Figure 3: 140% utilization, Figure 4: return to 80% utilization – Net Optics 10_100 to Triple-speed Port Aggregator User Manual
Page 11
10/100 to Triple-speed Port Aggregator
7
10/100 to
Triple-speed
Port Aggregator
State 2: Side A + Side B becomes greater than
100% of the NIC's receive utilization
Side A +
Side B
limited to
100 Mbps
2
Memory
Traffic to the 100 Mbps
monitoring devices is limited
to 100 Mbps. The extra
40 Mbps of traffic is stored
in a 1 gigabyte buffer.
Memory continues to fill until
the 1 gigabyte capacity is
reached, or the burst ends.
Firewall
Router
Monitoring
Device 1
1
Using a single NIC each, both
monitoring devices receive all
combined traffic from Side A
and Side B, including physical
layer errors.
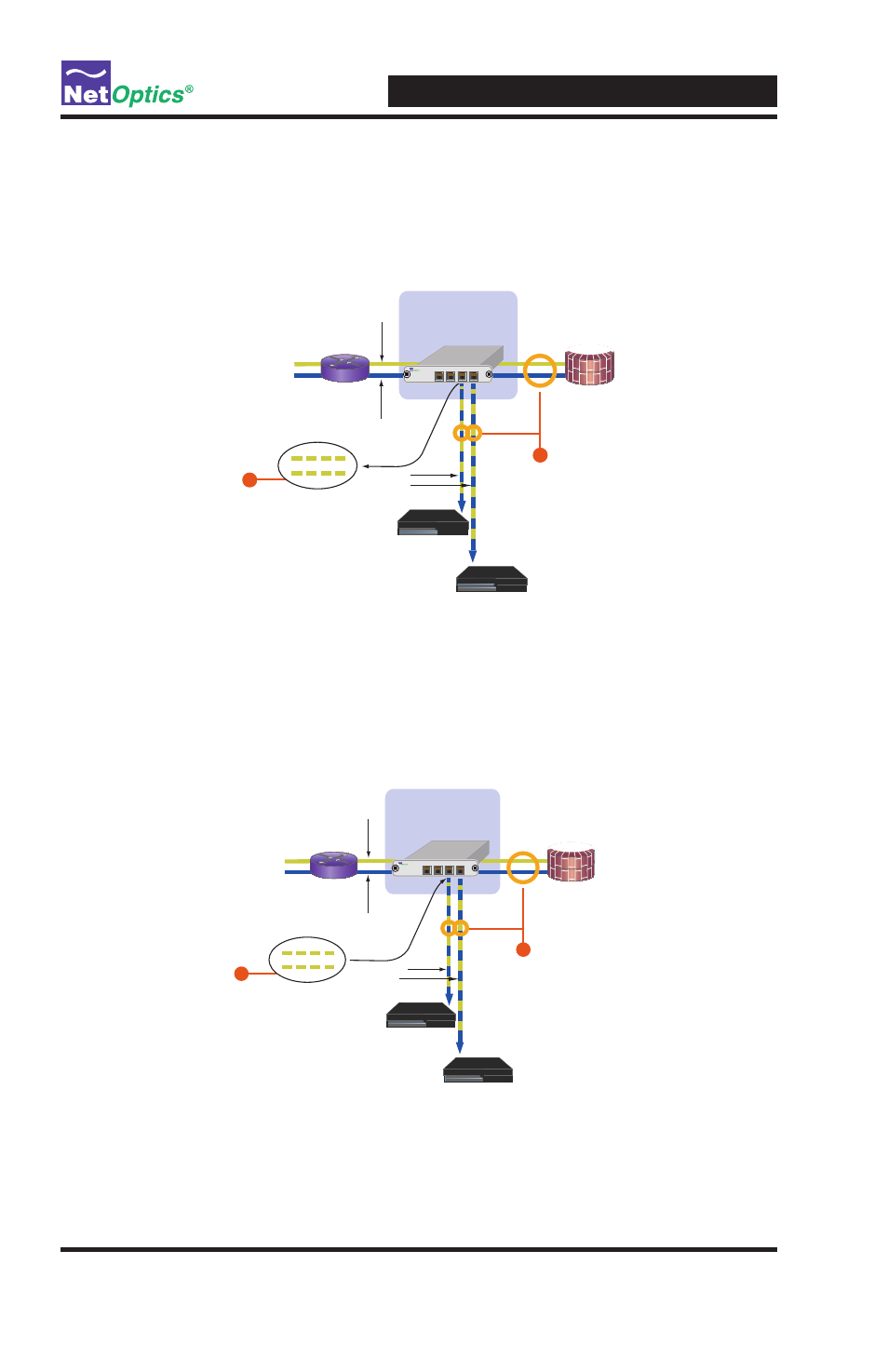
Example: There is a burst of traffic, so Side A is now at
90 Mbps while Side B remains at 50 Mbps. The NIC's
utilization is at 140%, requiring the use of memory
to help prevent data loss.
Monitoring
Device 2
B
2
1
A
96443
Side A
90 Mbps
Side B
50 Mbps
Figure 3: 140% Utilization
10/100 to
Triple-speed
Port Aggregator
State 3: Side A + Side B is once again less
than 100% of the NIC's receive utilization
Side A +
Side B
1
Memory
The Tap applies a first-in, first-out
process to all packets. Once the
burst has ended and the NIC's
utilization is again below 100
percent, the Tap first processes
the packets that were stored in
memory. As long as the NICʼs
utilization remains below 100
percent, this process continues
uninterrupted until the memory clears.
Firewall
Router
Monitoring
Device 1
2
Once the memory has cleared, the
monitoring devices begins receiving
new data directly from the link. Using
a single NIC each, both monitoring
devices again receive all traffic from
Side A and Side B, including physical
layer errors.
Example: On a 100 Mbps link, Side A is again at 30 Mbps and
Side B remains at 50 Mbps. The NIC's utilization is again at 80%.
Monitoring
Device 2
B
2
1
A
96443
Side A
30 Mbps
Side B
50 Mbps
Figure 4: Return to 80% Utilization
