7 ac power draw and thermal dissipation – Crown Audio Macro-Tech Series (600, 1200 & 2400) User Manual
Page 36
Macro-Tech 600/1200/2400 Power Amplifiers
Page 36
Reference Manual
7 AC Power Draw and
Thermal Dissipation
This section provides detailed information about the
amount of power and current drawn from the AC mains
by the Macro-Tech
600, 1200 and 2400 amplifiers and
the amount of heat produced under various conditions.
The calculations presented here are intended to pro-
vide a realistic and reliable depiction of the amplifiers.
The following assumptions or approximations were
made:
• The amplifier’s available channels are loaded and full
power is being delivered.
• The amplifier efficiency at standard 1-kHz power is
estimated to be 65%.
• Quiescent power draw is 90 watts (an almost negli-
gible amount for full-power calculations).
• Quiescent thermal dissipation equals 105 btu/hr at
90 watts.
• The estimated duty cycles take into account the typi-
cal crest factor for each type of source material.
• Duty cycle of pink noise is 50%.
• Duty cycle of highly compressed rock ‘n’ roll mid-
range is 40%.
• Duty cycle of rock ‘n’ roll is 30%.
• Duty cycle of background music is 20%.
• Duty cycle of continuous speech is 10%.
• Duty cycle of infrequent, short duration paging is 1%.
Here are the equations used to calculate the data pre-
sented in Figures 7.1 through 7.3:
AC Mains Power
Draw (watts)
=
Total output power with all
channels driven (watts)
x Duty
Cycle
Amplifier Efficiency (.65)
+ Quiescent Power
Draw (watts)
The quiescent power draw of 90 watts is a maximum
value and includes power drawn by the fan. The follow-
ing equation converts power draw in watts to current
draw in amperes:
Current Draw
(amperes)
=
AC Mains Power
Draw (watts)
x
AC Mains
Voltage
Power
Factor (.83)
The power factor of 0.83 is needed to compensate for
the difference in phase between the AC mains voltage
and current. The following equation is used to calculate
thermal dissipation:
Total output power with all
channels driven (watts)
Thermal
Dissipation
(btu/hr)
=
+
Quiescent Power
Draw (watts)
x Duty
Cycle
Amplifier Efficiency (.65)
(
)
x 3.415
.35
x
The constant 0.35 is inefficiency (1.00–0.65) and the
factor 3.415 converts watts to btu/hr. Thermal dissipa-
tion in btu is divided by the constant 3.968 to get kcal. If
you plan to measure output power under real-world
conditions, the following equation may also be helpful:
Total measured output power
from all channels (watts)
Thermal
Dissipation
(btu/hr)
=
+
Quiescent Power
Draw (watts)
.35
x
Amplifier Efficiency (.65)
(
)
x 3.415
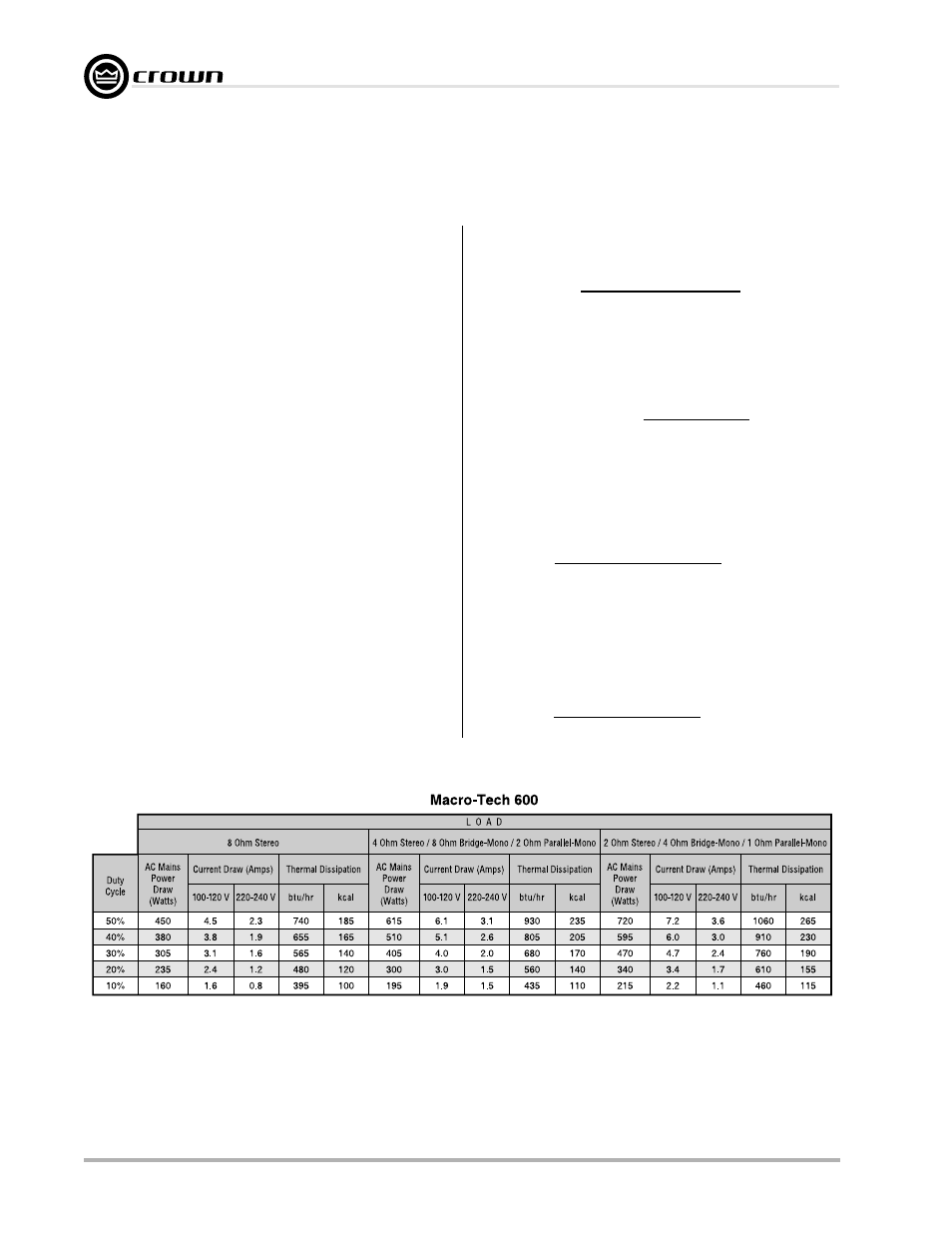
Fig. 7.1 Macro-Tech 600 Power Draw, Current Draw and
Thermal Dissipation at Various Duty Cycles
