3B Scientific Electrochemistry Kit User Manual
Page 17
18
Experiment 6 - Measuring voltage Teacher's instructions
Measuring the standard electrochemical potentials of various non-metals
Chemicals Hazard
symbols
R phrases
S phrases
Equipment
Meter
Sodium chloride
---
---
Electrodes:
2 C, 1 Pt gauze
Potassium bromide
---
---
2 Experiment cables
Sodium iodide
---
---
1 Mains power supply
Hydrochloric acid 1 mol/l
36/37/38 26
2
Pipettes
Distilled water
---
---
1 3V adapter
Warning: Please take care: Hydrochloric acid is corrosive!
Experiment procedure:
1. The prepared 1.0 molar electrolyte solutions should be given to the students. Students require no more than 10 ml of
the relevant solution each.
2. Assemble the battery block as described.
3. Add the 1 molar hydrochloric acid to one chamber of the battery block using the pipette and insert the platinum
gauze electrode into this cell.
4. Add a 1 molar NaCl solution to a second chamber (opposite the platinum gauze electrode) and insert a carbon
electrode.
5. To form a normalized hydrogen electrode, a 3V adapter is connected to the power supply. Connect the negative
pole of the 3V adapter to the platinum gauze electrode and the positive pole to the carbon electrode using
experiment cables. Connect the power supply to the 230 V mains and electrolyze the platinum gauze for about 30
seconds. Hydrogen forms at the platinum gauze and completely surrounds the gauze.
6. The 3V adapter is then replaced by the meter and the Cl
-
/ Cl
2
voltage can then be read off.
7. Proceed as in steps 4 to 6 with each of the other non metals dipping the carbon electrode into potassium bromide
and potassium iodide solutions one after the other to determine the electrochemical potentials of Br
-
/ Br
2
and I
-
/ I
2
.
Observation and evaluation:
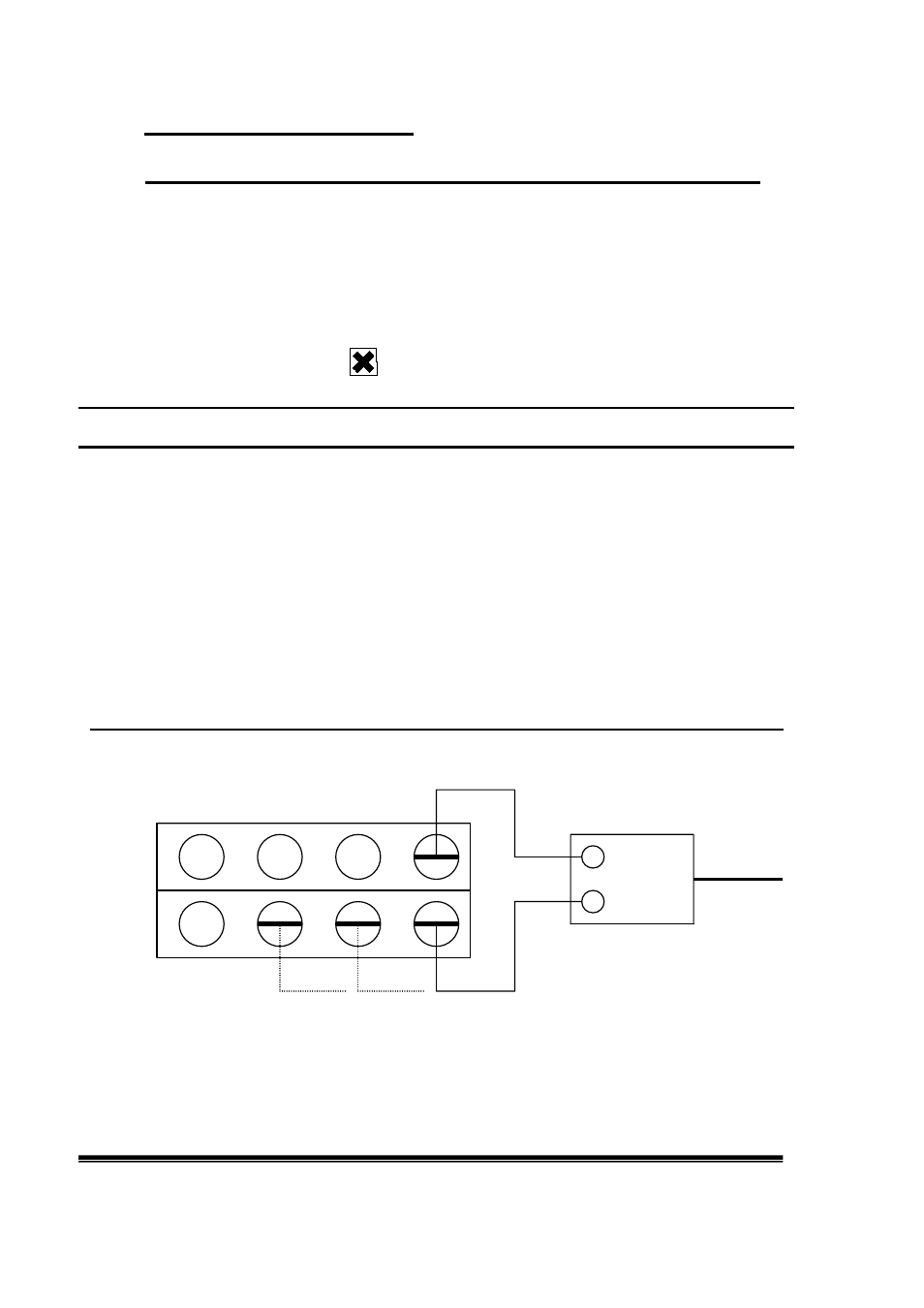
Pt _ connection
3V adapter
+ 230V
C C C
(3) (2) (1)
For each redox pair, the standard electrochemical potentials as measured should be:
(1) Cl
-
/ Cl
2
= + 1.35 V, (2) Br
-
/ Br
2
= + 1.06 V, (3) I
-
/ I
2
= + 0.54 V
Calculation of masses required to prepare 1 liter of a 1 molar solution:
1.
For an NaCl solution 58.44 g of NaCl is needed.
2.
For a KBr solution 119.01 g of KBr is needed.
3.
For a KI solution 166.00 g of KI is needed.
