KYORITSU 4202 User Manual
Page 7
̶ 5 ̶
Auto power-off
Turns power off about 10 minutes after the last
button operation.
Applicable standards
IEC61010-1 (CAT. IV 300V Pollution degree2)
IEC61010-2-032
IEC61326-2-2 (EMC standard)
External communication Bluetooth Ver2.1+EDR Class2
method
Withstand voltage
AC5160Vrms/ 5 seconds
Between the Transformer jaws fitted parts and Case
enclosure (except for jaws)
Insulation resistance
50MΩ or more at 1000V
Between the Transformer jaws fitted parts and Case
enclosure (except for jaws)
Conductor size
Approx. 32mm in diameter max.
Dimension
246(L) x 120(W) x 54(D)mm
Weight
Approx. 780g (including batteries)
Accessories
Battery R6P: 4pcs (MODEL4200)
LR6: 4pcs (KEW4202)
Instruction manual
: 1pce
Resistor for operation check : 1pce
(MODEL8304)
Hard case MODEL9166
: 1pce (MODEL4200)
MODEL9167
: 1pce (KEW4202)
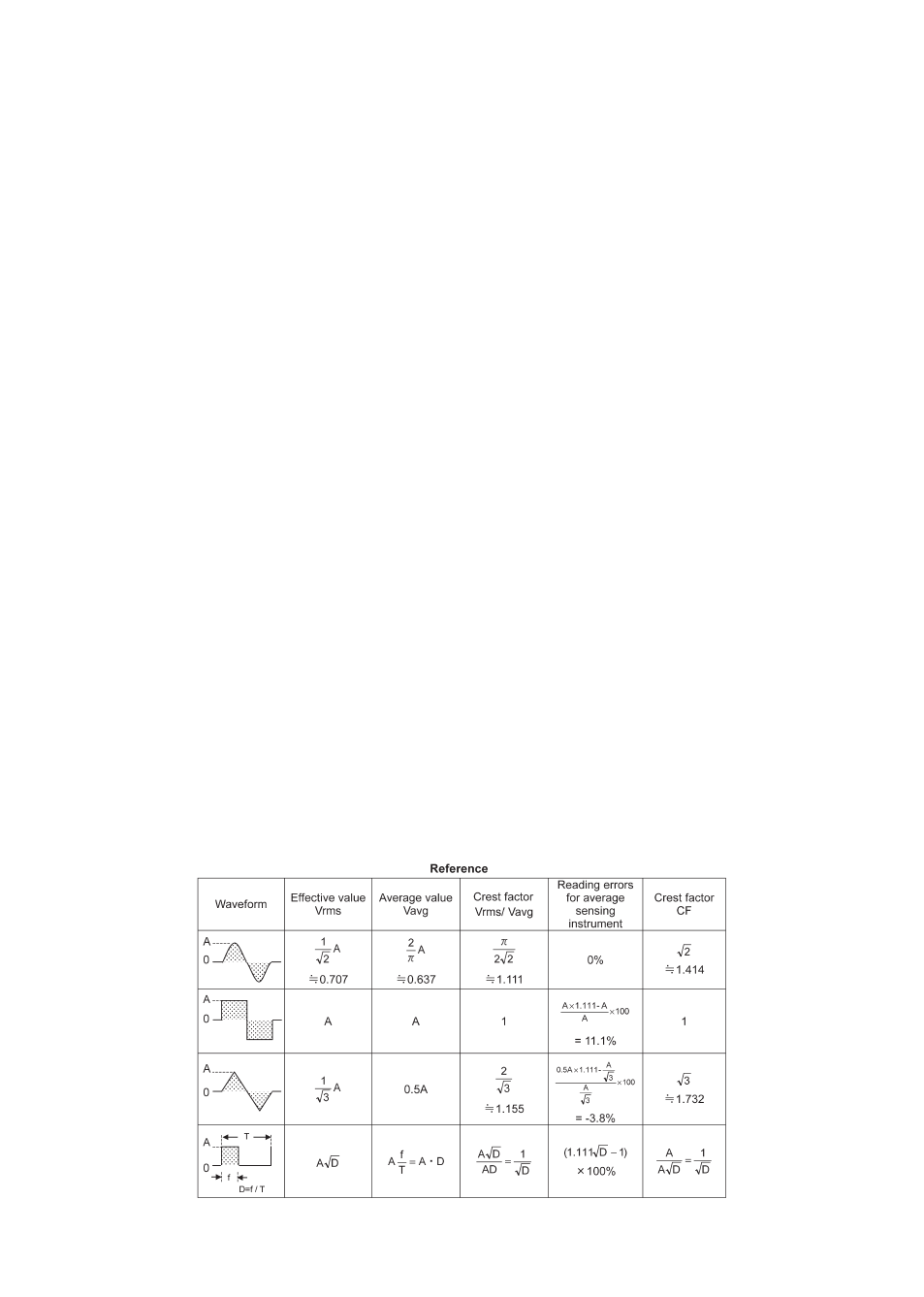
○ Effective value (RMS)
Most alternating currents and voltages are expressed in effective values, which are also
referred to as RMS (Root-Mean-Square) values. The effective value is the square root of
the average of square of alternating current or voltage values. Many clamp meters using
a conventional rectifying circuit have "RMS" scales for AC measurement. The scales are,
however, actually calibrated in terms of the effective value of a sine wave though the clamp
meter is responding to the average value. The calibration is done with a conversion factor of
1.111 for sine wave, which is found by dividing the effective value by the average value.
These instruments are therefore in error if the input voltage or current has some other shape
than sine wave.
○ CF (Crest Factor) is found by dividing the peak value by the effective value.
Examples:
Sine wave: CF=1.414 Square wave with a 1: 9 duty ratio: CF=3
