0 battery symptoms and solutions, continued – Alpha Technologies AlphaCell GelCell User Manual
Page 24
745-680-C0-002, Rev.B1
24
5.0
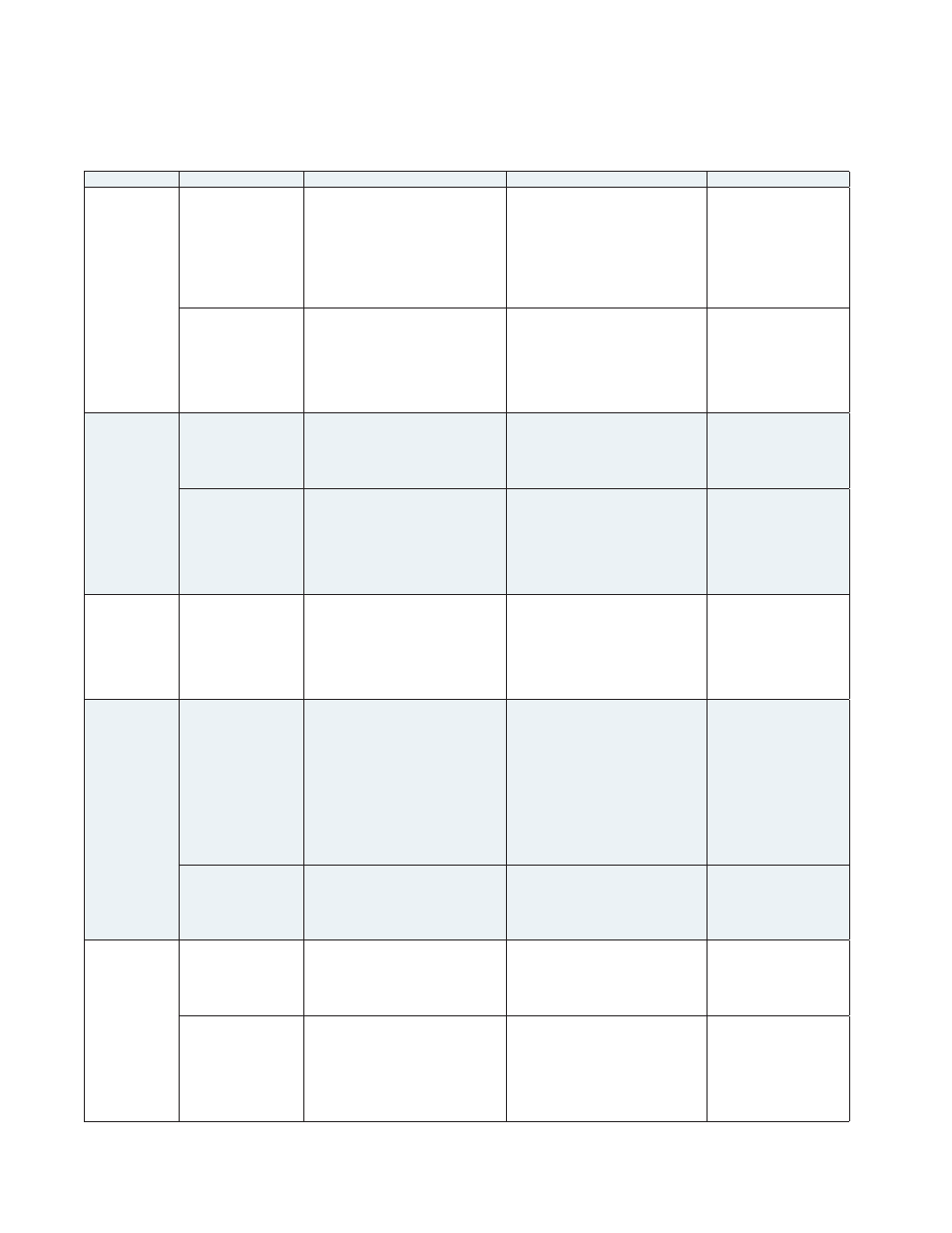
Battery Symptoms and Solutions, continued
Type
Symptom
Possible Causes
Possible Result
Corrective Action
Float Charging
Current
Checks
Float current to
string is zero
A battery or connection in series
string is open. Verify via the float
voltage check or AC ripple voltage
or impedance check of individual
batteries.
•
Failure to support load. If an
internal arc occurs during
discharge, can ignite gasses
internal to cell.
•
If there is an open/loose
connection in external con-
ductive path, can damage
termination under load.
Replace battery with
open cell or repair
open/loose external
connection.
Float current
exceeds 3.0
milliamperes per
ampere hour of
rated capacity at
77°F(25°C) at float
voltage.
•
Batteries not fully recharged.
•
Batteries above 77°F(25°C)
•
Potentially shorted cells in
battery
•
Depending on degree, bat-
tery entering or in thermal
runaway
•
Not at 100% capacity
•
Conducive to thermal
runaway
•
Thermal runaway results in
eventual meltdown of battery
and potential of hydrogen
sulfide emissions and fire.
Determine specific
cause; take corrective
action.
High Rate 10
Second Load
Test
Terminal voltage
marginally below
minimum voltage
specified for 10
second point.
Battery perhaps not fully charged
or is older, in service battery and
has somewhat lower capacity.
Perhaps reduced operating time.
Fully recharge battery.
Terminal voltage
significantly below
minimum voltage
specified for 10
second point.
•
Battery discharged of
battery conductive path,
plate grid, or active material
or electrolyte volume
deterioration.
•
Shorted.
•
Open cells.
•
Reduced operating time.
•
Conducive to thermal
runaway
•
Will not support load
Charge, retest battery
or replace as required.
Battery
Impedance/
Conductance
Test
Impedance /
resistance increase
by 50% from
original values
or conductance
decline to 50% of
the value when new.
•
Battery discharged or battery
conductive path, plate grid or
active material, or electrolyte
volume deterioration.
•
Shorted cells
•
Open cells
•
Reduced operating time
•
Conducive to thermal
runaway
•
Will not support load
Charge and retest
battery or replace as
required.
Connection
Hardware
Resistance
/ Tightness
Check
Connection
resistance increase
20% or more from
original value.
•
Repetitive cycles results
in heating and cooling of
connection, resulting in
relaxation of torque, increase
in connection resistance.
•
Contamination within
the connection results in
corrosion and high terminal
resistance.
•
Loose connections result
in heat damaged or melted
terminals during high rate
discharge.
•
Excessive voltage drop
during high rate discharge
and resulting reduced
operating time
•
Retorque
connection as
required
•
Correct source
of contamination,
clean contact
surface areas,
grease contact
surfaces with anti-
oxidant grease,
reassemble.
Connection
hardware tightness
is less than the
specified "retorque"
value.
Repetitive cycles results in heat-
ing and cooling of connection re-
sulting in relaxation of torque and
increase in connection resistance.
Loose connections result in heat
damaged or melted terminals
during high rate discharge
Retorque the
connection as required
AC Ripple
Voltage
Checks
AC ripple (p-p)
voltage on system
<4% of the value of
the DC float voltage
Poor filtering of charger output.
Excessive AC ripple could cause
the battery to cycle at the ripple
frequency and result in heating
and deterioration of the plate ac-
tive material
Improve the charger
output filtering.
Individual battery in
string exhibits AC
ripple voltage twice
that of other typical
batteries in string.
Battery with high AC ripple
voltage has proportionately
higher impedance. Evaluate
for performance. Subject
battery could have deteriorating
conductive path or dry, shorted or
open cell.
•
Reduced operating time.
•
Potential conditions could
be conducive to thermal
runaway.
Verify battery condition.
Replace as required.
Table 2, Battery Symptoms and Solutions, continued
