Basic anatomy of a script – Brocade Virtual ADX OpenScript Programmer’s Guide (Supporting ADX v03.1.00) User Manual
Page 17
Brocade Virtual ADX OpenScript Programmer’s Guide
9
53-1003244-01
Basic anatomy of a script
2
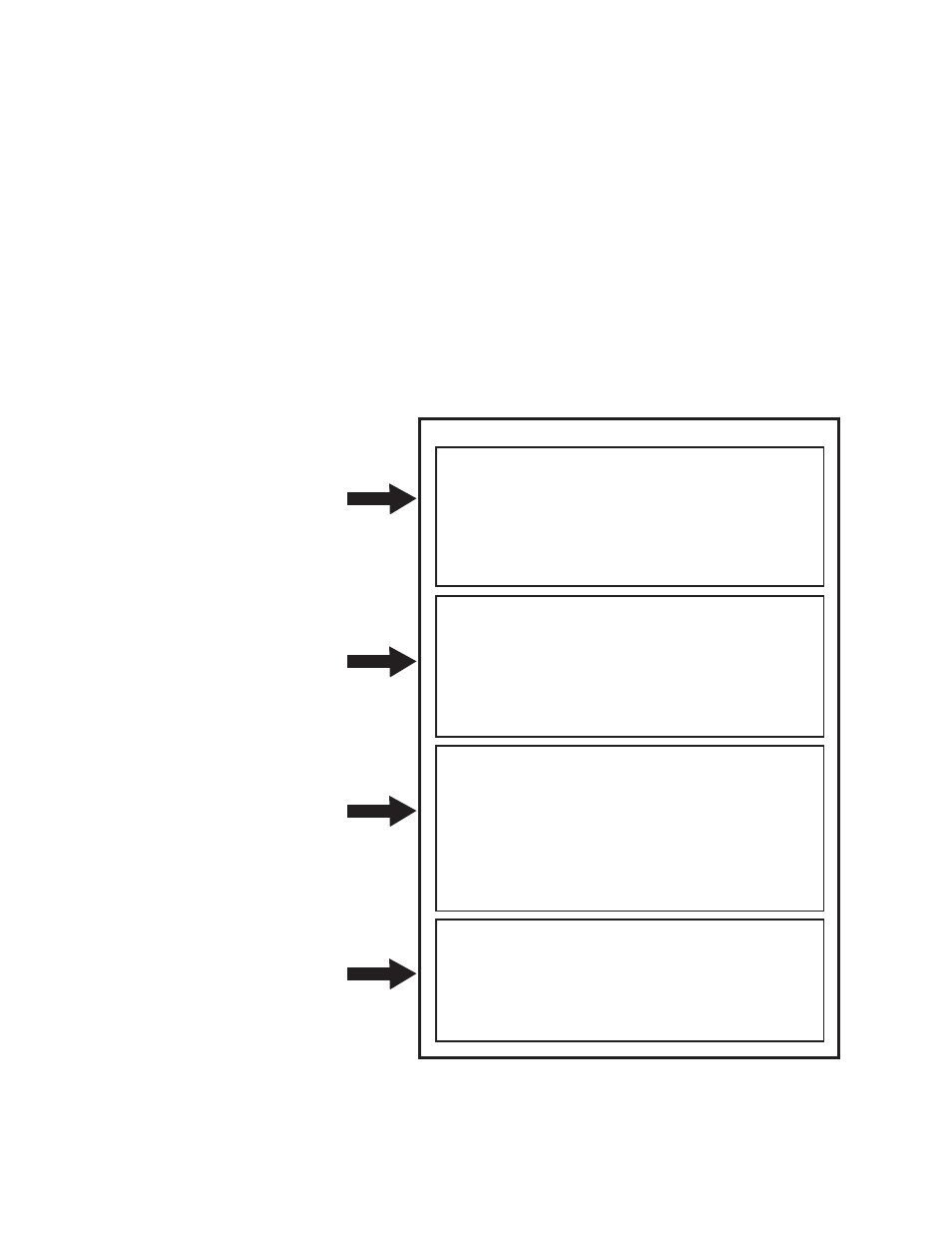
Basic anatomy of a script
The basic example script (abc.pl) is designed to exercise access control based on a client’s IP
address and a running count of the total number of connections per virtual server port. As
displayed, it consists of the following elements:
•
Declaration Block – Declares the packages being used by the script.
•
Initialization block – Only evaluated once before the first run of the script.
•
User-defined method 1 – Method 1 is designed to handle a new TCP client connection request.
It is invoked on every TCP SYN received on the vport bind point.
•
User-defined method 2– Method 2 is designed to run on receiving a TCP CLOSE request from a
client.
# Access control based on client IP address
# and a running count of total number of
# connections per vip:vport.
use OS_TCP;
use OS_IP;
use feature 'State';
Declaration
Block
Initialization
Block
BEGIN {
# total_conns must persist across runs
state $total_conns;
# We want a /24 match. Could be an array too
$bad_ip = "171.68.2.";
}
User-defined
Method 1
sub TCP_CLIENT_SYN {
# Look for blacklisted subnet in src ip
if (OS_IP::src =~ m/$bad_ip/)
OS_TCP::reset;
else
$total_conns++;
}
User-defined
Method 2
sub TCP_CLIENT_CLOSE {
# If we let it in, no need to check really
if (OS_IP::src !~ m/$bad_ip/)
$total_conns--;
}
Script: “abc.pl”
