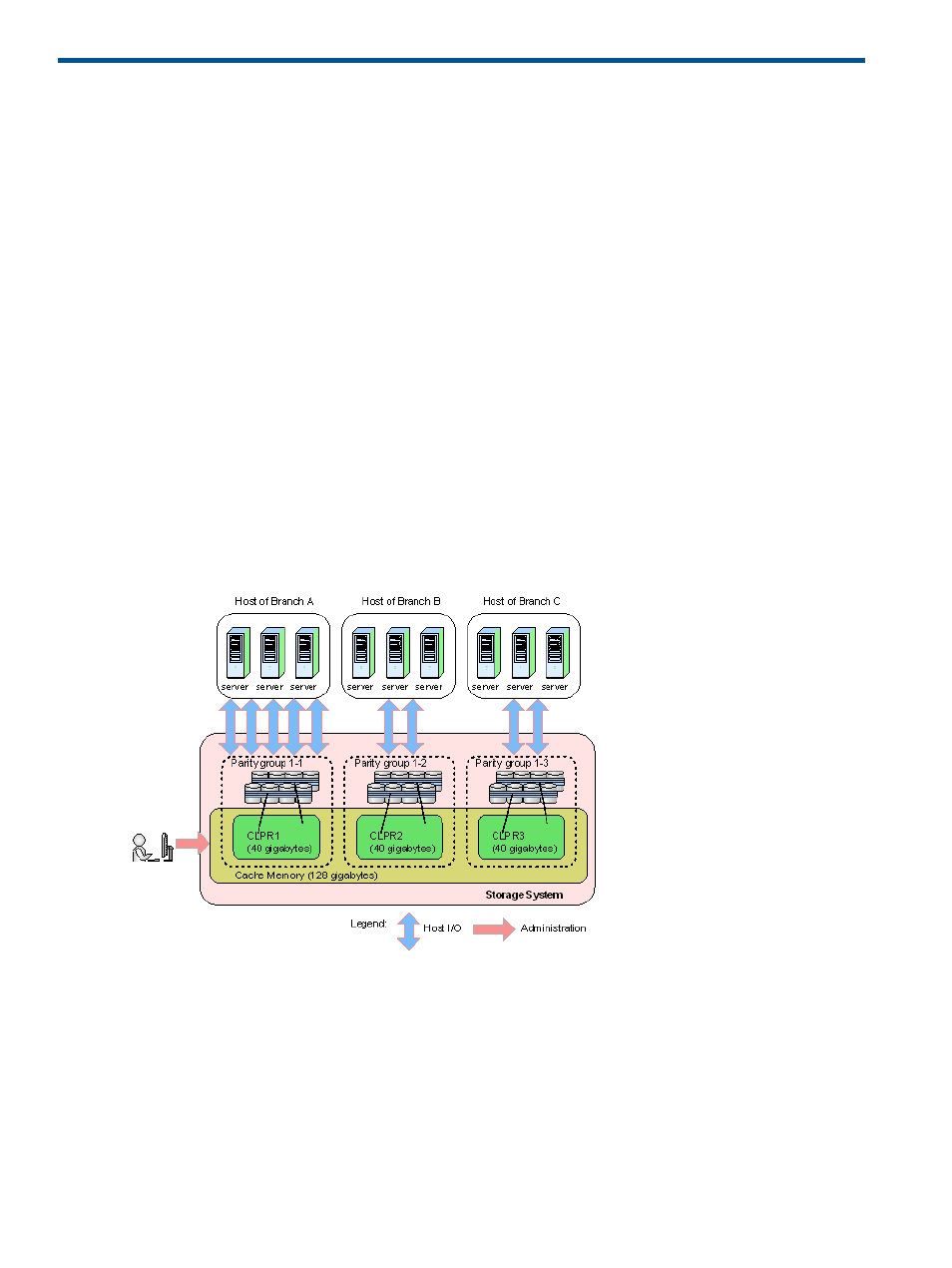
The following illustrates the use of cache memory within a corporation. In this example, cache
memory is partitioned into three segments of 40 GB, each of which is allocated to a branch office.
The host of branch A has a heavy I/O load. Because the cache memory is partitioned, that heavy
I/O load does not impact the cache memory for the other two branches.
Cache capacity for a CLPR
A CLPR is a pool of the cache and parity groups in the storage system. Partitioning cache into one
or more CLPRs allows storage administrators to dedicate individual CLPRs to a different host,
preventing I/O contention for cache memory.
Before you partition cache memory into CLPRs, calculate the cache capacity that will be needed
on your storage system. If necessary, install additional cache memory.
When you create a CLPR, the recommended cache capacity is determined by the conditions such
as: the number of mounted processor blades, RAID level, the number of drives that are installed
4
Creating virtual cache partitions
