3B Scientific Electrochemistry Kit User Manual
Page 9
10
Experiment 2 - Measuring voltage Teacher's instructions
Measuring the voltage of a Daniell cell
Chemicals Hazard
symbols
R phrases
S phrases Equipment
Meter
Copper (II)-sulfate-(5 H
2
O)
22-36/38-50/53 22-60-61 Electrodes:
1 Cu, 1 Zn
Zinc sulfate-(7H
2
O)
36/38-50/53 22-25-60-61
2 Experiment cables
Distilled water
--- ---
2
Pipettes
Warning: Please take care: Salts of heavy metals are poisonous!
Experiment procedure:
1. The prepared 0.1 molar electrolyte solutions should be given to the students. Students require no more than 10 ml of
the relevant solution each.
2. Assemble the battery block as described.
3. Fill one chamber each with electrolyte using the pipette (included in the case). Clean the pipette thoroughly before
using it add the next electrolyte.
4. Insert the appropriate electrodes into the electrolyte solutions, CuSO
4
/ Cu and ZnSO
4
/ Zn.
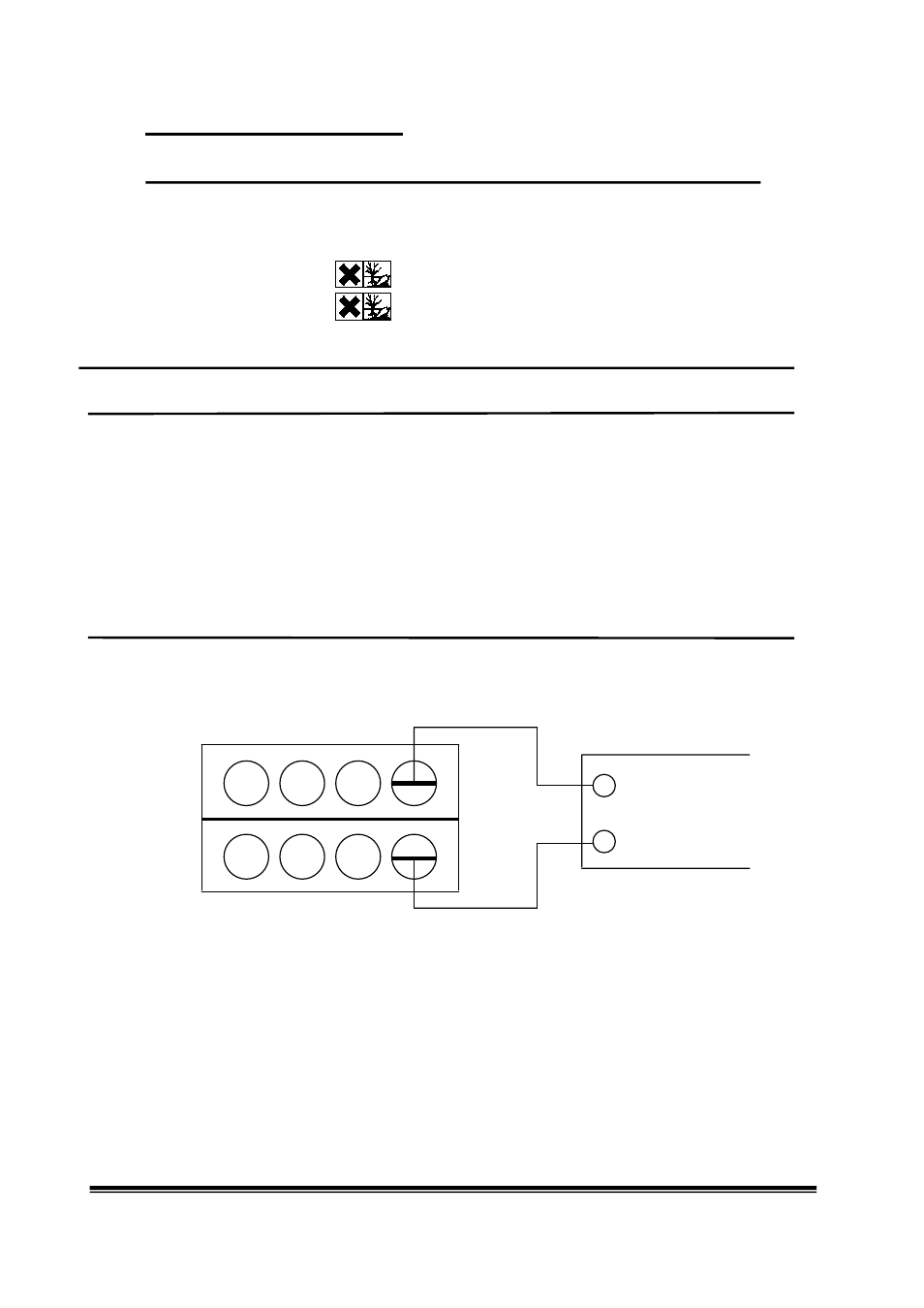
5. After the chambers have been prepared for the experiment as described, connect the experiment cables to the
meter and start measuring voltages. If a negative voltage is displayed, reverse the polarity of the two electrode
connections.
6. The experiment can also be repeated using 1.0 molar copper sulfate and zinc sulfate solutions.
Observation and evaluation:
Sketch of experiment set-up:
Cu
+ +
Meter
-
Zn
The electrolyte solutions should be made up by the teacher in sufficient quantities (usually 1 liter suffices) in advance of the lesson.
Calculation of masses required to prepare a 0.1 molar solution:
1.
1 liter of 0.1 molar CuSO
4
solution: Add water to 24.95 g CuSO
4
(5 H
2
O) up to 1 liter in a measuring flask.
2.
1 liter of 0.1 molar ZnSO
4
solution: Add water to 28.74 g ZnSO
4
(7 H
2
O) up to 1 liter in a measuring flask.
Calculation of masses required to prepare a 1.0 molar solution:
1.
1 liter of 1.0 molar CuSO
4
solution: Add water to 249.50 g CuSO
4
(5 H
2
O) up to 1 liter in a measuring flask.
2.
1 liter of 1.0 molar ZnSO
4
solution: Add water to 287.40 g ZnSO
4
(7 H
2
O) up to 1 liter in a measuring flask.
When the meter is connected to the Daniell cell with Cu / CuSO
4
or Zn / ZnSO
4
the measured voltage should theoretically be 1.08 V for
an electrolyte concentration of 0.1 mol/l. The result of the actual measurement is usually slightly less than the theoretical value at
1.06 V.
If a 1.0 molar solution is used in the Daniell cell, the measured voltage should still be 1.06 V.
