5 for statements, Execution of a – Teledyne LeCroy LeCroy Analyzers File Based Decoding Manual User Manual
Page 29
File-based Decoding User Manual
Chapter 7: Statements
LeCroy Corporation
23
7.5 for Statements
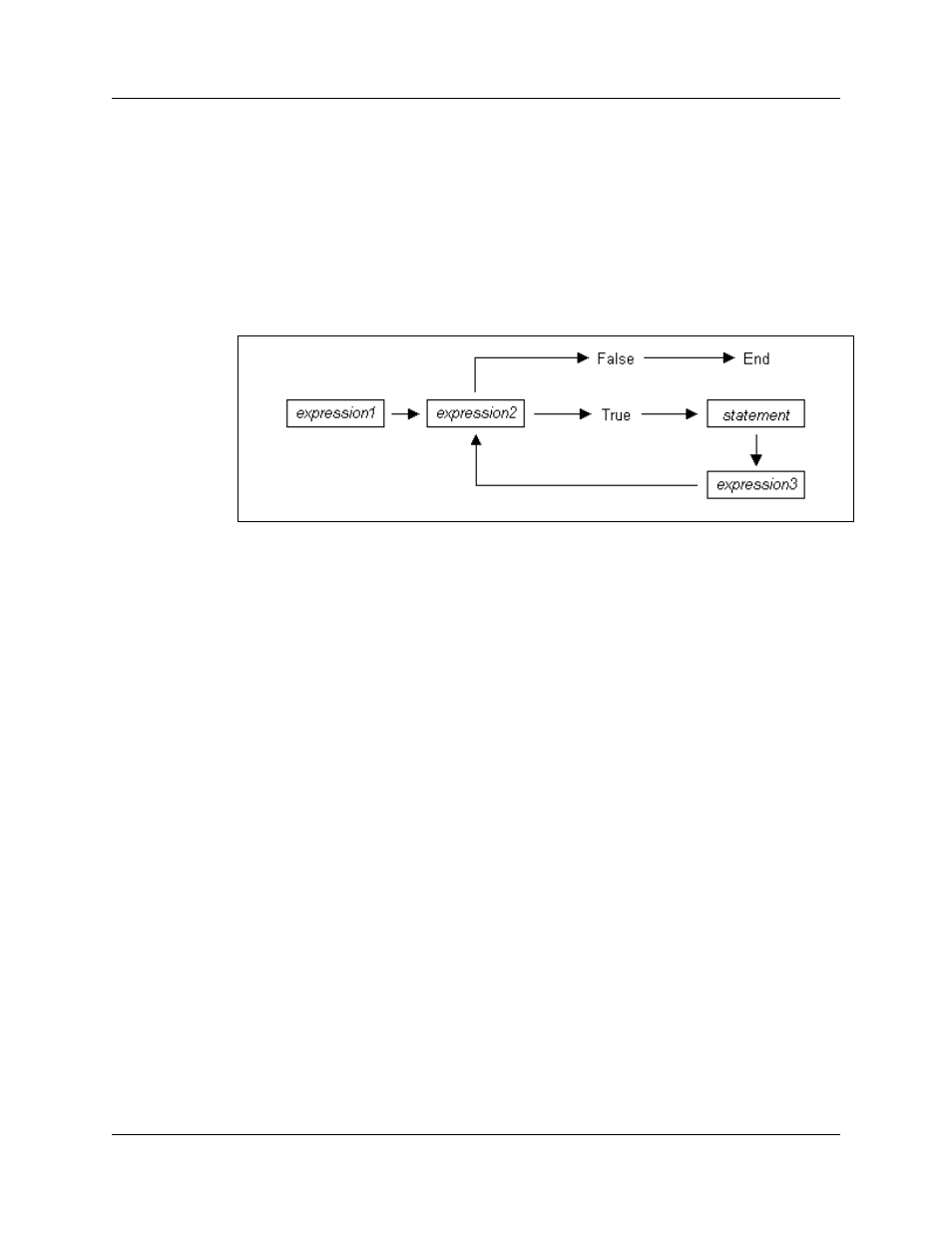
A for statement takes the form:
for (<expression1>; <expression2>; <expression3>) <statement>
The first expression initializes, or sets, the starting value for x. It is executed one time,
before the loop begins. The second expression is a conditional expression. It determines
whether the loop continues. If it evaluates true, the function keeps executing and
proceeds to the statement. If it evaluates false, the loop ends. The third expression is
executed after every iteration of the statement.
The example
for ( x = 2; x < 5; x = x + 1 ) Trace ( x, "\n" );
would output
2
3
4
The example above works out like this: the expression x = 2 is executed. The value of
x is passed to x < 5
,
resulting in 2 < 5. This evaluates to true, so the statement
Trace (x, "\n" )
is performed, causing 2 and a new line to print. Next, the third
expression is executed, and the value of x is increased to 3. Now, x < 5 is executed
again, and is again true, so the Trace statement is executed, causing 3 and a new line
to print. The third expression increases the value of x to 4; 4 < 5 is true, so 4 and a new
line are printed by the Trace statement. Next, the value of x increases to 5. 5 < 5 is not
true, so the loop ends.
Figure 1: Execution of a for Statement
