General Tools and Instruments CA10 User Manual
Page 6
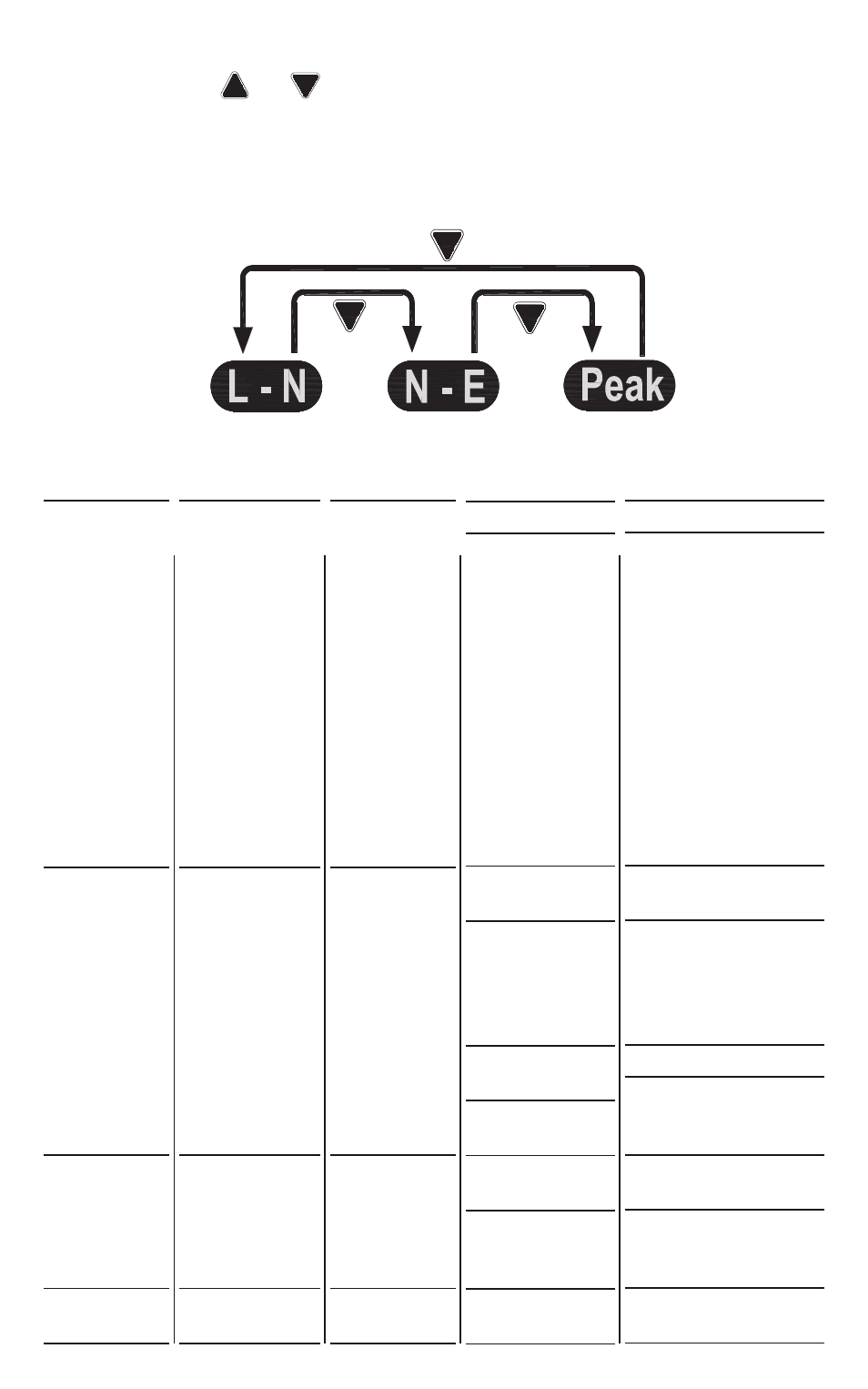
To begin, plug the free end of the test cable into any outlet of the circuit to be
tested. Press the
or
button to cycle through the three submenu options
in either direction, as shown in the figure below. The text icon of the parameter
being measured appears at the left of the display. The table below the figure
shows the normal measurement result for each of the four parameters. It also
lists possible causes of, and remedies for, abnormal results.
6
Parameter
Phase Voltage
L-N (Nominal
Voltage ± 10%)
Voltage to earth
of neutral line
N-E
Peak Voltage
(1.414 x Phase
Voltage, or TRMS
value of Phase
Voltage)
Frequency
Normal
Measurement
Result
108 to 132V
(120V circuit)
198 to 242V
(240V circuit)
>2V
153 to 185V
(120V circuit)
280 to 342V
(240V circuit)
60Hz (120V circuit)
50Hz (240V circuit)
Actual Result
Voltage is too
high or too low
>2V
Voltage is too
high or too low
Frequency is too
high or too low
Possible Cause
of Abnormal
Result
Circuit is overloaded
High impedance
point(s) in breaker
box or circuit
Supply voltage is too
high or too low
Leakage current
Three-phase
imbalance
Harmonic
interference
Supply voltage is too
high or too low
Electronic device in
circuit is distorting
the AC sine wave
Supply frequency is
too high or too low
Remedy
Redistribute circuit load
Visually inspect all
connection points to detect
or rule out loose
connections and defective
outlets. If none are
apparent, locate points of
high impedance using an
infrared thermometer (IRT)
to detect their heat, or a
voltmeter to detect
excessive voltage drops
across parts. Repair or
replace defective
wiring/parts.
Consult your electricity
provider
Find source of leakage
(a multi-point ground,
a device or piece of
equipment) and repair
or replace
Check and redistribute load
Install spectral filter or take
other steps to reduce
interference
Consult your electricity
provider
Identify and relocate (if
necessary) the device
Consult your electricity
provider
