Maximum ratings, Thermal characteristics, Electrical characteristics – Diodes D5V0L1B2WS User Manual
Page 2
D5V0L1B2WS
Document number: DS35429 Rev. 4 - 2
2 of 4
January 2012
© Diodes Incorporated
D5V0L1B2WS
ADVAN
CE I
N
F
O
RM
ATI
O
N
Maximum Ratings
@T
A
= 25°C unless otherwise specified
Characteristic Symbol
Value
Unit
Conditions
Peak Pulse Power Dissipation
P
PP
84 W
8/20
μs, Per Fig. 1
Peak Pulse Current
I
PP
6 A
8/20
μs, Per Fig. 1
ESD Protection – Contact Discharge
V
ESD_Contact
±30 kV
Standard
IEC
61000-4-2
ESD Protection – Air Discharge
V
ESD_Air
±30 kV
Standard
IEC
61000-4-2
Thermal Characteristics
Characteristic Symbol
Value
Unit
Package Power Dissipation (Note 4)
P
D
200 mW
Thermal Resistance, Junction to Ambient (Note 4)
R
θJA
625
°C/W
Operating and Storage Temperature Range
T
J
, T
STG
-65 to +150
°C
Electrical Characteristics
@T
A
= 25°C unless otherwise specified
Characteristic
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Test Conditions
Reverse Standoff Voltage
V
RWM
- - 5 V
-
Channel Leakage Current (Note 5)
I
RM
- 10
100 nA
V
RWM
= 5V
Clamping Voltage, Positive Transients
V
CL
-
-
-
-
7.0
8.7
10.5
11.5
9.0
10.7
12.0
14.0
V
I
PP
= 1A, t
p
= 8/20
μS
I
PP
= 3A, t
p
= 8/20
μS
I
PP
= 5A, t
p
= 8/20
μS
I
PP
= 6A, t
p
= 8/20
μS
Breakdown Voltage
V
BR
6 7 8 V
I
R
= 1mA
Differential Resistance
R
DIF
-
0.2 -
Ω
I
R
= 1A, tp = 8/20
μS
Channel Input Capacitance
C
T
- 15 20 pF
V
R
= 0V, f = 1MHz
Notes:
4. Device mounted on FR-4 PCB pad layout (2oz copper) as shown on Diodes, Inc. suggested pad layout AP02001, which can be found on our website at
5. Short duration pulse test used to minimize self-heating effect.
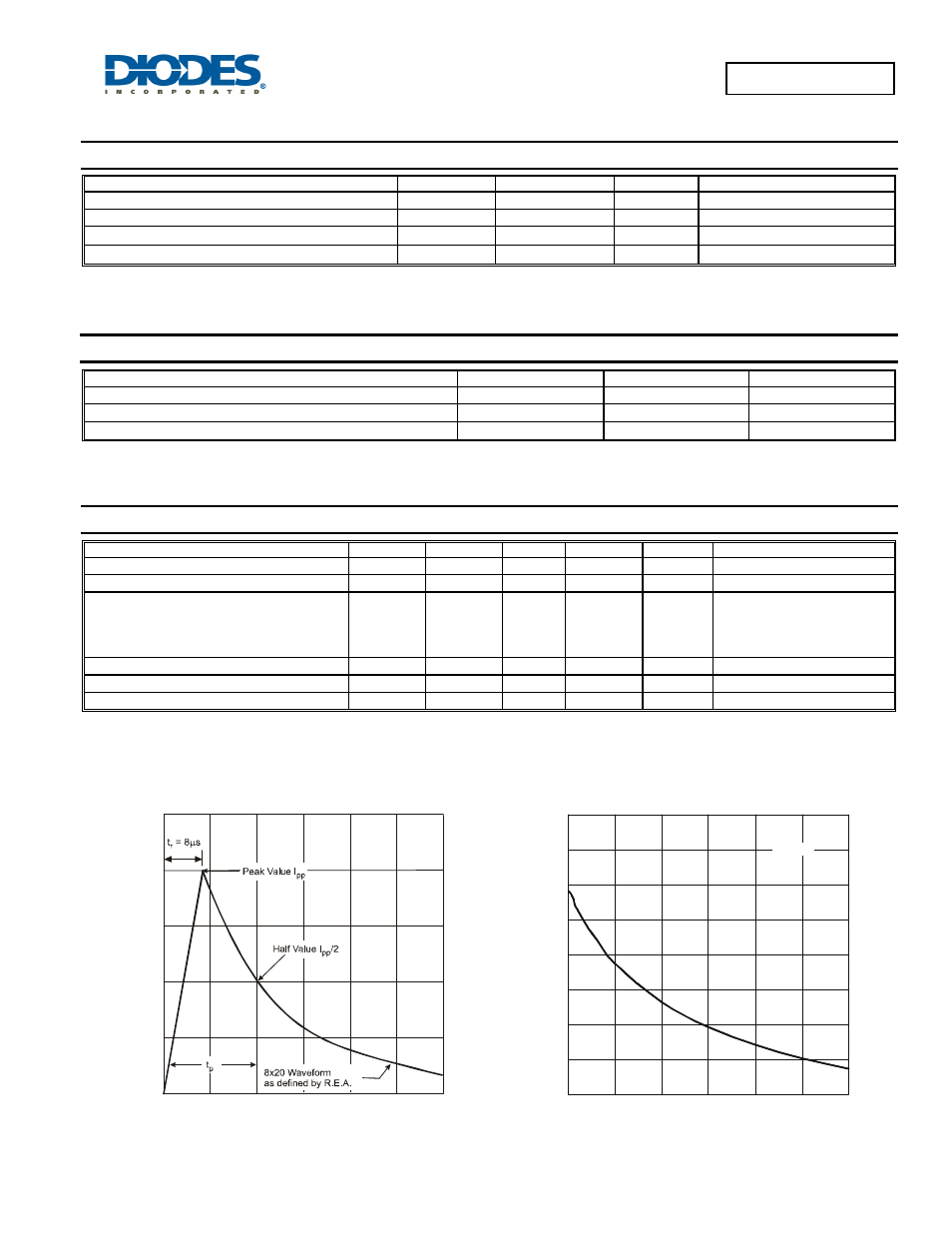
0
t, TIME ( s)
Fig. 1 Pulse Waveform
μ
20
40
60
100
50
0
I
, PE
AK P
U
L
S
E
CURRENT
(
%
I
)
Pp
p
P
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
V , REVERSE VOLTAGE (V)
Fig. 2 Typical Total Capacitance vs. Reverse Voltage
R
C
,
T
O
T
AL
C
A
P
A
C
IT
AN
C
E (
p
F)
T
f = 1MHz
